Method and kit for detecting nucleotide sequence
A target sequence and polynucleotide technology, applied in the field of a method and kit for detecting the presence of one or more polynucleotide sequences in a sample, can solve the problem of limited sample processing multiplex, probe length limitation, insufficient flexibility etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
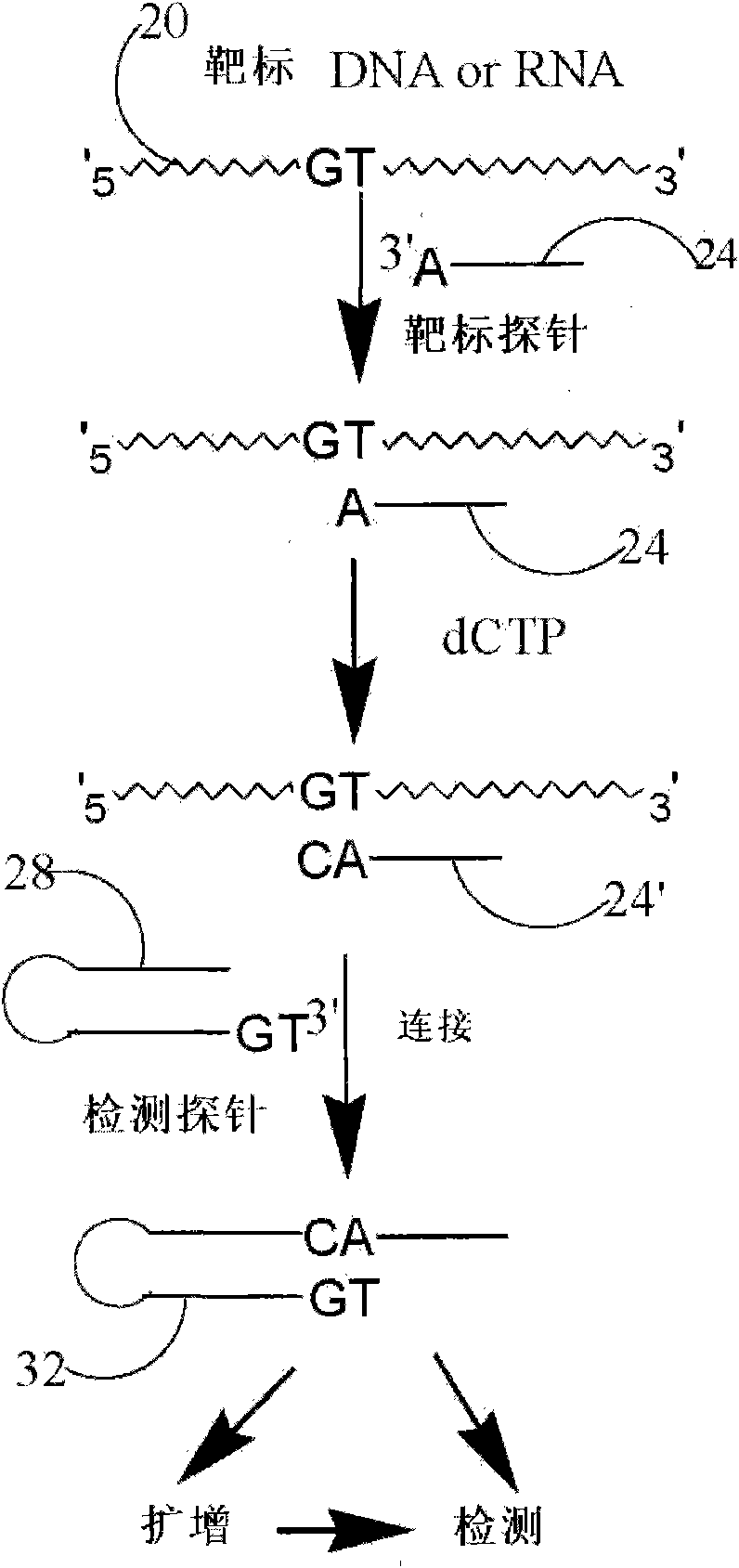
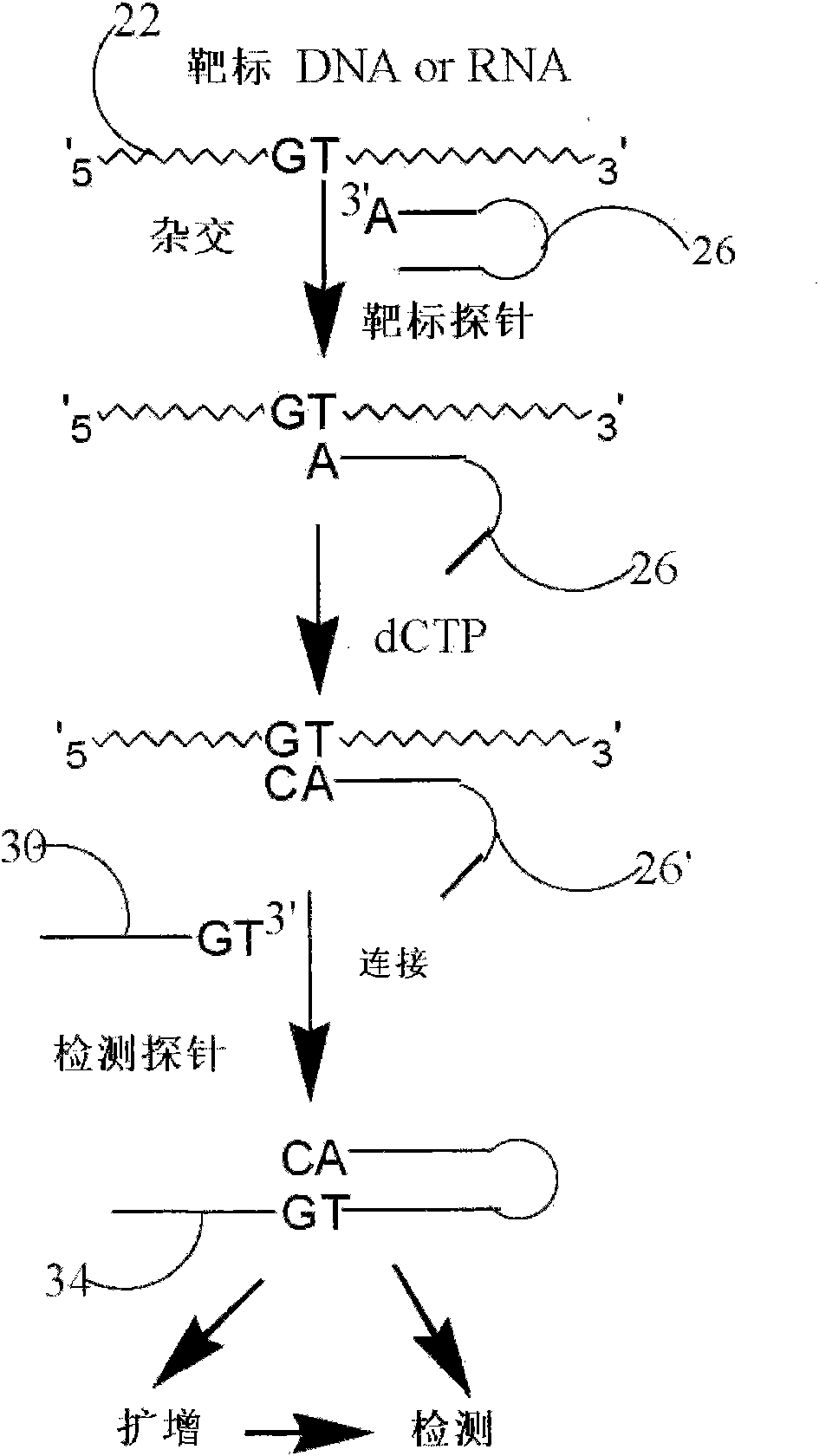
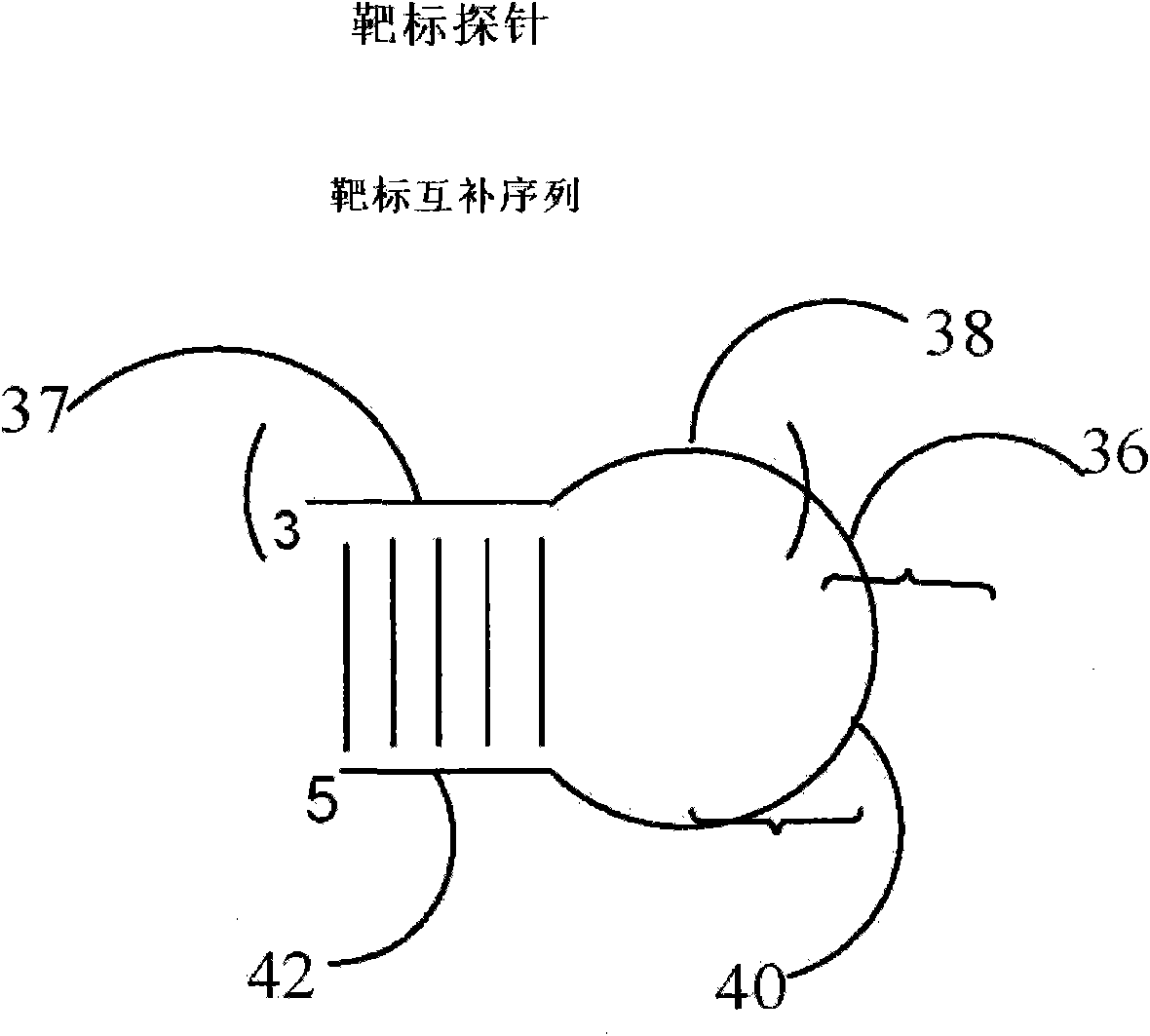
[0180] Target probe extension based on allele-specific hybridization
[0181] This example demonstrates that a target probe with a self-complementary sequence (hairpin structure) forms a hybrid complex with the target sequence under hybridization conditions. If the 3' end of the target probe is complementary to an allelic fragment-specific nucleotide in the target sequence under polymerization conditions, the 3' end of the target probe can be based on the type or number of added nucleotides. Add one or more nucleotides to the end. This extension will make the 3' end sequence of the target probe complementary to the 3' end sequence of the detection probe, making it possible to ligate the two probes. A hairpin probe named Oct-25-2005-R was designed and ordered from Integrated DNA Technology for testing this extension reaction. Two synthetic target sequences were designed to test for allele-specific extension. One of the target sequences is named RS1389629-G, which is fully ...
Embodiment 2
[0218] Target probes adjacent to the SNP site are extended by a single nucleotide for SNP detection.
[0219] This example describes the extension of a target probe adjacent to a SNP site by a single nucleotide for SNP detection. Target probes hybridize to target sequences adjacent to the SNP site. Only target probes with the correct bases added at their 3' ends can be ligated with detection probes to form ligated circular products. SNPs are identified according to the type of nucleotide added. The reaction between the extended target probe and the detection probe is sticky end ligation. If only the correct single nucleoside triphosphate and DNA polymerase are present in the reaction, the 3' end of the target hairpin probe that anneals to the target sequence is extended by one nucleotide from the 3' end of the hairpin sequence. With more cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension, the number of base-extended target probes in the reaction mixture will increase. In t...
Embodiment 3
[0295] by increasing the amount of extended target probe based on thermal cycling the probe extension reaction. Row Sensitivity Test
[0296] The reaction was cycled 1, 10, 15, 25, 35, 50 times for probe annealing and extension: set up the reaction in a 200 μl PCR tube containing 2.5 units of AmpliTag DNA polymerase Stoffel fragment (Application Biotechnology ), 10mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 10mM KCl, 4mM MgCl 2 , 0.15 mM dGTP. Reactions contained 5 μM extension probe and 1.5 μM target DNA. The cycling program consisted of an initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 minutes followed by 50 cycles of 95°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 58°C and extension for 1 minute. A final extension was performed at 72°C for 5 minutes.
[0297] Detection probes were used after exonuclease treatment to estimate the amount of extension product produced with increasing cycle numbers based on the ligation reaction products. Figure 11 The results (lanes 4 and 9) clearly show that increasing cycles of p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com