Amino acid pairing-based self assembling peptides and methods
An amino acid and self-assembly technology, which is applied in the preparation methods of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., and can solve the problems of inability to self-assemble molecules.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
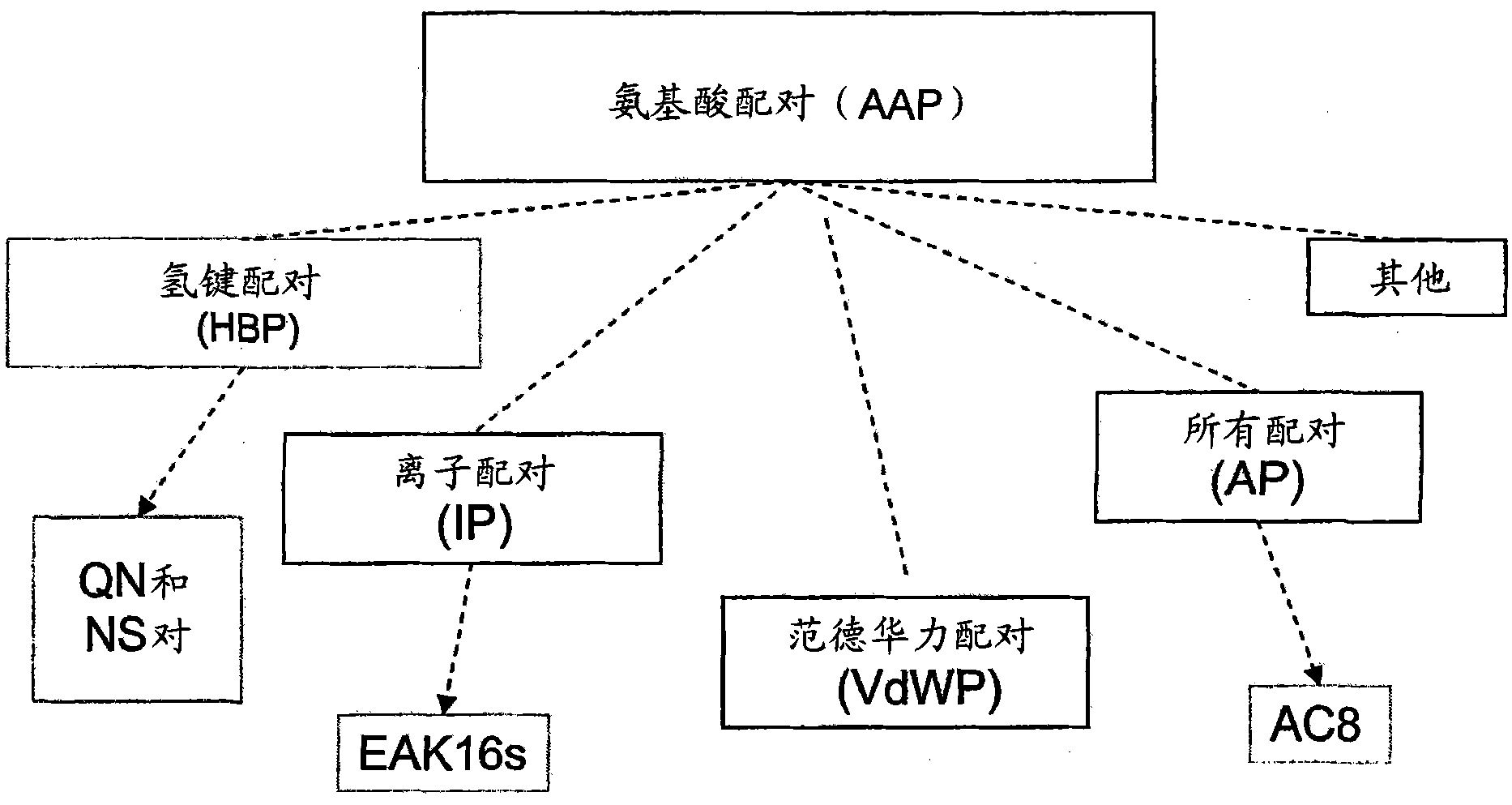
[0222] In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method for preparing self-assembled amino acid peptides with amino acid pairing properties for producing nanostructures. The method comprises the following steps: designing a β-chain peptide whose amino acids and their complementary amino acids can form at least one of the following interactions: hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals interactions; such polypeptide chains contain 2 Up to 40 amino acids, containing at least one amino acid pair capable of forming at least one of the following forces, hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interaction, hydrophobic interaction, and van der Waals interaction, and having complementary amino acid pairing and steric complementarity to a second polypeptide.
[0223] Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), circular dichroism (CD) and Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence spectroscopy can be used to analyze the secondary structure of pept...
Embodiment 1
[0263] Example 1: Hydrogen Bonded Amino Acid Pairing (AAP)
[0264] Table 1 lists amino acids that can form hydrogen bonds, and their atomic positions that can act as proton donors and proton acceptors. The amino acids that can be paired are listed in Table 2. Soluble and less soluble hydrogen bonded amino acid pairs are listed in Tables 3 and 4, respectively. When amino acids are charged, the presence of repulsive forces inhibits hydrogen bond pairing (see Table 3). Therefore, uncharged amino acid pairs capable of forming hydrogen bonds are of particular interest.
[0265] Table 1. Amino acids that form hydrogen bonds and the positions of atoms in the amino acids that can act as acceptors and donors.
[0266] amino acid
[0267] S
[0268] Table 2. Classification of amino acids forming hydrogen bonds according to their function (donor or acceptor) and the positions of atoms in the amino acid as proton donors and proton acceptors.
[0269] hyd...
Embodiment 2
[0287] Example 2: Amino Acid Pairing Peptides Based on Full Complementarity
[0288] A peptide is designed to contain hydrogen bonds, electrostatic and hydrophobic bonds for each of the amino acid pairings. The resulting peptide was called AC8. AC8 consists of 8 amino acids in sequence, including a typical hydrogen bond pairing (QN), a typical ion complementary pairing (EK), and 2 hydrophobic residue pairings (FF) ( Figure 13 A). The introduction of hydrophobic amino acids is to form a hydrophobic interior to encapsulate and stabilize hydrophobic substances ( Figure 13 B). These hydrophobic residues also strengthen the combination between polypeptides; the charged amino acid side chains improve the solubility of polypeptides and their polymers; hydrogen bond amino acid pairing can also stabilize these polypeptides and their polymers.
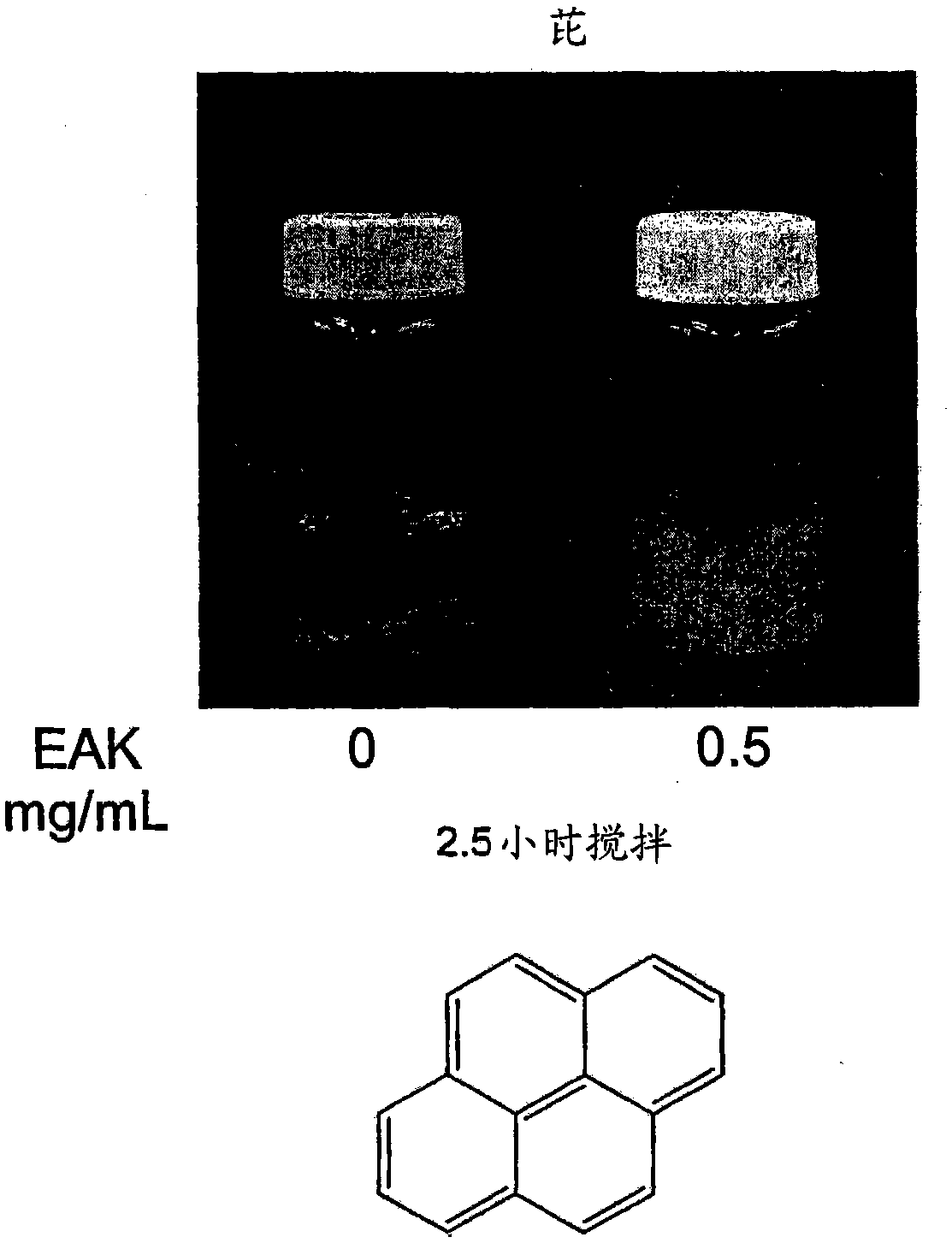
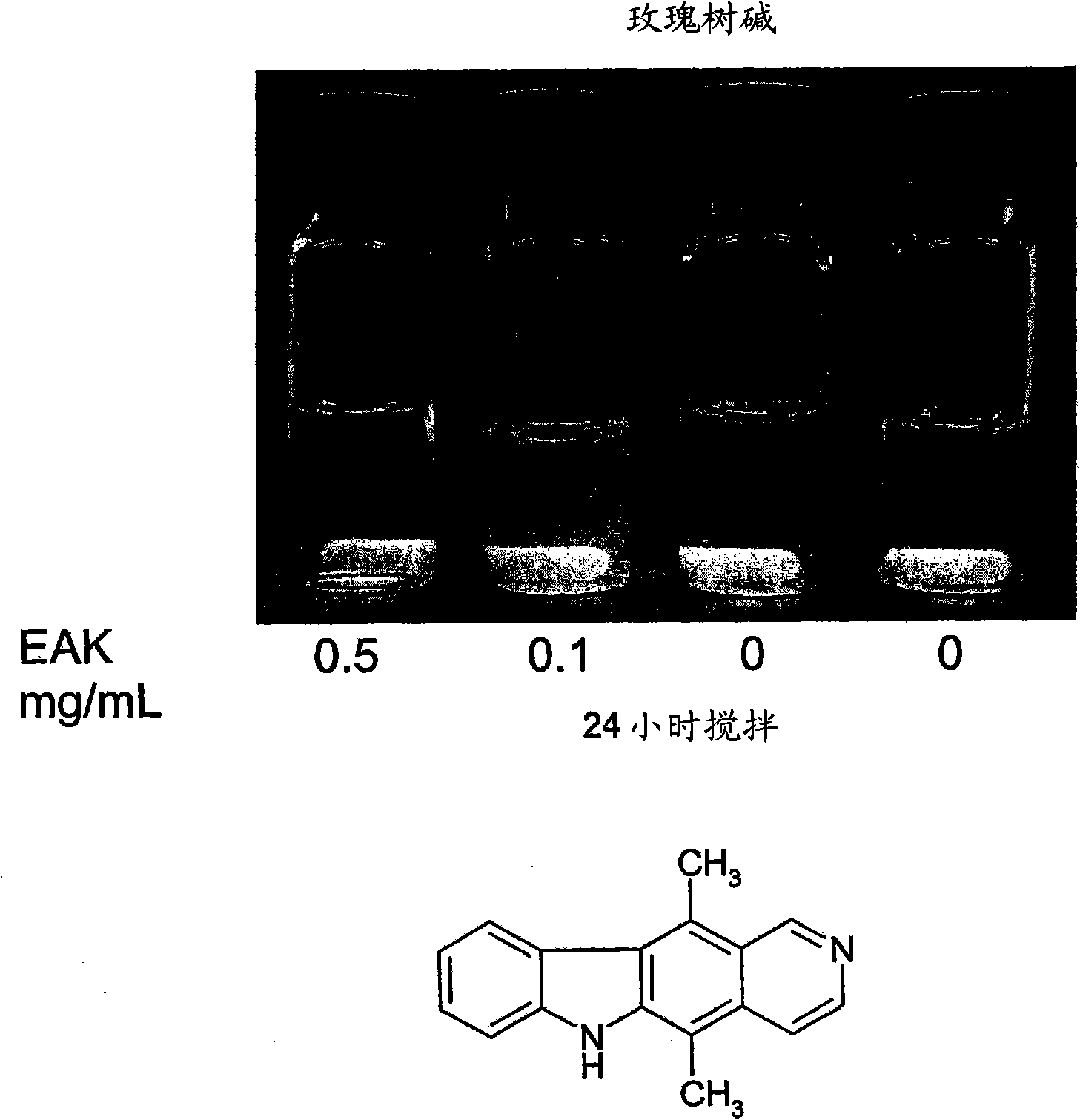
[0289] Concentration-dependent AC8 peptide assembly studies used the following method: surface tension measurements ( Figure 14A and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com