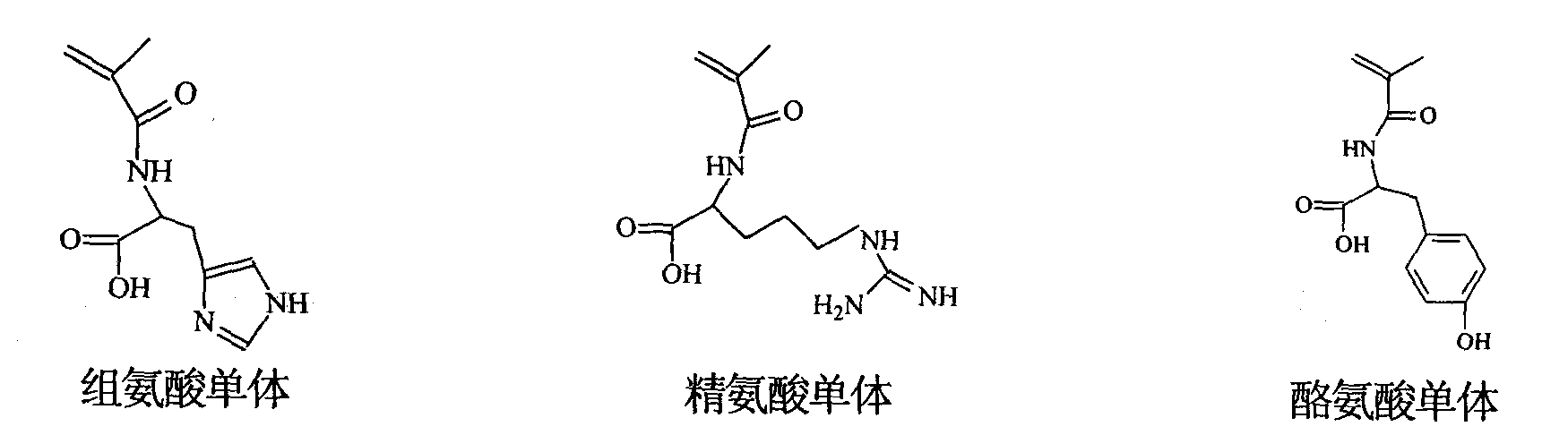
Surface imprinted polymer for catalyzing degradation of organophosphorus pesticide and preparation method thereof
An organophosphorus pesticide, surface imprinting technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability and high production costs, achieve good mechanical properties, and overcome catalytic degradation reactions. , the effect of overcoming heterogeneous characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1. Preparation of Polystyrene Seeds
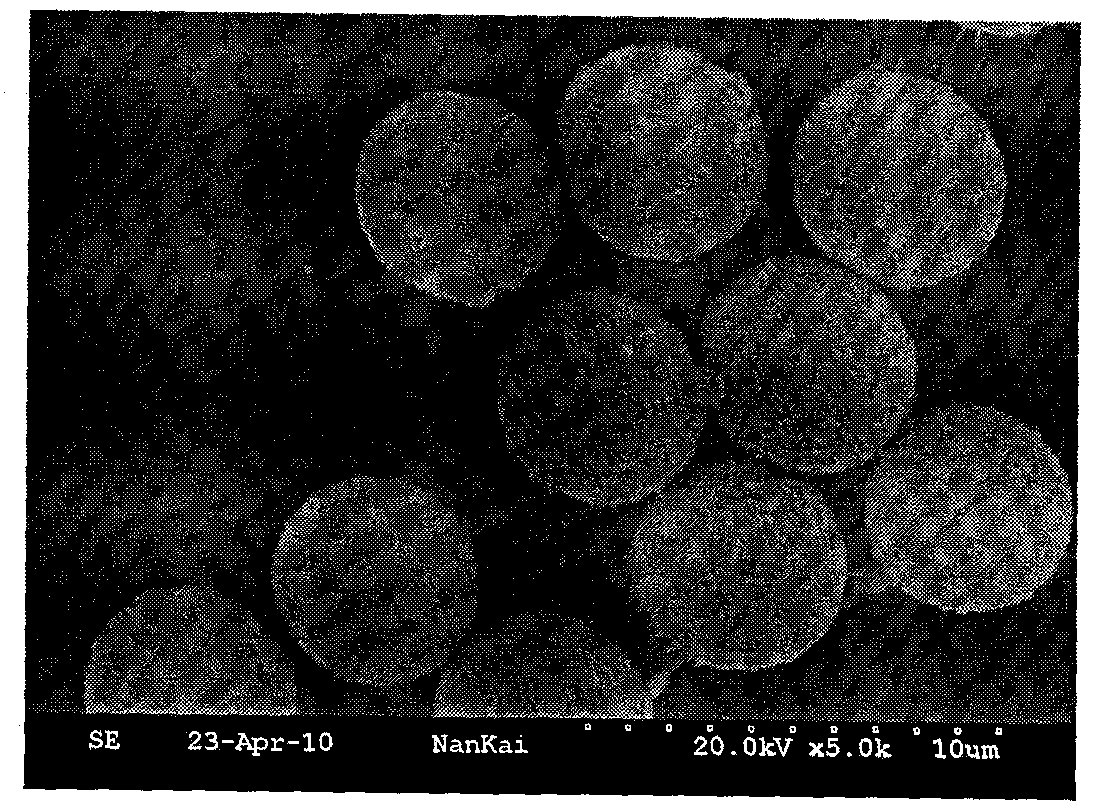
[0036] With potassium persulfate (KSP) as initiator, prepare monodisperse polystyrene seed emulsion with soap-free emulsion polymerization method, solid content 6.1% (mass fraction), average particle diameter 500nm, polydispersity index 1.02 (see attached figure 2 ).
[0037] 2. Preparation of Polystyrene Microspheres
[0038] Add 0.4ml of dibutyl phthalate (DBP), 5ml of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, 2% aqueous solution) and 25ml of deionized water into a small beaker, and ultrasonically disperse. Then add styrene seed 1ml wherein, stir and swell; 4ml toluene, 0.08g dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO) are added in another small beaker, then add 15ml polyvinyl alcohol (PVA, 2% aqueous solution) wherein, 1ml of SDS (2% aqueous solution) and 14.0ml of water, after ultrasonic emulsification, add it to the swollen solution in the first step, continue to stir and swell; take another small beaker, add 3.7g of styrene, 0.3g of diethylene Benzene (D...
Embodiment 2
[0054] 1. Preparation of polystyrene seeds
[0055] Using potassium persulfate (KSP) as an initiator, prepare a monodisperse polystyrene seed emulsion with a soap-free emulsion polymerization method, with a solid content of 6.0% (mass fraction), an average particle diameter of 1.3 μm, and a polydispersity index of 1.02 (see attached Figure 5 ).
[0056] 2. Preparation of polystyrene microspheres
[0057] Add 0.4ml of dibutyl phthalate (DBP), 5ml of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, 2% aqueous solution) and 25ml of deionized water into a small beaker, and ultrasonically disperse. Then add 1ml of styrene seeds to it, stir and swell; add 4ml of toluene, 0.08g of dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO) into the small beaker, then add 15ml of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA, 2% aqueous solution), 1ml of SDS (2% aqueous solution) and 14.0ml water, after ultrasonic emulsification, add it to the solution swollen in the first step, continue to stir and swell; take another small beaker, add 3.7g styrene, 0.3g di...
Embodiment 3
[0074] 1. Preparation of polystyrene seeds
[0075] Using potassium persulfate (KSP) as an initiator, a monodisperse polystyrene seed emulsion was prepared by soap-free emulsion polymerization, with a solid content of 6.1% (mass fraction), an average particle size of 500nm, and a polydispersity index of 1.02.
[0076] 2. Preparation of polystyrene microspheres
[0077] (1) Add 0.3ml of dibutyl phthalate (DBP), 5ml of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, 2% aqueous solution) and 25ml of deionized water into a small beaker, and ultrasonically disperse. Then add 1ml of styrene seeds to it, stir and swell; add 3ml of toluene, 0.08g of dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO) into the small beaker, then add 15ml of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA, 2% aqueous solution), 1ml of SDS (2% aqueous solution) and 14.0ml water, after ultrasonic emulsification, add it to the solution swollen in the first step, continue to stir and swell; take another small beaker, add 2.5g styrene, 0.2g divinylbenzene (DVB), 15ml of 2% PV...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dispersity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com