Preparation method of polyol glucoside
A technology of glucoside and polyol, which is applied in the field of preparation of polyol glucoside, can solve problems such as difficulties in the distillation process, and achieve the effect of strong water-locking performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Add 16.7kg of glycerin to the reaction pot, stir and heat to 130°C, then add 8.2kg of glucose monohydrate, at this time the temperature in the pot drops to 90°C, quickly add 0.176kg of phosphoric acid, and then vacuumize and reduce the pressure in the pot Reduce the pressure to 0.09MPa, continue heating to raise the temperature in the pot to 100°C, and keep it at this temperature. When the water output in the pot reaches 1.2kg, stop heating, cool the reaction system to 80°C with a cold water bath, and then add 0.255kg 60wt% potassium hydroxide aqueous solution neutralizes the acid catalyst to make the product weakly alkaline, and the pH value measured is 8. Continue cooling to room temperature to obtain a nearly colorless and transparent product. Glycosides are predominant and contain relatively high levels of unreacted glucose.
Embodiment 2
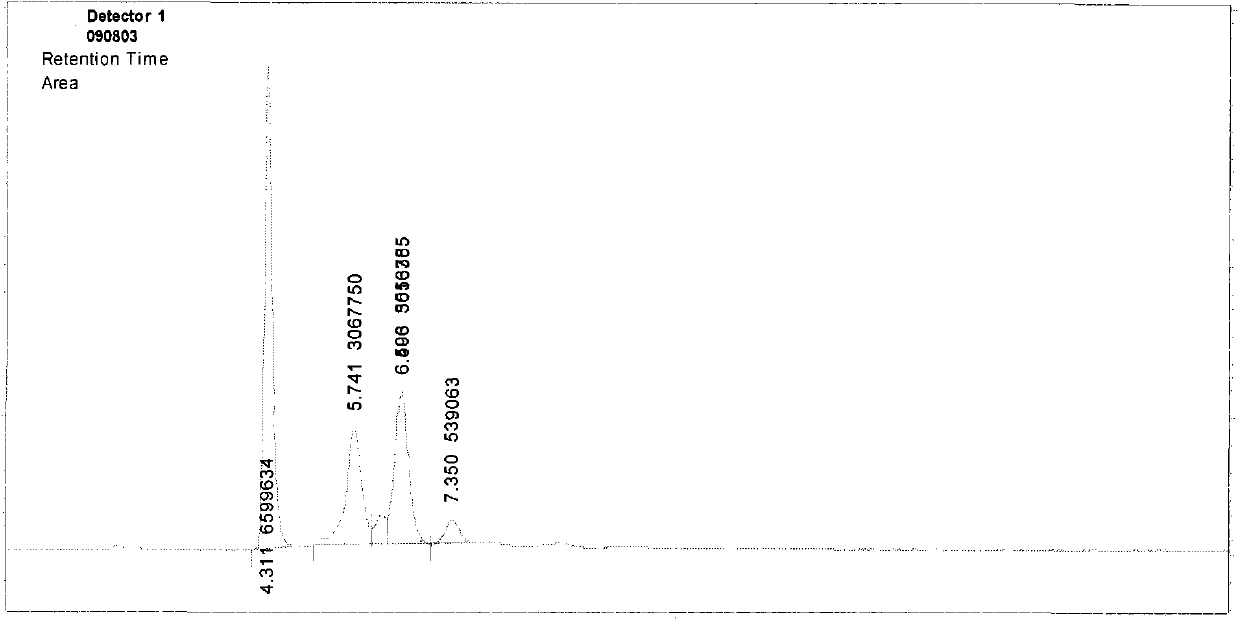
[0035] Add 16.7kg of glycerin to the reaction pot, stir and heat to 130°C, add 8.2kg of glucose monohydrate, at this time the temperature in the pot drops to 90°C, quickly add 0.176kg of phosphoric acid, then vacuumize and reduce the pressure in the pot Drop to 0.09MPa, continue heating to make the temperature in the pot rise to 100°C, and keep it at this temperature. When the water output in the pot reaches 1.2kg, stop heating. The difference from Example 1 is that 0.255 kg 60wt% potassium hydroxide aqueous solution neutralizes the acid catalyst, makes the product weakly alkaline, cools to room temperature, and obtains a light amber product, which is mainly based on glyceryl-glucoside and contains higher The amount of unreacted glucose. Analysis results see figure 1 .
[0036] figure 1 It is the high-efficiency liquid chromatography analysis figure of embodiment 2, and wherein, the horizontal axis represents the peak time of each component, i.e. retention time t; Retentio...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Add 16.7kg of glycerin to the reaction tank, heat it to 130°C under stirring, add 8.2kg of glucose monohydrate, at this time, the temperature in the tank drops to 90°C, quickly add 0.176kg of phosphoric acid, then reduce the pressure to 0.09MPa, and continue heating to 130°C, kept at this temperature, when the water yield reached 1.2kg, stop heating, cool the reaction system to 80°C with a cold water bath, then add 0.255kg 60wt% potassium hydroxide aqueous solution to neutralize the acid catalyst, until the pH value is 7, Continue to cool to room temperature, the color of the obtained product is almost colorless and transparent, and through high-performance liquid chromatography analysis, the content of glucose is relatively low, indicating that the raw material glucose is running out, and the glyceryl monoglucoside and glyceryl diglucoside in the product The content is equivalent.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com