Composition comprising the extracts of lysimachia clethroides for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
A technology for preventing and treating cardiovascular disease and a composition, which is applied in the field of functional health food to achieve the effect of strong vasodilation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the crude extract of pearl vegetable
[0065]Pearl vegetables collected from the province of Kangwon-do are rinsed with water to remove impurities. Then dry and pulverize. In the extraction container, add 25g of pulverized pearls, and a total amount of 500ml70wt% ethanol aqueous solution, and carry out heat extraction at 70°C under reflux cooling, repeat three times, each for three hours. The resulting product was filtered with filter paper, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure in a 40°C water bath and lyophilized. As a result, 5.3 g of a crude extract of loosestrife was obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2: the preparation of the fraction of loose extract of pearl
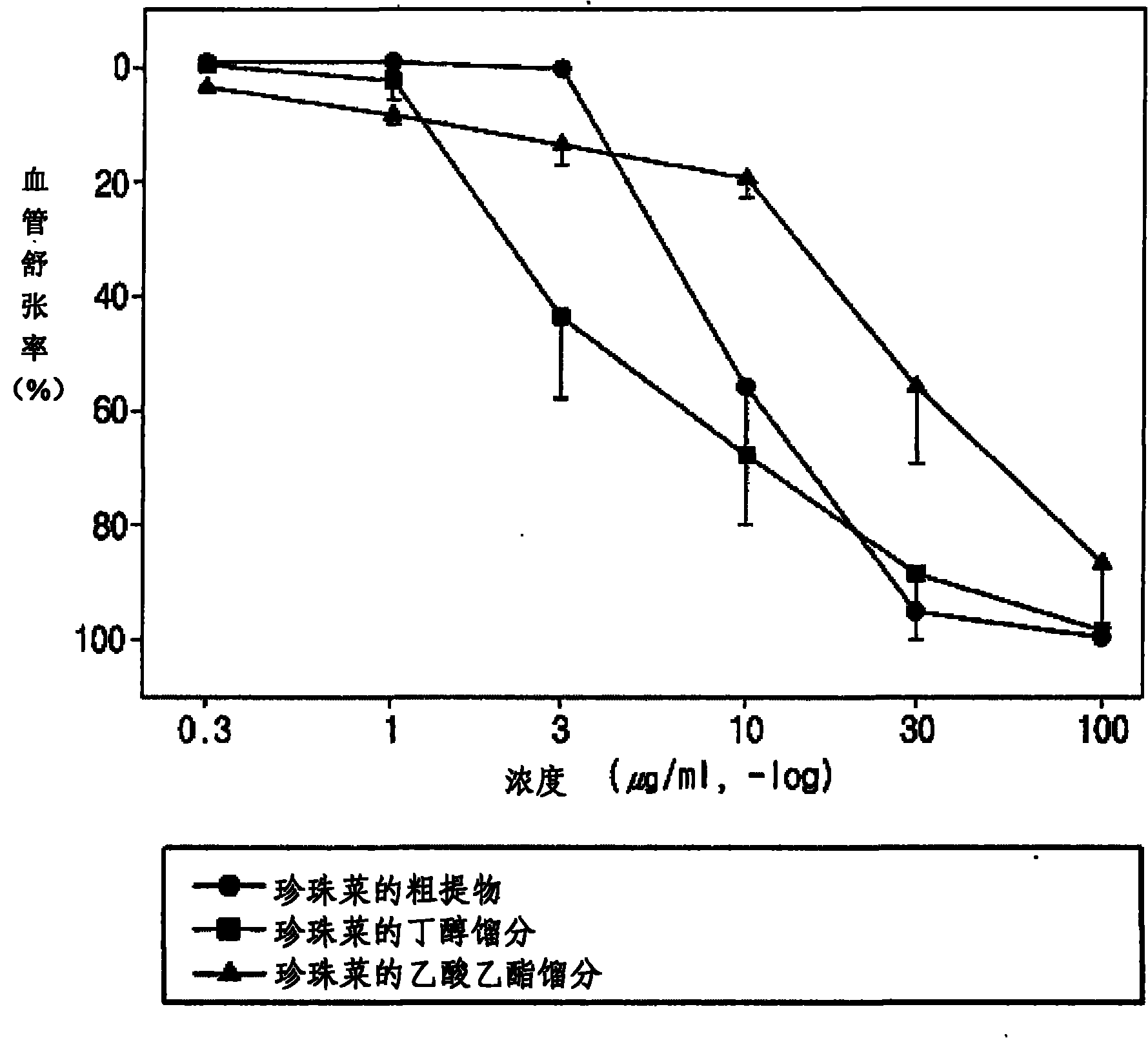
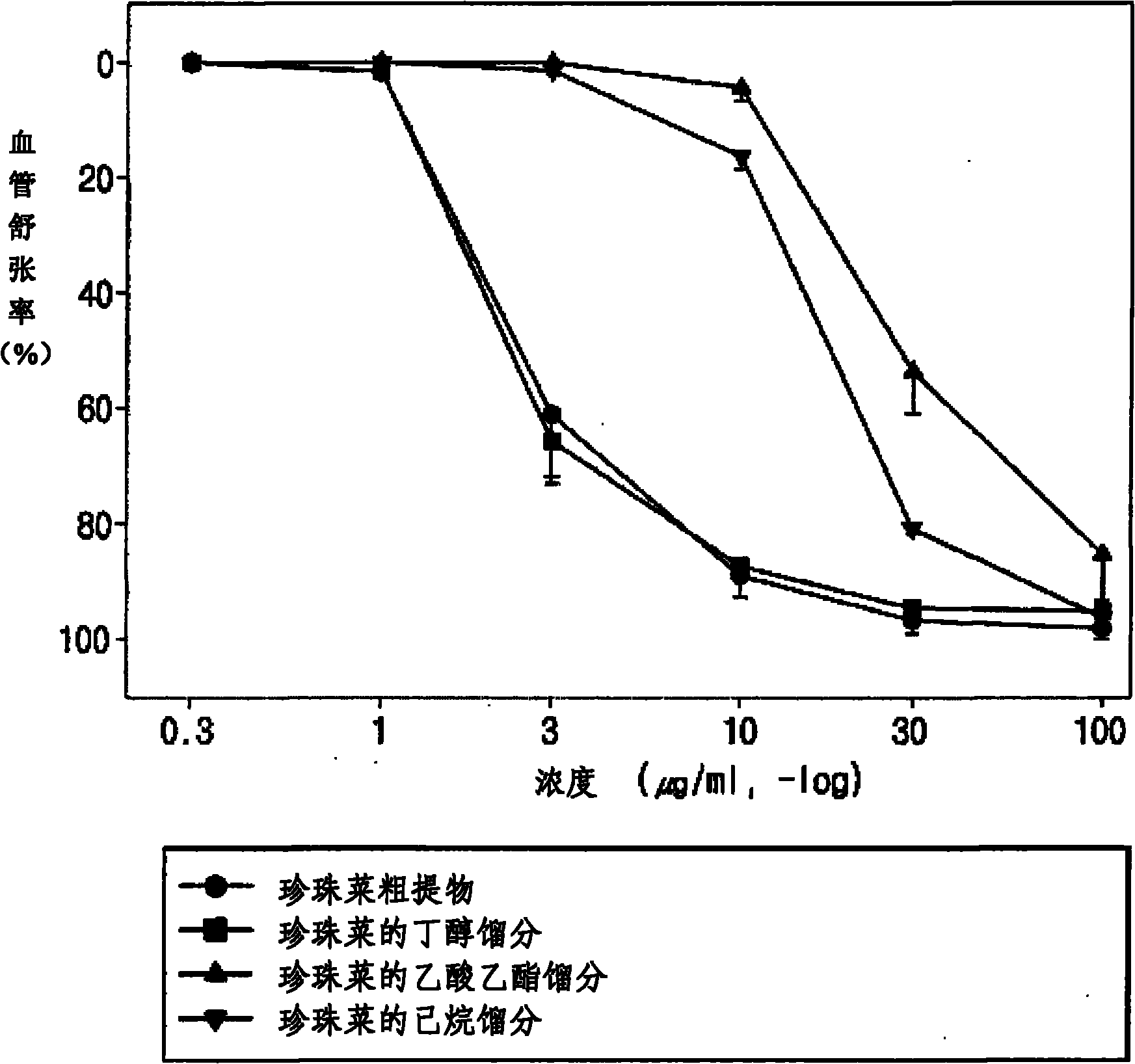
[0067] The crude extract of loosestrife obtained in Example 1, each part of 5g, was suspended in 50ml of purified water respectively, in the order of hexane, ethyl acetate and n-butanol, each solvent 50ml, and the obtained product was subjected to sequential solvent fractionation respectively , extracted three times to obtain fractions of each solvent respectively, and concentrated these fractions under reduced pressure. As a result, the hexane fraction, ethyl acetate fraction and n-butanol fraction of loosestrife were obtained.
experiment example 1
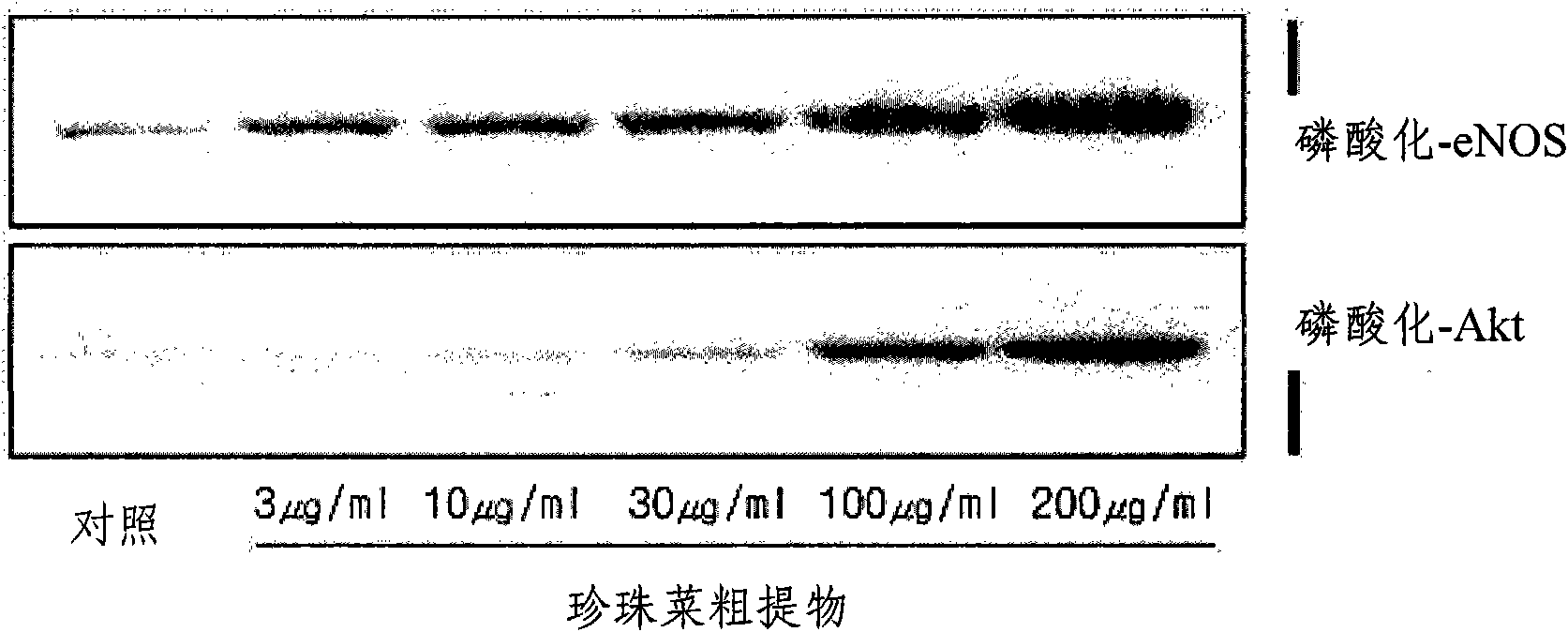
[0068] Experimental Example 1: Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of the Crude Extract of Pearl Vegetables on NAD(P)H Oxidase Activity
[0069] The effect of the crude extract and fractions obtained in the above-mentioned Examples 1 and 2 on inhibiting the activity of NAD(P)H oxidase was determined, and NAD(P)H oxidase is an index enzyme for the development of cardiovascular diseases. For this purpose, rat arterial smooth muscle cells (rat arterial smooth muscle cells; RASMC) and bovine vascular endothelial cells (bovine aortic endothelial cells; BAECs) were used to compare the changes in NAD(P)H oxidase activity. See Table 1 for the results. First, arterial smooth muscle cells and vascular endothelial cells were mixed with MEM (minimal essential medium), DMEM (Dulbecco's minimal medium) and 10% FBS (fetal bovine serum) solutions, respectively, and these cells were incubated in 5% CO 2 / 37°C and cultured in 96-well plates for 24 hours. They were then cultured for anoth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com