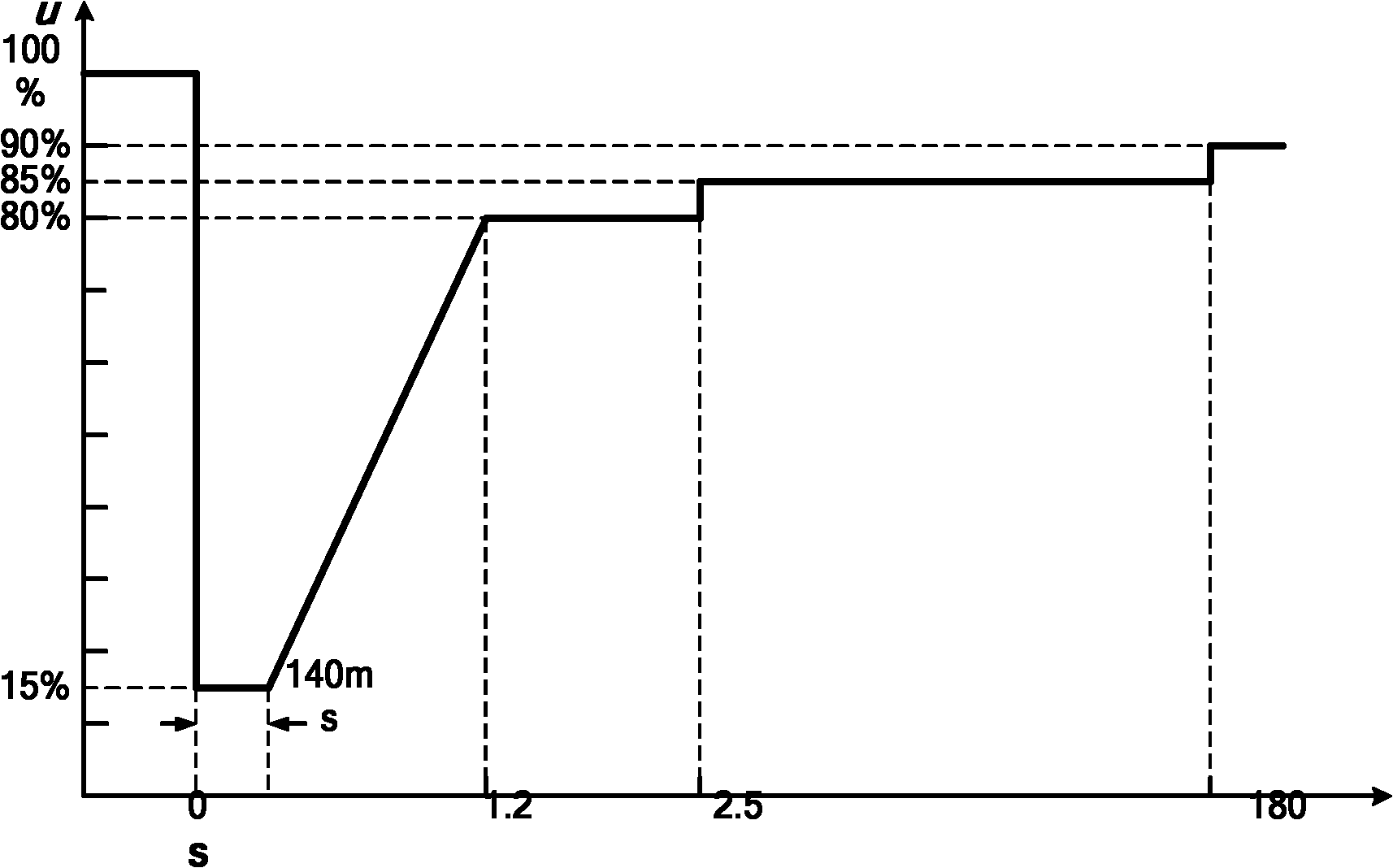
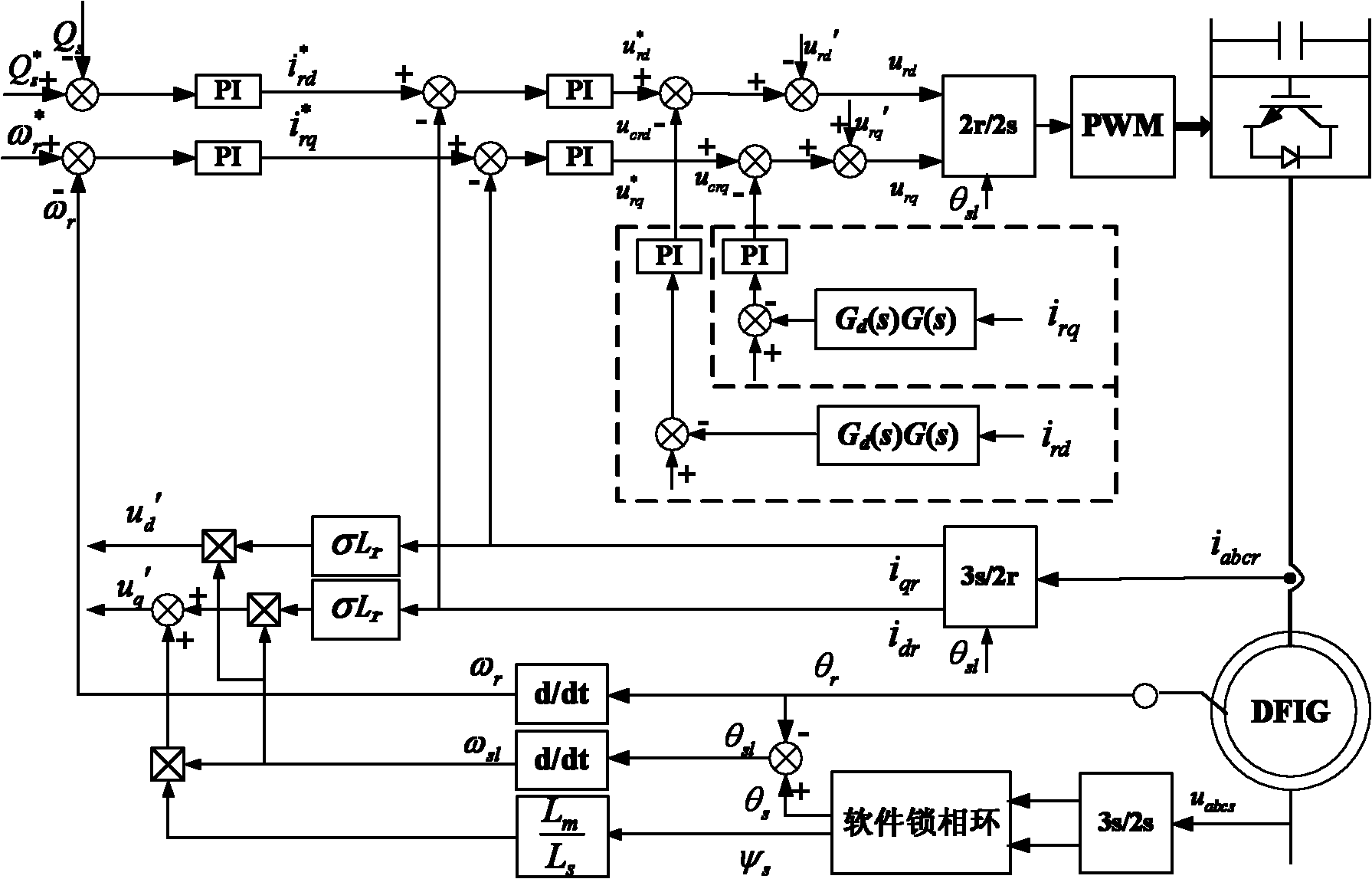
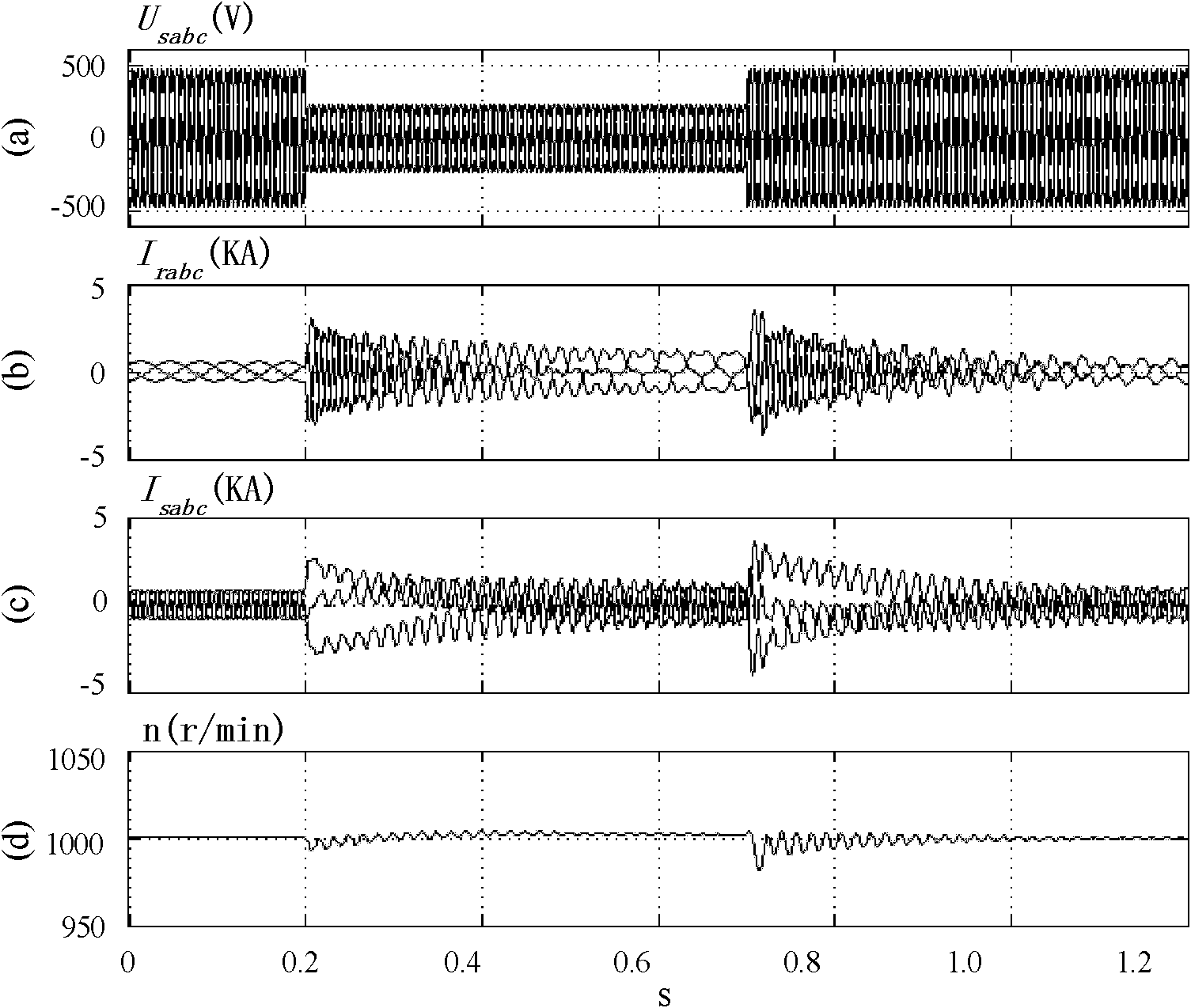
Control method of double-fed induction generator under power grid voltage three-phase symmetrical drop fault
A technology for wind power generators and grid voltage, which is applied in the direction of motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, and control of generators, etc. It can solve the problem that the power grid cannot play a positive role in supporting normal operation, deteriorates the power grid, and increases system costs. and other problems, to achieve the effect of non-off-grid operation, rotor current suppression, and stable control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0025] Compared with single-phase voltage dips and two-phase-to-ground voltage dips, three-phase symmetrical dips are usually the most harmful short-circuit faults in power systems. The grid voltage three-phase symmetrical drop fault will cause the generator stator voltage to drop, and the change of the stator voltage will cause the generator stator flux linkage to change. Under normal circumstances, the stator and rotor voltage equations of the generator can be expressed in space vector form:
[0026] u s s = R s i s s + d ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com