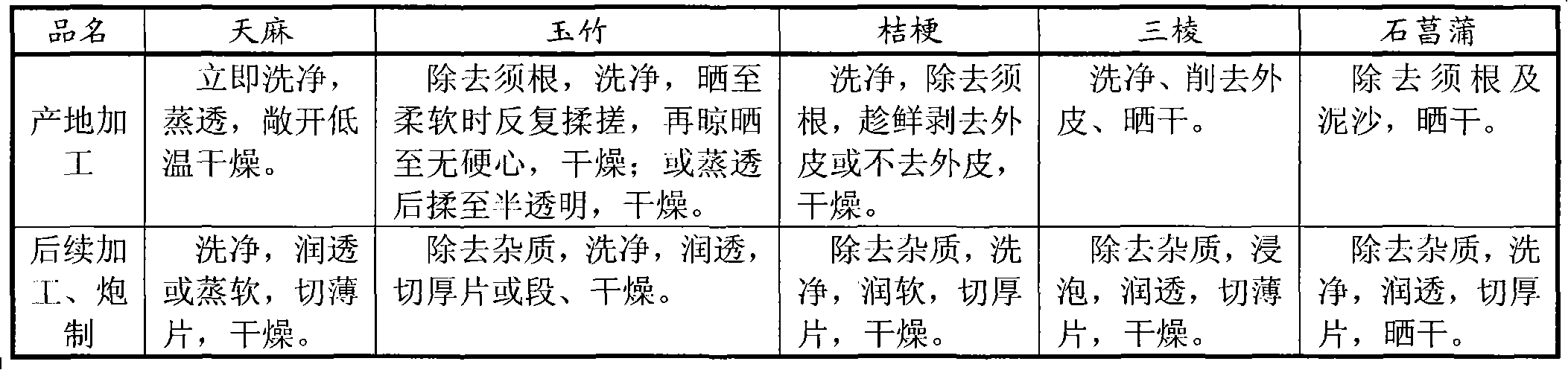
Fresh processing technology of traditional Chinese plant medicine at producing site
A processing technology and technology of Chinese herbal medicines, applied in plant raw materials, plant/algae/fungus/moss ingredients, medical formulas, etc., can solve the problems of loss of active ingredients of Chinese herbal medicines, backward processing methods, etc., to achieve high content of medicinal ingredients, Good quality of decoction pieces, remarkable economic and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] The present embodiment is example with Radix Paeoniae Alba.
[0045] 1. Harvesting: The harvesting time of Radix Paeoniae Alba is generally carried out on sunny days in August. First cut off the stems and leaves, dig up the roots, and shake off the soil.
[0046] 2. Purification: ①Manual purification: Cut off the peony root from the place where the peony head grows, then cut off the lateral roots above the thick heel, smooth the convex surface, cut off the head and tail, drive out the outer cork of the peony root, and remove the Dig out the insect eyes, and then divide them into three grades according to large, medium and small. ②Water washing system, use a drum type circulating water washing machine to spray water until the surface sediment is washed.
[0047] 3. Cutting: Use a flexible belt reciprocating herbal cutter to cut the cleaned peony roots into 0.5-0.8mm circular slices. Except for fresh-cut and fragile medicinal materials such as Zhebei and Yuanhu, medicin...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The present embodiment takes Fritillaria fritillaria as an example.
[0052] 1. Harvesting: Fritillaria fritillaria is generally harvested in early to mid-May, when the aboveground part is basically dry and has not completely dried up.
[0053] 2. Cleaning system: Use a drum-type circulating water washing machine to spray and rinse until the surface sediment is cleaned. Or put the Fritillaria on a drainable sieve and spray evenly with clean water. The number of spraying depends on how much soil the Fritillaria contains, generally 3 to 4 times. During the spraying process, clearing should be carried out in order to spray evenly.
[0054] 3. Cutting: Use an adaptive rotary slicer to cut the cleaned fritillaria into 2-3mm thin slices.
[0055] 4. Inactivation: Microwave drying is used to rapidly heat Fritillaria fritillata to 85°C-105°C for 5-8 seconds.
[0056] 5. Drying: put Fritillaria japonicus into a hot air dryer to dry at a drying temperature of 60°C, and take it...
Embodiment 3
[0058] This embodiment takes Yuan Hu as an example.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com