Method for preparing alpha-olefin from vegetable fat
A technology of vegetable oils and olefins, applied in the field of production of α-olefins, to achieve the effect of reducing the partial pressure of hydrocarbons, facilitating the production and stabilizing the supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
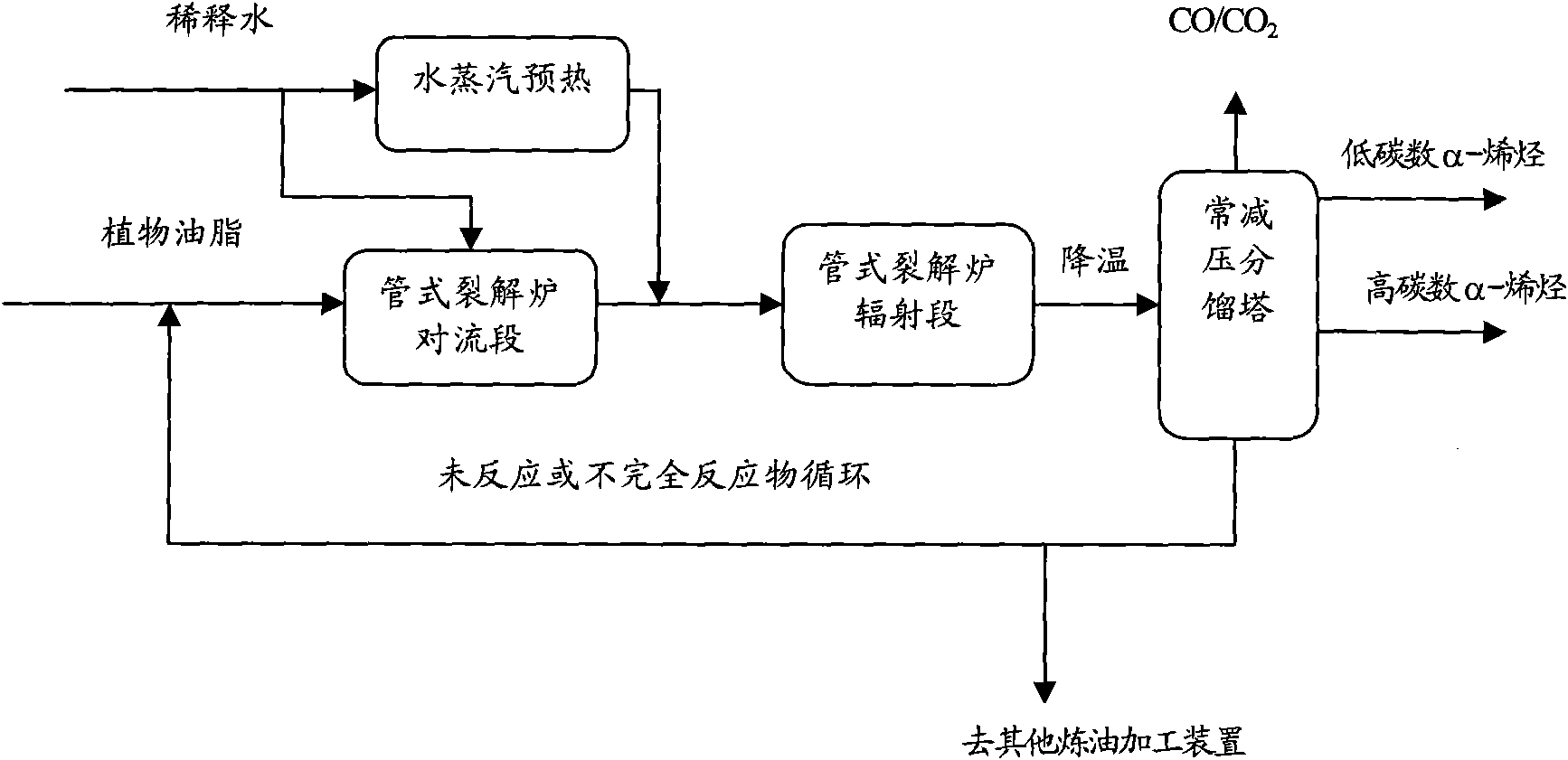
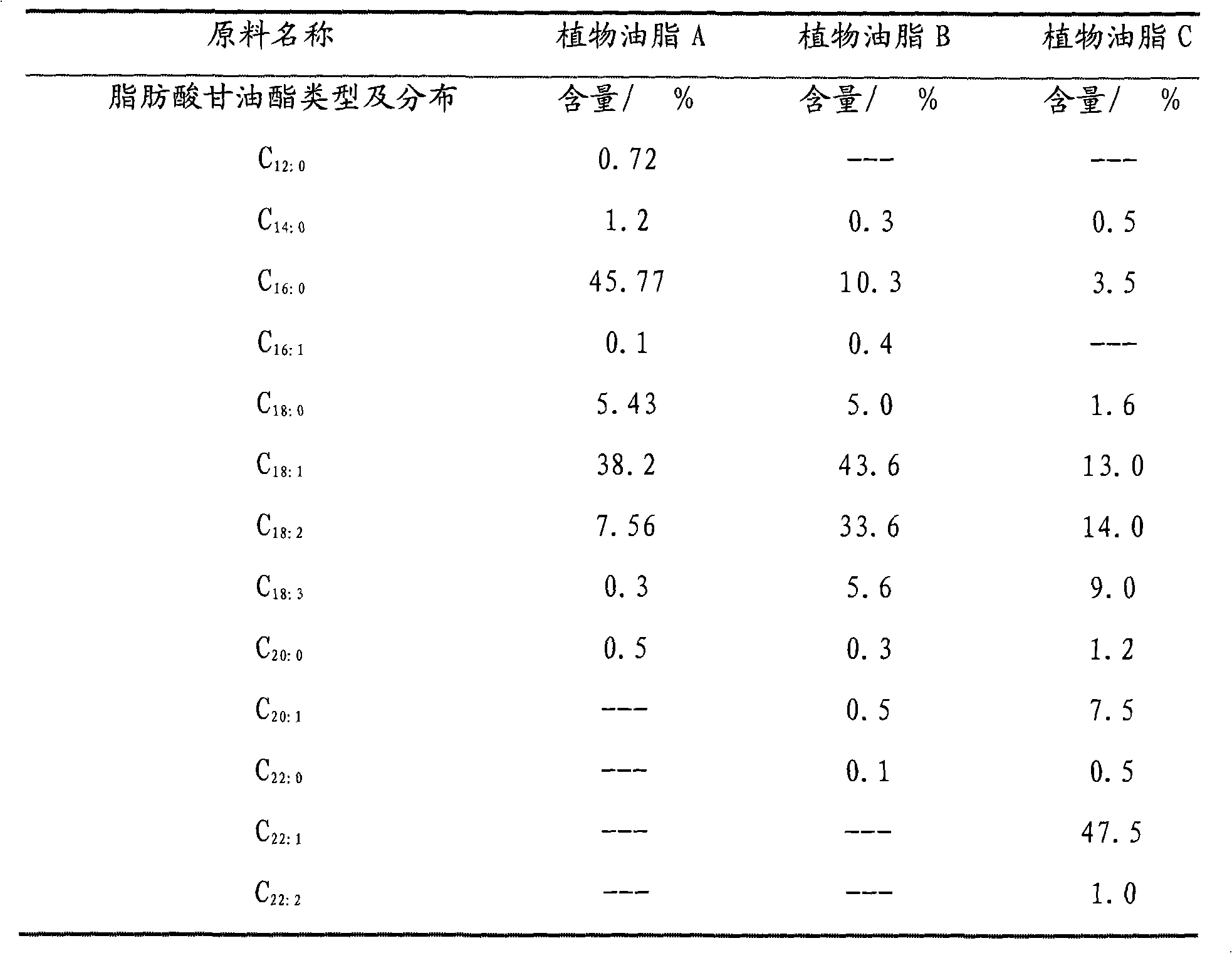
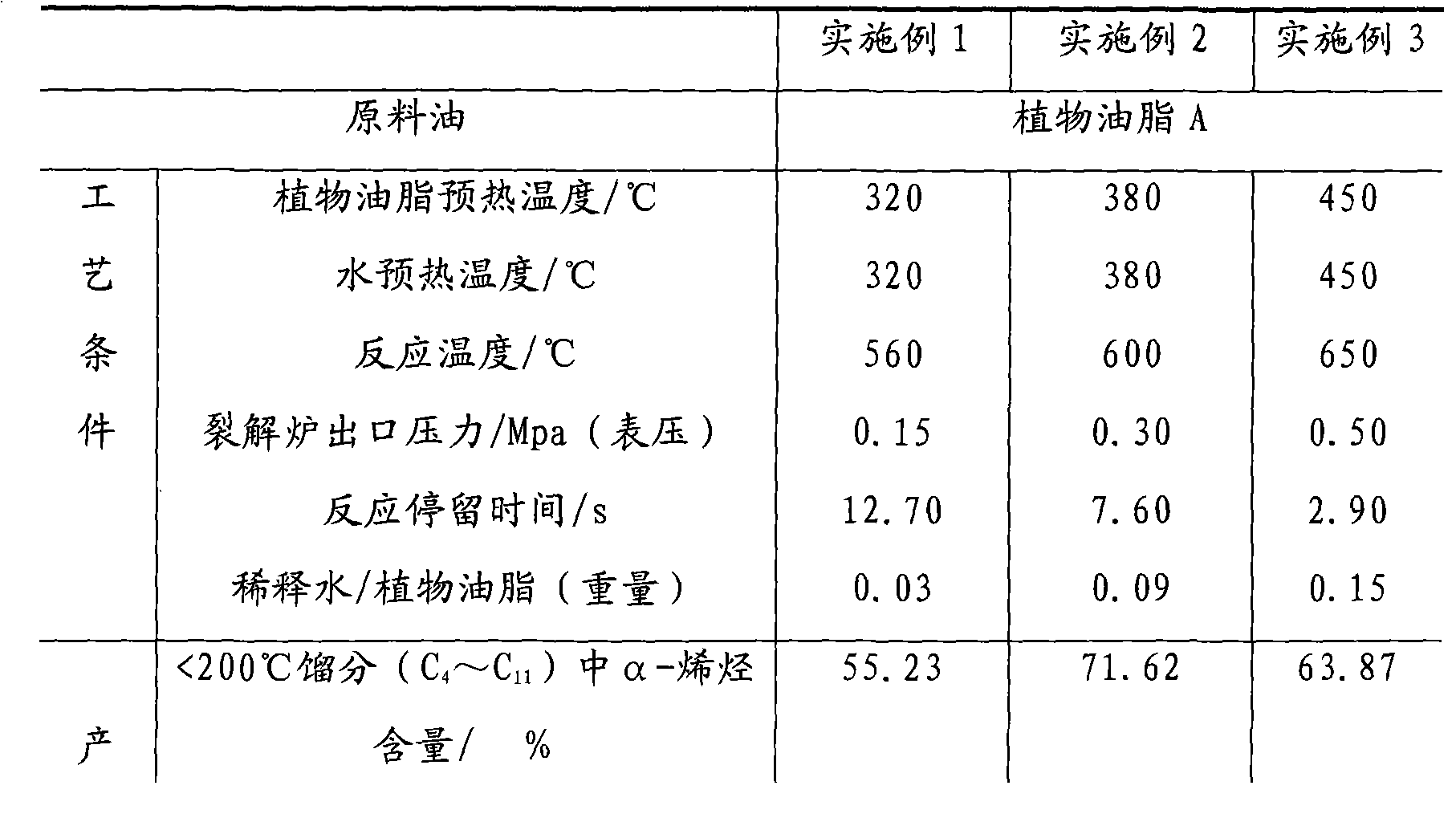
[0031]With a kind of vegetable oil A, its properties are shown in Table 1, and dilution water is separately used as the feed material of the simulated steam thermal cracking performance evaluation test device, and the simulated cracking evaluation test device is composed of a feed system, raw material preheating, cracking reaction system, and quenching system. The product separation system is composed of five parts, and the whole device is controlled and monitored by a computer. The generated pyrolysis products were separated according to the cut point of 200°C and 360°C, and the fraction >360°C was regarded as the unconverted substance. The main operating conditions for the process of pyrolysis to produce α-olefins are: vegetable oil preheating temperature 320°C, water preheating temperature controlled at 320°C (shared preheating section), thermal cracking reaction temperature: 560°C, cracking furnace outlet pressure: 0.15Mpa (gauge pressure), reaction residence time: 12.7s, ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Using the same test device, test method and steps as in Example 1, a vegetable oil A, whose properties are shown in Table 1, and dilution water are separately used as feed materials for the simulated thermal cracking performance evaluation test device, and thermal cracking produces α-olefins The main operating conditions of the process are: vegetable oil preheating temperature 380°C, water preheating temperature controlled at 380°C (shared preheating section), thermal cracking reaction temperature: 600°C, cracking furnace outlet pressure: 0.30Mpa (gauge pressure) , Reaction residence time: 7.6s, the weight ratio of dilution water and vegetable oil is 0.09, and the cracking evaluation test results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Using the same test device, test method and steps as in Example 1, a vegetable oil A, whose properties are shown in Table 1, and dilution water are separately used as feed materials for the simulated thermal cracking performance evaluation test device, and thermal cracking produces α-olefins The main operating conditions of the process are: vegetable oil preheating temperature 450°C, water preheating temperature controlled at 450°C (shared preheating section), thermal cracking reaction temperature: 650°C, cracking furnace outlet pressure: 0.50Mpa (gauge pressure) , Reaction residence time: 2.9s, the weight ratio of dilution water and vegetable oil is 0.15, and the cracking evaluation test results are shown in Table 2.
[0036] The data in table 2 shows: vegetable oil A carries out steam thermal cracking, and under the selected cracking reaction severity condition, all can generate higher proportion mixed α-olefin in embodiment 1, embodiment 2 and embodiment 3, no matter ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com