Low-molecular citrus pectin capable of being combined with clinical common chemotherapeutic drug for controlling cancer and cancer metastasis and diffusion
A low-molecular-weight, chemotherapeutic drug technology, which is applied in the application field of low-molecular-weight citrus pectin for the preparation of medicines, food or health products, and can solve the problems that low-molecular-weight citrus pectin has not been publicly reported.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
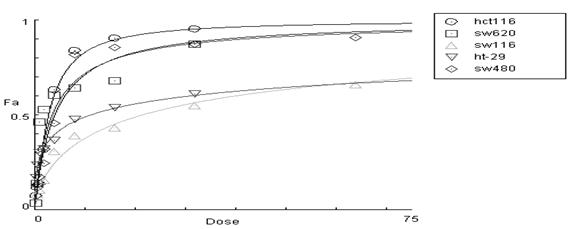
[0025] Colon cancer is a common malignant tumor, and cell metastasis is an important feature of malignant tumors, and the liver is the most frequently involved organ in colon cancer metastasis. In addition to surgical treatment, medical treatment plays an important role in the treatment of colon cancer. However, judging from the current clinical treatment effect, drug resistance and toxic side effects of commonly used chemotherapeutic drugs have become a difficult problem in the treatment of colon cancer.
[0026] The growth and metastasis of colon cancer is a complex process: it is related to abnormal cell differentiation, abnormal proliferation, abnormal growth, biological characteristics of cancer cells, immune status of the body and the microenvironment of the liver. Each step involves a variety of molecular events. Knowledge of these molecular events will provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of colon cancer and its liver metastases. In these mecha...
Embodiment 2
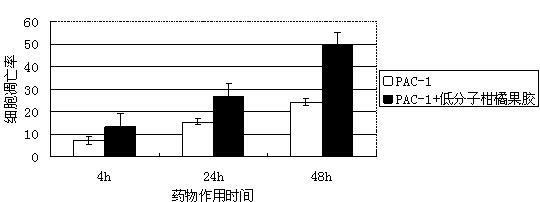
[0079] LCP-inhibitory effect on mouse liver cancer H22 tumor strain, CY is cyclophosphamide.
[0080]
[0081] During the experiment, the mice in each group had normal drinking water, coat color and activity status. Five days after the mice were inoculated with H22 cells, subcutaneous tumors could be touched in each group, and the activity status of the mice in the LCP-administered groups was normal during the test. Animals were sacrificed on the 10th day, and it was found during anatomy that, compared with NS group, the tumor infiltration range of each LCP group was smaller, the depth was limited, and the tumor body was easily peeled off. The tumor inhibition rate of combined application of LCP and CY was significantly higher than that of each group, with statistical significance (P<0.001). There was no significant difference in body weight of mice in LCP group compared with NS group, and the body weight of mice in single CY group was significantly lower than that of NS gr...
Embodiment 3
[0084] LCP-inhibitory effect on mouse cervical cancer U14 tumor strain, DOX is doxorubicin.
[0085]
[0086] During the experiment, the mice in each group had normal drinking water, coat color and activity status. The mice were inoculated with U14 cells for 8 days, and the animals were sacrificed 10 days after administration, and the tumor inhibition rate was calculated by dissection. Compared with the NS group, the tumor infiltration range of the LCP groups was smaller, the depth was limited, and the tumors were easy to peel off. The tumor inhibition rate of combined application of LCP and DOX was significantly higher than that of each group, which was statistically significant (P<0.01).
[0087] The experimental results showed that the inhibitory effect of LCP on tumor growth was dose-dependent, and the tumor inhibition rate of combined application of LCP and DOX was significantly higher than that of each group, which was statistically significant (P<0.01).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com