Analysis method of boron and phosphor in Ga-doped CZ silicon rod and ingredients
An analysis method and silicon rod technology, applied in the direction of material resistance, can solve the problems of delaying analysis time and increasing costs, and achieve the effect of improving the process level and reducing the cost of quality identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
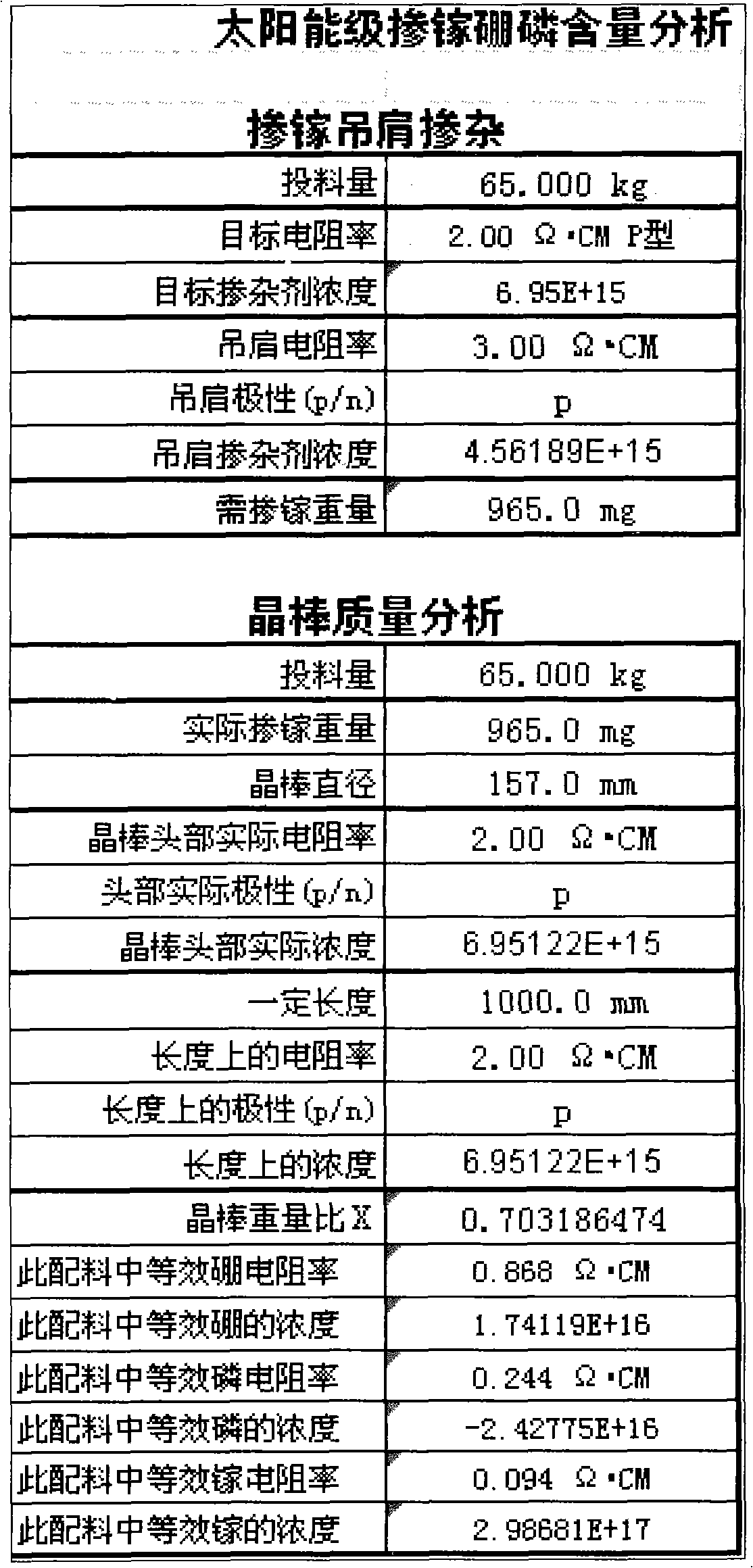
[0070] Production of monocrystalline silicon ingots with an average diameter of 157mm and a casting capacity of 65kg. The resistivity measured by the hanging shoulder is P-type 3Ω·CM, and 965mg of gallium is doped. After the silicon ingots are produced, the resistivity of the ingot head is P-type 2Ω. CM, at 1000mm ingot, the resistivity is P-type 2Ω CM:
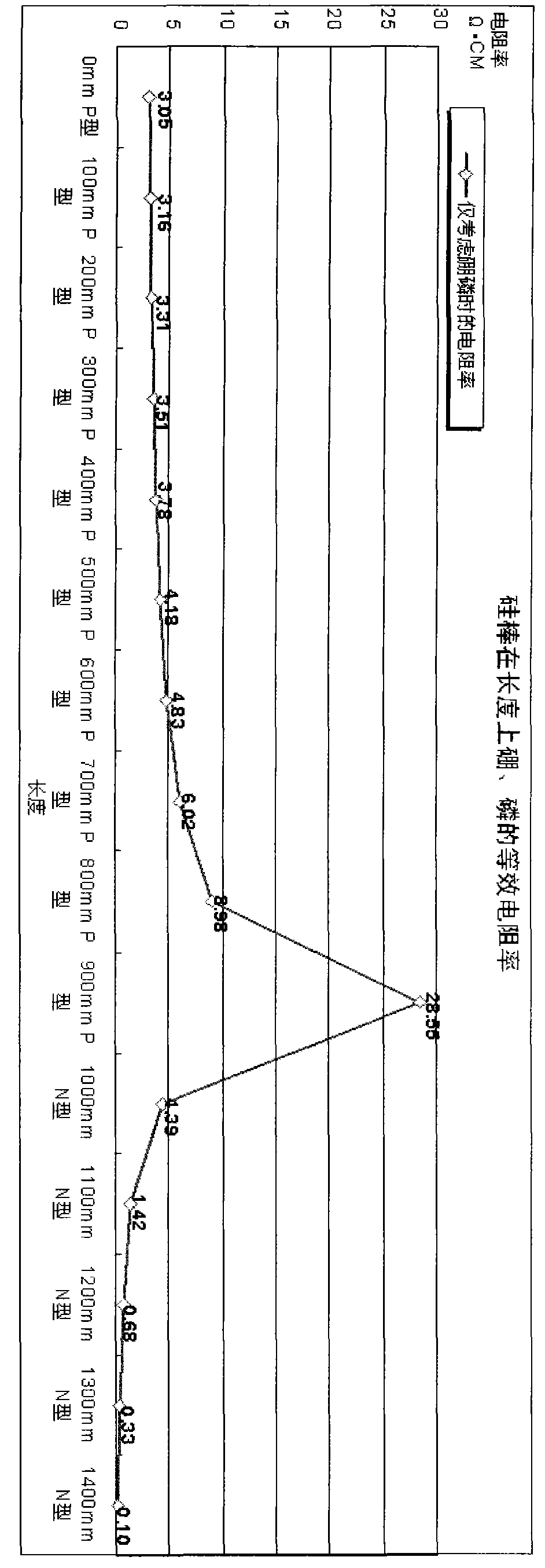
[0071] According to the above method: to produce this silicon rod, the equivalent resistivity of phosphorus in the ingredients is 0.244Ω·CM, and the concentration is 2.43*10 16 / cm 3 , the equivalent resistivity of boron is 0.87Ω·CM, and the concentration is 1.74*10 16 / cm 3 , the resistivity at 500mm of the silicon rod is P-type 2.03Ω·CM, and the corresponding resistivity of boron at 600mm of the silicon rod is 0.99Ω·CM.
[0072] See figure 1 , 2 , 3, 4, 5.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com