Drying method of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers
An ultra-high molecular weight, polyethylene fiber technology, applied in the direction of one-component polyolefin rayon filament, rayon filament cleaning/drying, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the impact resistance of stab-resistant fabrics, weak adhesion, and thread drying. sufficient and other problems to achieve uniform mechanical properties, stable mechanical properties, and high puncture resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
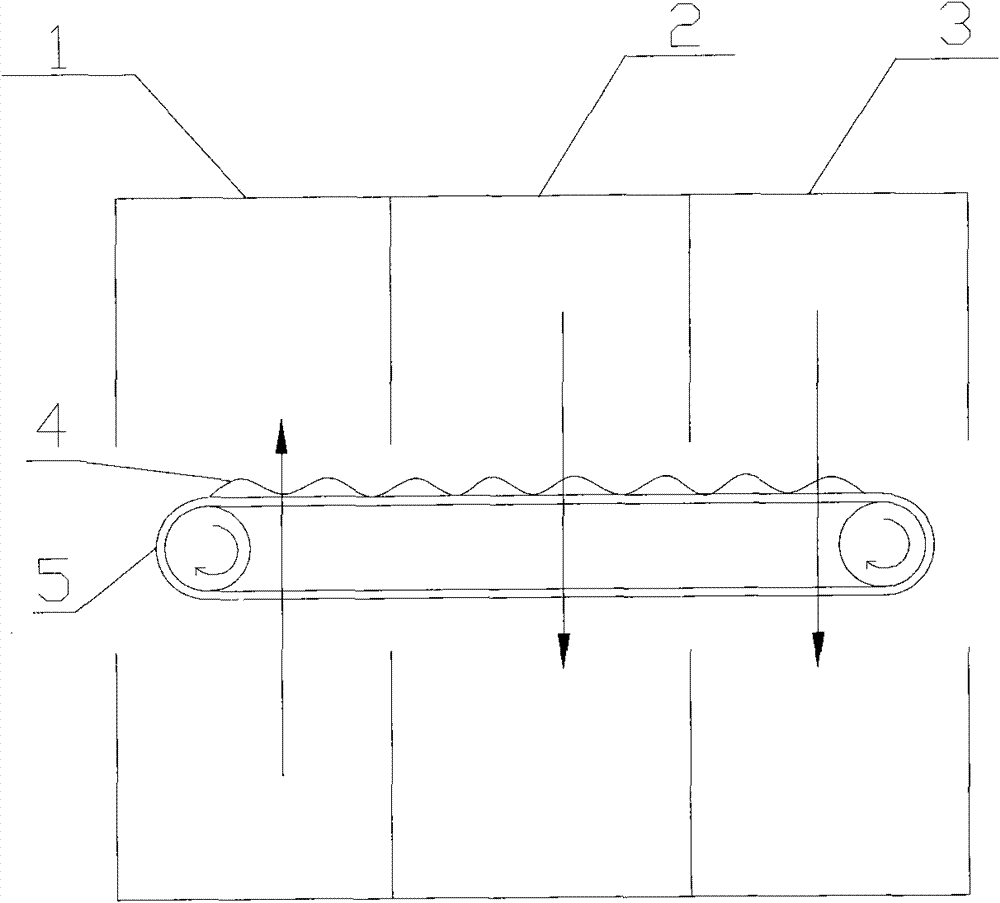
[0041] 1. Place the 400-denier RYX90 ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber produced by Ningbo Rongyi Chemical Fiber Technology Co., Ltd. on the creel.
[0042] 2. The crimped ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 is pre-dried, first-stage drying, second-stage drying, and third-stage drying in sequence:
[0043] pre-dried
[0044] The crimped ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers 5 are introduced into the pre-drying chamber for first-stage drying, the direction of the hot air is controlled to blow from the bottom of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers 5 to the top, the drying temperature is set at 105° C., and the vehicle speed is set at 90 m / min.
[0045] first stage drying
[0046] The pre-dried ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 is introduced into the first drying chamber 1 for first-stage drying, the direction of the hot air is controlled to blow from the bottom of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibe...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0062] 2. The crimped ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 is sequentially subjected to first-stage drying, second-stage drying, and third-stage drying:
[0063] first stage drying
[0064] The crimped ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 is introduced into the first drying chamber 1 for first-stage drying, the direction of the hot air is controlled to blow from the bottom of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 to the top, the drying temperature is set at 100° C., and the vehicle speed is set at 85 m / h min.
[0065] second stage drying
[0066] The ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 after the first-stage drying is introduced into the second drying chamber 2 for second-stage drying, the direction of the hot air is controlled to blow from above the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 to the bottom, and the drying temperature is set at 70°C. ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0071] 2. The crimped ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 is sequentially subjected to first-stage drying, second-stage drying, and third-stage drying:
[0072] first stage drying
[0073] The crimped ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 is introduced into the first drying chamber 1 for first-stage drying, and the direction of the hot air is controlled to blow upward from the bottom of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5. The drying temperature is set at 110° C., and the vehicle speed is set at 95 m / h min.
[0074] second stage drying
[0075] The ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 after the first-stage drying is introduced into the second drying chamber 2 for second-stage drying, the direction of the hot air is controlled to blow from the top of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber 5 to the bottom, and the drying temperature is set at 10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com