Lamination type efficient air-cooled resistive heat exchanger for high-temperature superconducting large current lead
A current lead and high-temperature superconducting technology, applied in superconducting magnets/coils, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as small heat transfer area, increased temperature difference between heat exchanger and airflow, and low-efficiency heat exchanger temperature , to achieve the effect of large heat transfer area, high heat transfer efficiency and low joint resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
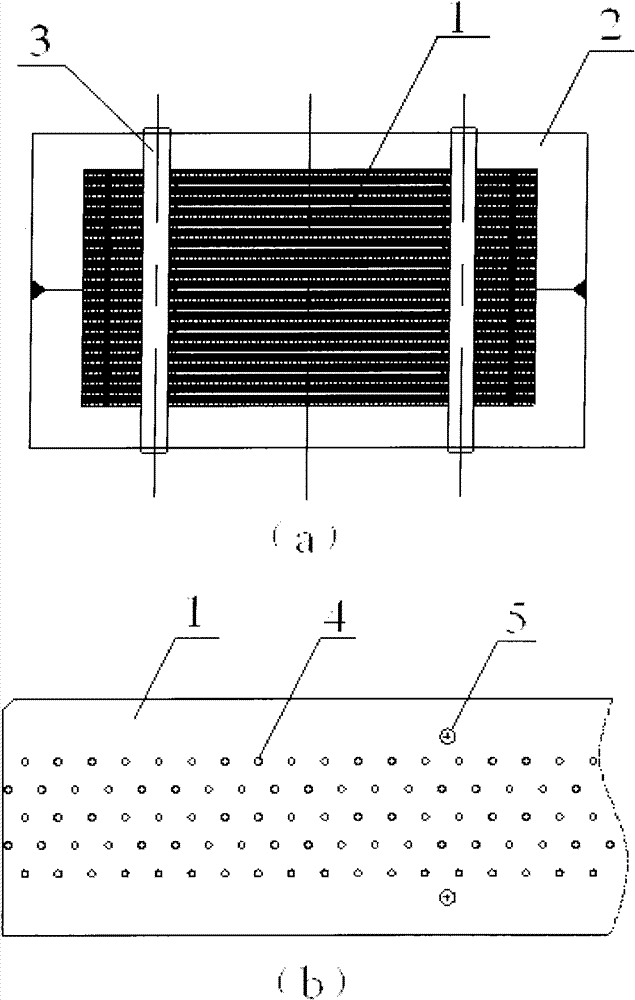
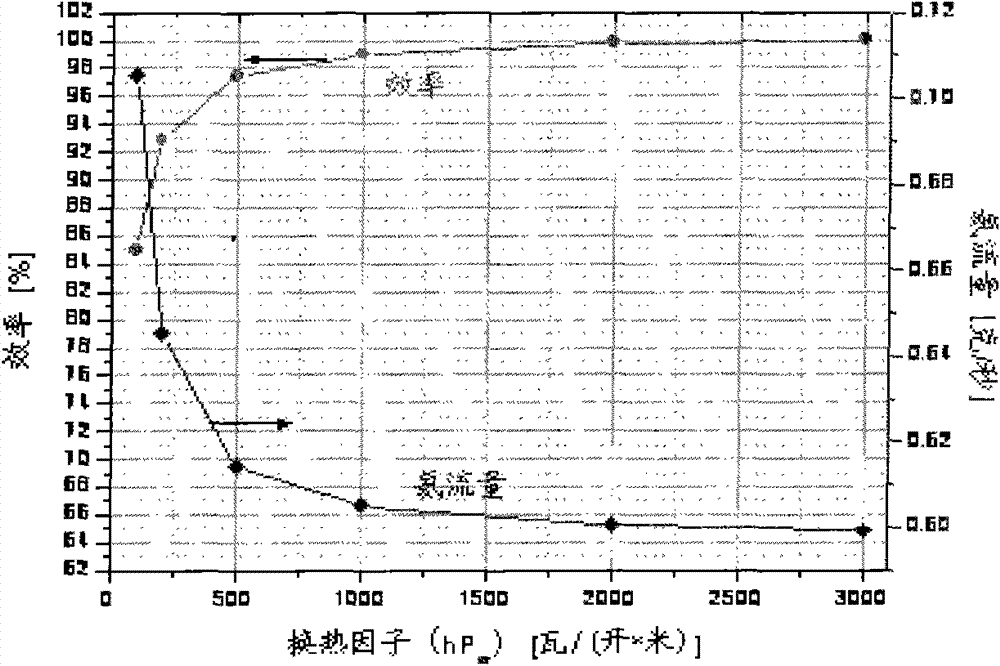
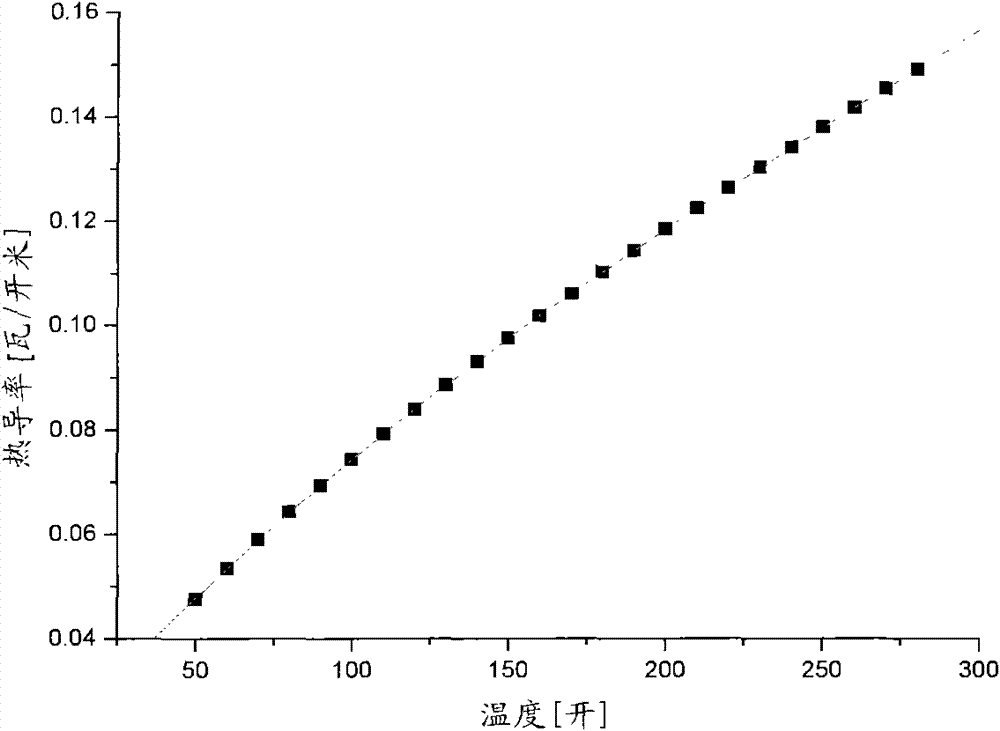
[0026] see figure 1, a laminated heat exchanger used between the room temperature section of the current lead of a large superconducting magnet and the high temperature superconducting section, including a plurality of thin copper plates that are stacked and fixed by rivets The heat exchanger core 1 is formed as a whole, and the thin copper plate is provided with regularly distributed through holes 4 and bumps 5; the upper and lower sides of the heat exchanger core 1 are respectively provided with thick copper plates 3 for protection, between the stacked thin copper plates The gaps in the heat exchanger form evenly distributed flow channels; the heat exchanger core 1 is electron beam welded to the current lead at both ends of the room temperature section and the high-temperature superconducting section copper parts, and the flow channel of the heat exchanger core 1 communicates with the flow channels at both ends; Heater core body 1 is externally packaged with stainless steel ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com