Method for cultivating earthworms for experiment
A breeding method and experimental technology, applied in animal husbandry and other directions, can solve the problems of poor parallelism, laboratory environment impact, complicated method operation, etc., and achieve the effect of maintaining quantity and activity, occupying small space and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Breeding box: This embodiment uses a large finishing box. The height is 50 cm in length, 35 cm in width, and 35 cm in height. The lid has vent holes with a diameter of φ2. Earthworms dig and collect earthworms from the wild as earthworm species.
[0026] Breeding method: Spread a layer of sponge on the bottom of the culture box and spray tap water to moisten the surface; the depth of the breeding bed of E. vulgaris is 25 cm, and the depth of the breeding bed of E. vulgaris is 18 cm; the depth of the breeding bed is 18 cm; The aquaculture volume is controlled below 150-180, and the aquaculture volume of Eisenia vulgaris is controlled below 300-400. The breeding bed uses soil with a total organic carbon content of 2.5%. A mixture of cow dung and straw (with a ratio of 8: 2) was added at the initial stage of breeding. The initial input of the two types of earthworms was 0.5% and 1.0% of the soil weight, respectively. The positions of the bait were placed on the breeding bed...
Embodiment 2
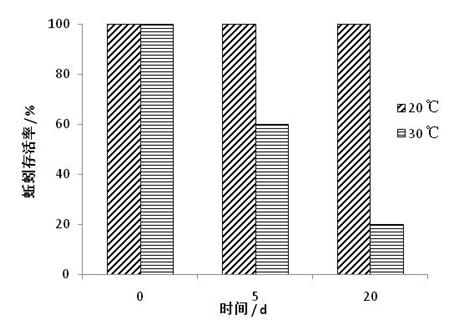
[0028] The earthworms raised by this method were used for the earthworm survival rate experiment. The breeding conditions were the same as in Example 1, except that the survival rate of earthworms at different temperatures was tested, and the results can be seen image 3 .
Embodiment 3
[0030] The earthworms raised by this method were used in the study of the accumulation and degradation kinetics of pentachlorophenol in the body of the worms. Each jar contains 100 g of soil and 6 earthworms, each of which is about 2 g. Except that no bait was added, the other conditions were the same as in Example 1. The results showed that after 40 days, the experimental earthworms had the same activity as the newly collected earthworms in the field, and there was no significant change in body weight. The specific statistical results are shown in the attachment. Figure 4 And Figure 5 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com