Continuously variable compression ratio engine and power output device thereof
An engine and compression ratio technology, applied in engine control, engine components, machines/engines, etc., can solve problems such as air distribution shock cooling and sealing engine body stability, cylinder bias pressure, and technical design difficulties of variable compression ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
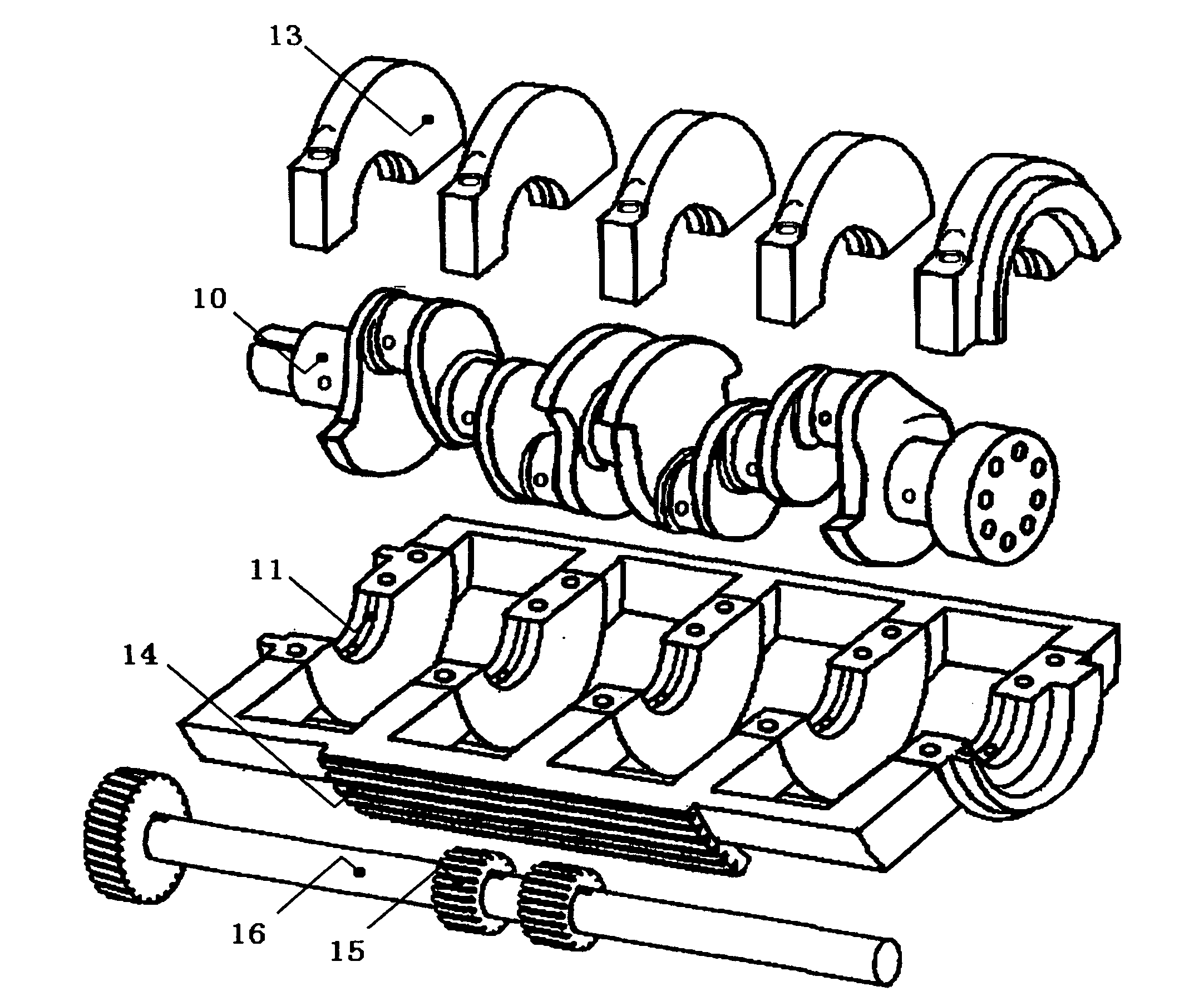
[0078] figure 1 This is an exploded three-dimensional view of the main components of the variable compression ratio engine of Embodiment 1. It can roughly understand the three-dimensional shape of some components, including the crankshaft 10, the crankshaft bearing cap 13, the crankshaft deflection support body 11 and its sector gear 14, the control gear 15 and Control axis 16.
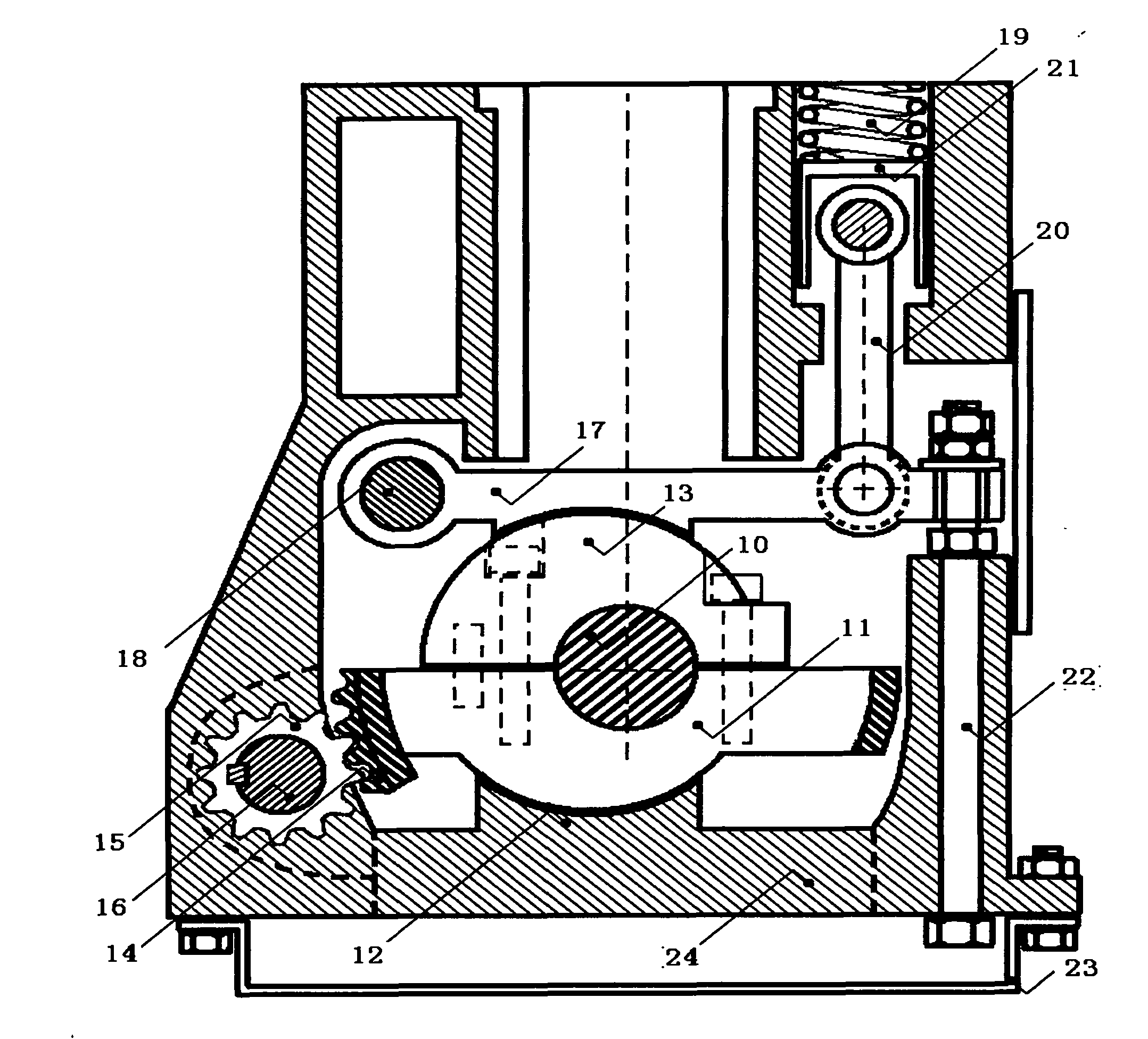
[0079] figure 2 It is a radial cross-sectional view of the first-type continuously variable compression ratio engine of Embodiment 1, which mainly includes the crankshaft 10, the crankshaft deflection support 11, the crankshaft bearing cover 13, the engine block 24, and the control drive mechanism. The control drive mechanism is divided into a switching maintenance part and an independent locking part according to its main functions. The switching maintenance part includes a control shaft 16 and its control gear 15, and the independent locking part includes a brake pressure plate 17 and a connection of t...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Figure 8 It is a radial cross-sectional view of the second type of continuously variable compression ratio engine used in Embodiment 2. It is easy to describe, and part of the radial cross section of the second type of continuously variable compression ratio engine shown is staggered. The space support of the crankshaft deflection support body 11 of the second type of continuously variable compression ratio engine is all borne by its outer arc-shaped end surface. The crankshaft bearing cover 13 can be provided without an outer arc-shaped end surface; because the crankshaft deflection support body 11 is very thick Therefore, only a single-sided connection is provided; because the upward force on the crankshaft deflection bracket 11 is not large, the slightly complicated control piston connecting rod mechanism is cancelled. The brake pressure plate is adjusted by the spring pad 19a and the adjusting screw 22, so that the crankshaft deflection bracket can be locked and rota...
Embodiment 3
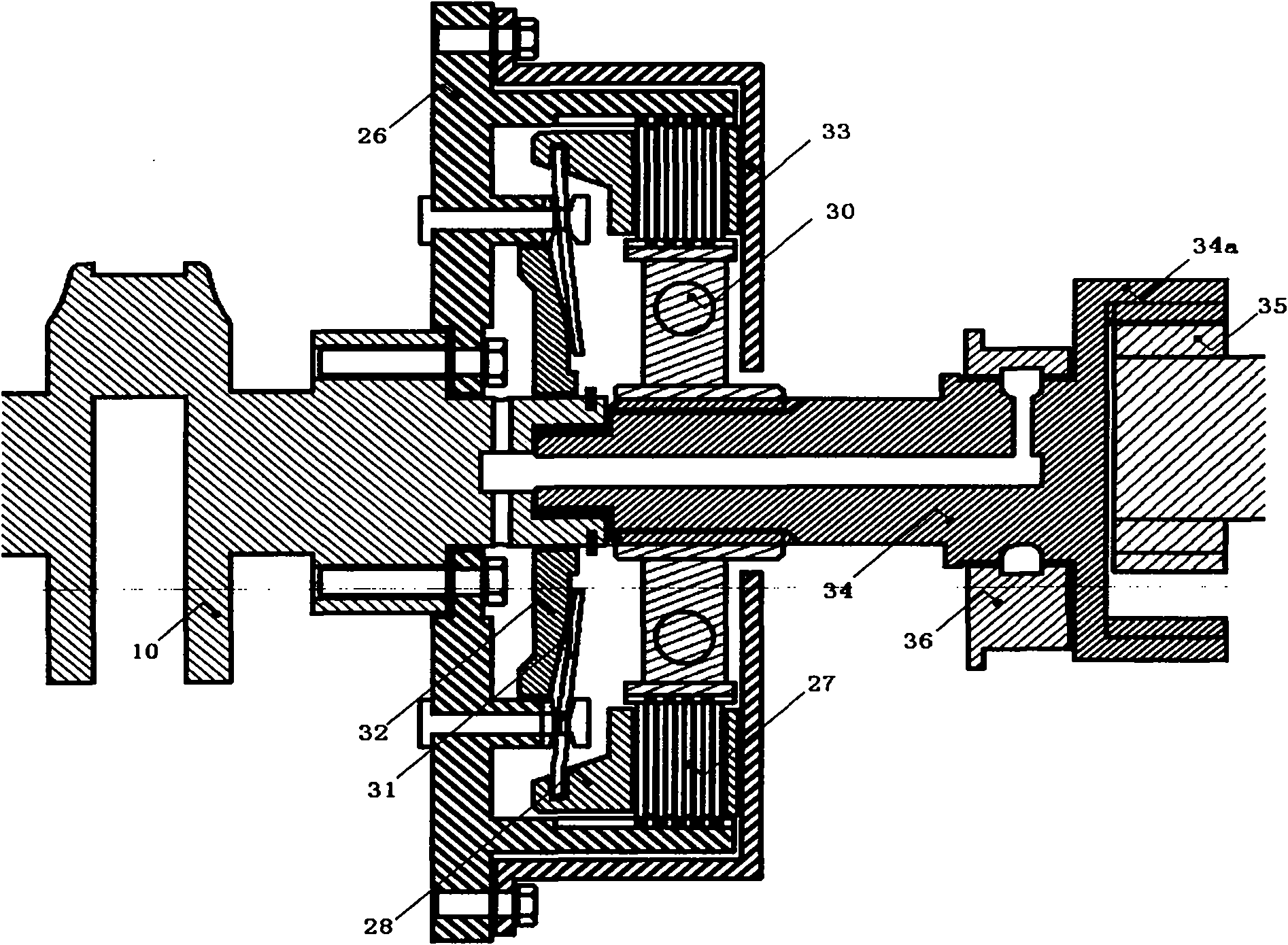
[0089] The variable compression ratio engine of the third embodiment is exactly the same as that of the first embodiment. The difference is that an eccentric clutch in which the power output device of the first embodiment is replaced by a torque converter is provided. Picture 10 It is a schematic diagram of the combination of the hydraulic torque converter and the active eccentric support sleeve of the third embodiment. The active eccentric support sleeve 36 a shown is disposed on the transmission input shaft 34. When the engine compression ratio is switched, the crankshaft 10, the torque converter 42, the transmission input shaft 34, and the active eccentric support sleeve 36a simultaneously perform eccentric rotation. The present invention requires that the eccentric support sleeve must be able to rotate. Therefore, for the torque converter 40 with flexible force coupling, an active eccentric support sleeve 36a is generally provided. Figure 7 Shown in A is a schematic diagra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com