Ammonia production using an integrated intensification approach
A production method and a synthesis gas technology, applied in the field of ammonia production, can solve problems such as inefficiency, and achieve the effect of improving ammonia production efficiency, stabilizing mechanical properties and thermal adsorption machinery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
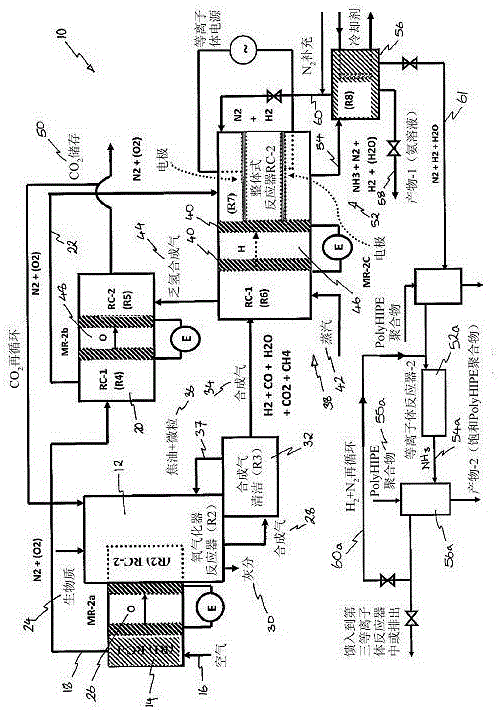
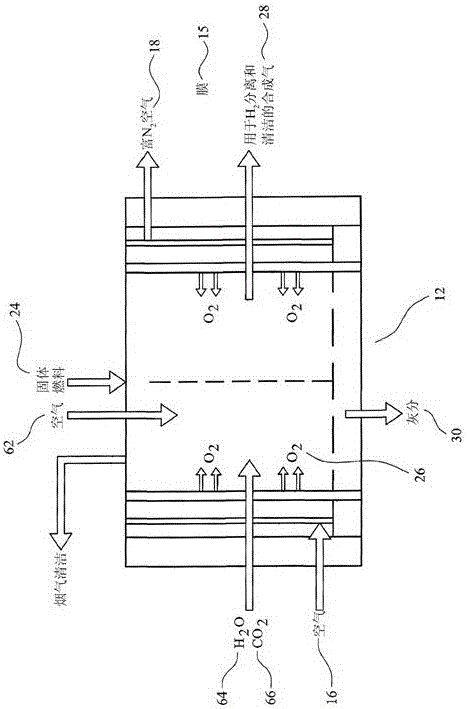
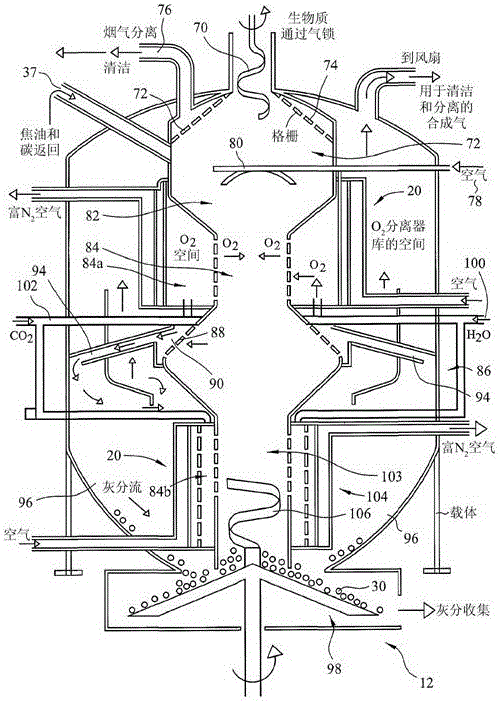
[0133] In the catalytic plasma synthesis of ammonia and its recovery, the following steps are taken: a) preparation of solid acid and water absorbent, which are ultimately used as synthetic rhizosphere in soil to promote plant growth; b) preparation of grading of pores in the reactor and high surface area structured catalysts; c) use of high dielectric constant catalysts in plasma reactors where at least one electrode is in contact with the catalyst; d) configuration of the plasma reactors so that the ammonia yield Maximize and minimize energy consumption. The following examples are provided to illustrate these steps.
example A
[0134] Example A. Preparation of PolyHIPE Polymer for Ammonia and Water Adsorption and Formation of Synthetic Rhizosphere (SRS) Media and Slow Release Fertilizer Substances for Preparation of Synthetic Rhizosphere (SRS) Media Polymers
[0135] All chemicals are reagent grade. Monomer (styrene), crosslinker (divinylbenzene, DVB), polymerization initiator (potassium persulfate), sulfonating agent (0.97 g sulfuric acid / g solution) were all supplied by Aldrich.
[0136] Preparation of synthetic rhizosphere media polymers
[0137] SRS media polymers are nanostructured cross-linked hydrophilic elastic ionic microporous materials, generally referred to as PolyHIPE polymers (PHP), which are passed through high internal phase emulsions as disclosed in U.S. Patent 7 820 729 by Akai et al. (HIPE) polymerization and subsequent functionalization route to prepare. The preparation of functionalized PHP has 3 stages: 1) stable HIPE formation; 2) polymerization; and 3) functionalization.
...
example B
[0147] Example B. Preparation of Nanostructured Microporous Supported Catalysts
[0148] The prior art for the preparation of supported metal catalysts uses particulate porous supports such as oxides of aluminum (Al 2 o 3 ; aluminum oxide) or silicon oxide (SiO 2 ; silica). Aqueous solutions of metal catalyst precursor salts (e.g. nickel, cobalt, iron, ruthenium nitrates) are used to impregnate the support and the resulting system is heat treated at high temperature (typically 600°C) to decompose the catalyst precursor salts to obtain metal oxides , which are then reduced at similar temperatures to reduce metal oxides to active metal catalysts.
[0149] We have found that instead of using porous solid catalyst supports, high surface area supported catalysts can be obtained by using stable nanoscale support particles dispersed in water that also contain catalyst precursor salts (such as Ni(NO 3 ) 2 ), because the nitrates of the catalytic metals are highly soluble in water...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com