Method for bioconverting conjugated linoleic acid by using Lactobacillus plantarum
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and conjugated linoleic acid, which is applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of cumbersome purification process and poor separation efficiency of active CLA, and achieve the effects of convenient product separation, avoiding coenzyme regeneration, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] After the Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) lp15-2-1 is activated twice, it is inoculated into 300ml MRS liquid medium with 1% inoculum size, and the emulsified linoleic acid solution is added so that the LA weight percent concentration reaches 0.5%, After anaerobic shaking culture (180r / min) at 30°C for 24h, high-speed refrigerated centrifugation for 5-20min (10000r / min, 4°C), the bacteria were collected and washed three times with normal saline to obtain resting cells.
[0024] Resuspend the resting cells in citric acid-sodium citrate buffer (0.15mol / L, pH5.5) to a concentration of 0.3mg / mL, and add the emulsified substrate LA to a concentration of 3mg / ml , 30°C shaking culture (180r / min) for 84h, and the output of CLA was detected and calculated by the following method, which reached 0.32mg / ml, and the conversion rate was 10%.
[0025] UV spectrophotometry was used for detection. Conjugated linoleic acid had an obvious absorption peak at 233nm. Using ...
Embodiment 2
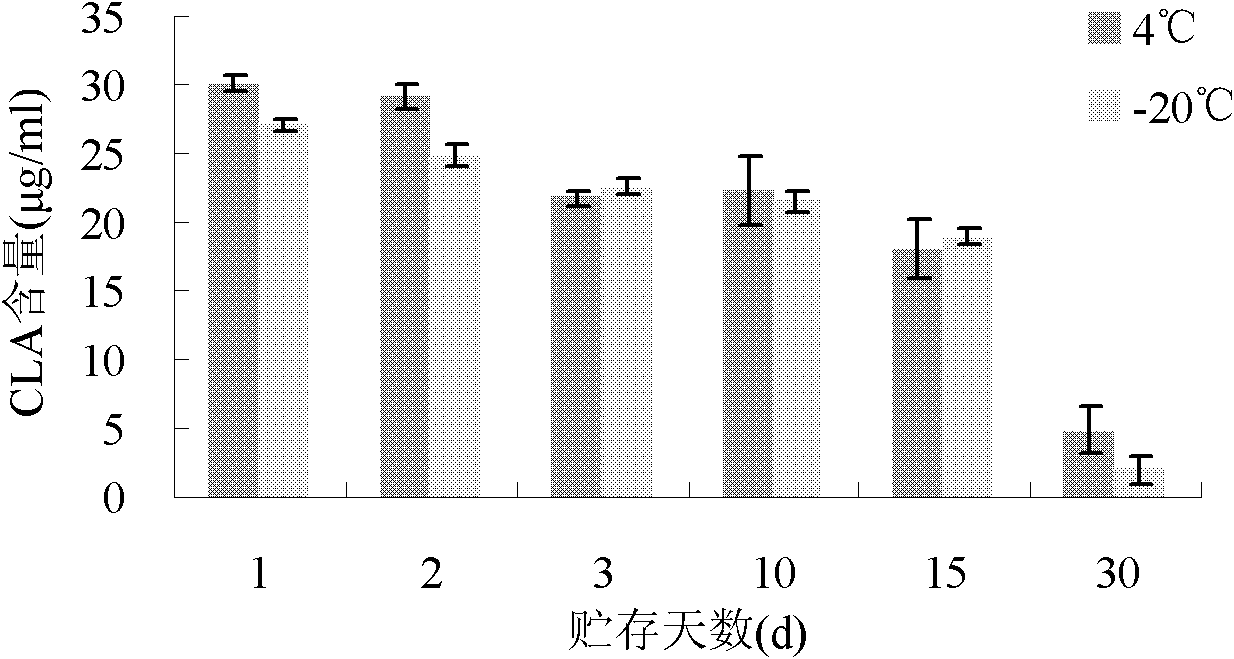
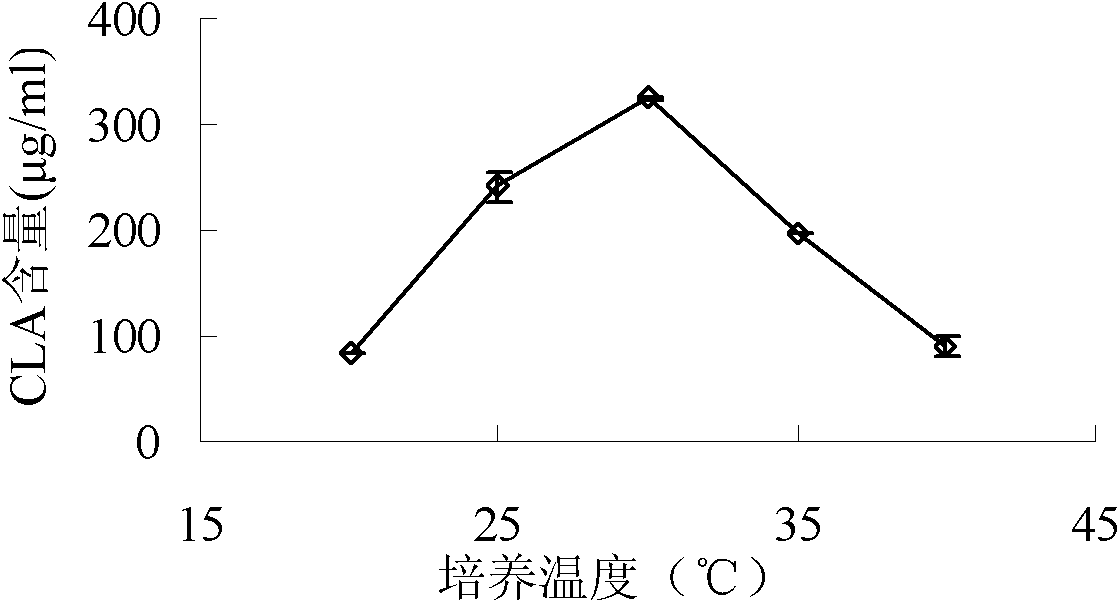
[0029] The present invention also investigates the effects of different pre-cultivation methods, different storage conditions of resting cells, different shaking culture temperatures and different LA concentrations on the final CLA production.
[0030] (1) Effect of pre-culture method on CLA production
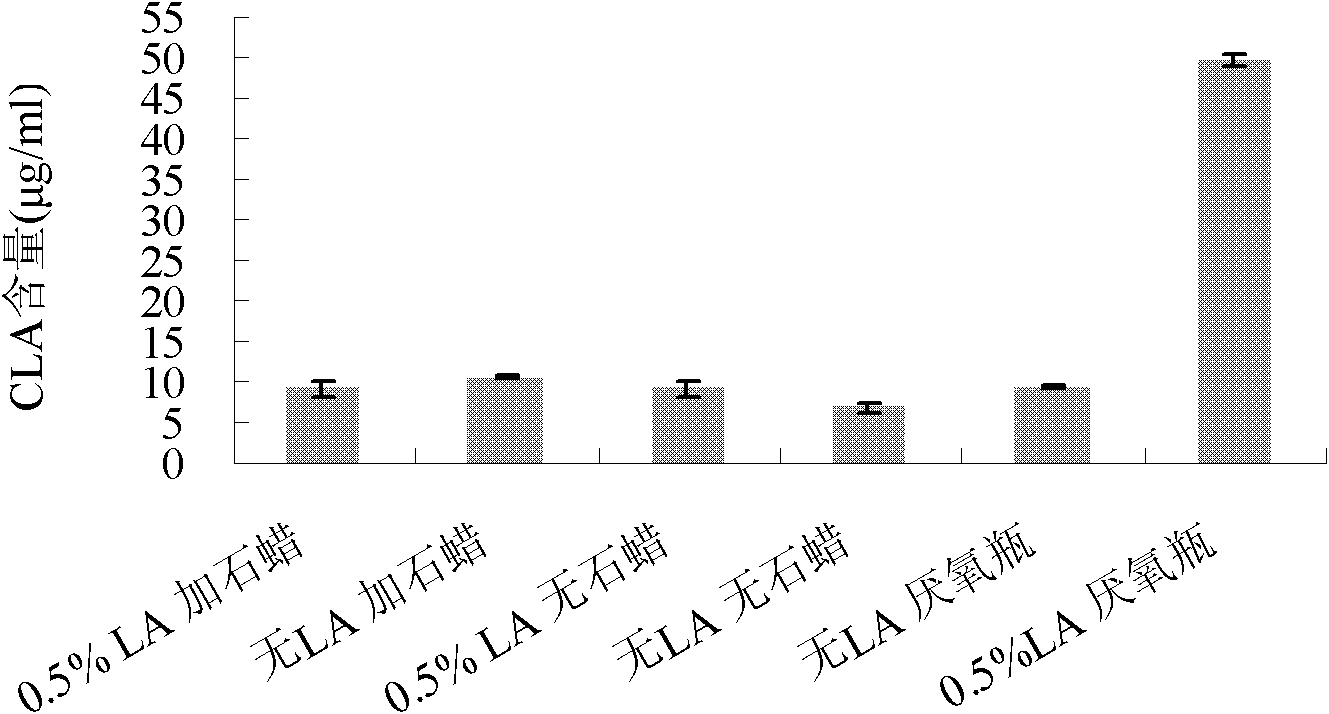
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, a total of 6 pre-culture conditions were set up, which were paraffin sealing + no addition of LA, paraffin sealing + addition of 0.5% LA, no paraffin sealing + no addition of LA, no paraffin sealing + addition of 0.5% LA, anaerobic bottle culture + No addition of LA, anaerobic bottle culture + addition of 0.5% LA, cell concentration of resting cells 0.3mg / mL, citric acid-sodium citrate buffer (0.1mol / L, pH6.0), reaction temperature 30°C, rotation speed 180r / min, reaction time 24h, LA concentration in citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution is 0.5mg / ml.
[0032] from figure 1 It can be concluded that under the pre-culture condition of ana...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com