Single-fiber bidirectional transceiver module and capsulation thereof
A technology of single-fiber bidirectional transceiver and installation end, which is applied to the coupling of optics, instruments, and optical waveguides, and can solve the problems of large volume of optical transceiver modules, conflicts, and large structural dimensions of single-fiber bidirectional components, achieving size reduction and area small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
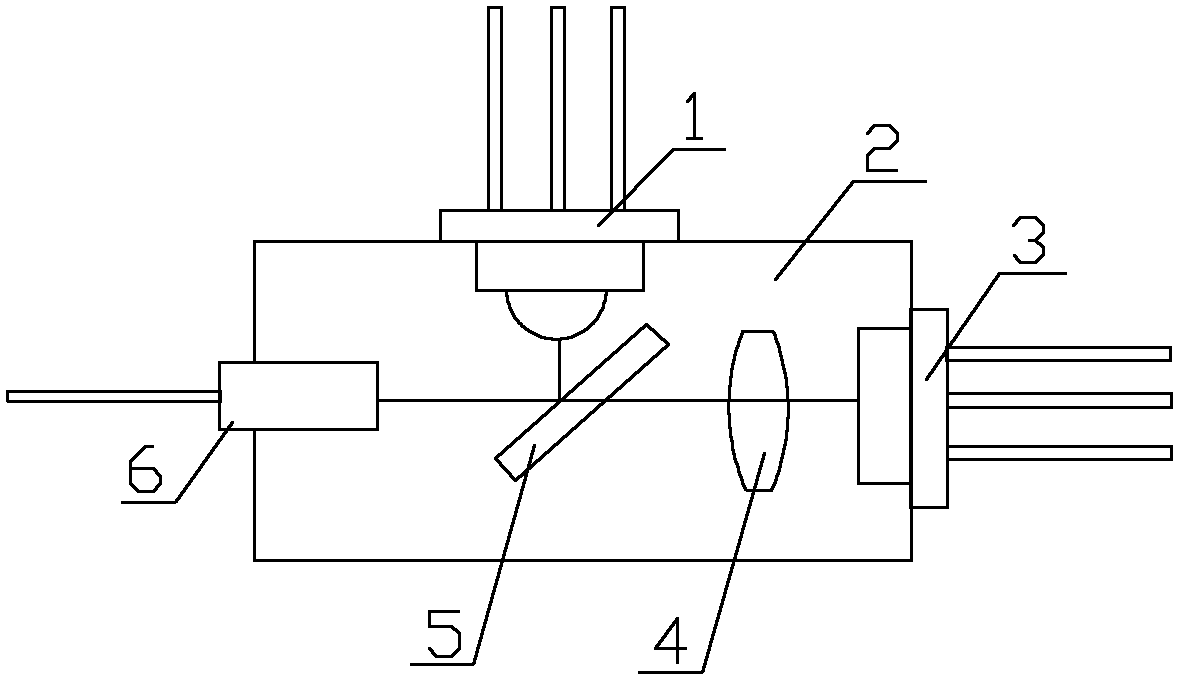
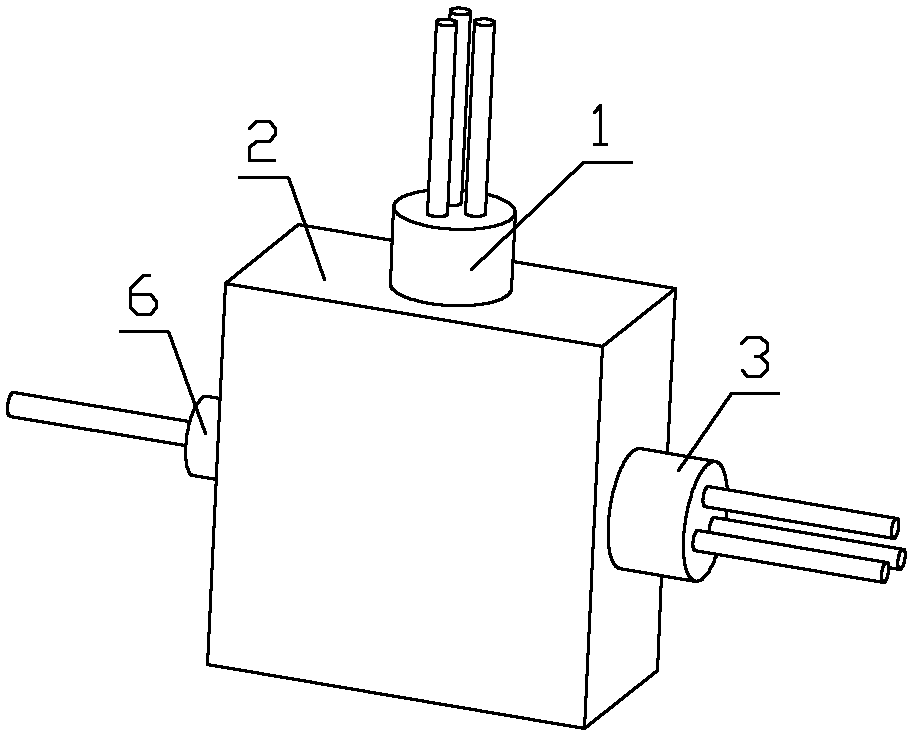
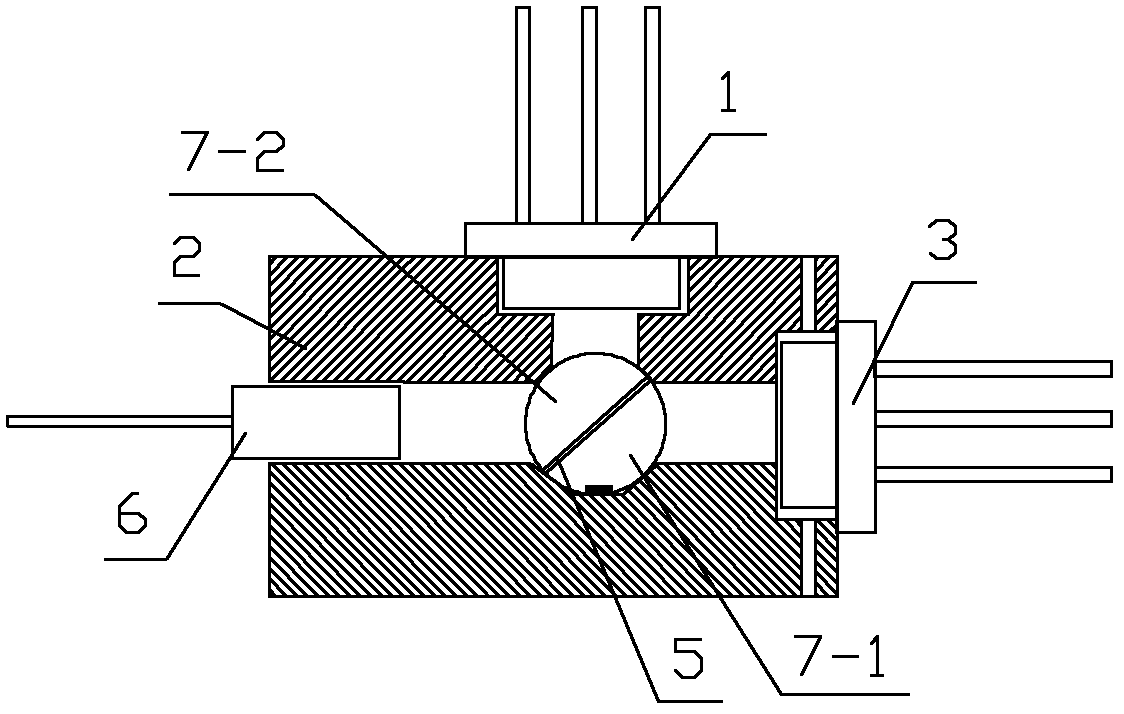
[0062] See figure 2 with image 3 The single-fiber bidirectional transceiver module shown includes a first hemispherical lens 7-1, a second hemispherical lens 7-2, and a beam splitter 5. The beam splitter 5 is arranged at an inclination angle of 45° in the optical path. The first hemispherical lens 7-1, The second hemispherical lens 7-2 and the beam splitter 5 are combined into a sphere; the laser diode 3 is placed at the focal point of the first hemispherical lens 7-1, and the photodiode 1 is placed at the focal point of the second hemispherical lens 7-2 At; the lower end of the first ball lens 7-1 located below is provided with a positioning groove. Package 2 applied to the light-emitting module (such as Figure 7 (Shown), including the laser diode mounting end 2-2, the photodiode mounting end 2-4, and the optical fiber mounting end 2-5. The package 2 has a cavity 9 corresponding to the beam splitter 5 and the hemispherical lens; cavity 9 The lower wall of the cavity 9 is pr...
Embodiment 2
[0065] See figure 2 , Figure 4 The single-fiber bidirectional transceiver module shown includes a hemispherical lens 7-1, a hemispherical lens 7-2, and a beam splitter 5. The beam splitter 5 is arranged at an inclination angle of 45° in the optical path. The first hemispherical lens 7-1 and the second hemispherical lens The plane of 7-2 is arranged on both sides of the beam splitter 5 in a vertical state; the two ends of the beam splitter 5 are fixed with the first hemispherical lens 7-1 and the second hemispherical lens 7-2 by bonding. Both ends of 5 are in contact with the first hemispherical lens 7-1 and the second hemispherical lens 7-2 respectively, wherein the laser diode 3 is placed at the focal point of the first hemispherical lens 7-1, and the beam splitter 5 is placed in the second hemisphere The focal point of lens 7-2.
[0066] Package 2 applied to the light-emitting module (such as Picture 9 Shown), including the laser diode mounting end 2-2, the photodiode mounti...
Embodiment 3
[0068] See figure 2 , Figure 5 , Picture 12 The single-fiber bidirectional transceiver module shown includes a hemispherical lens 7-1, a hemispherical lens 7-2, and a beam splitter 5. The beam splitter 5 is arranged at an inclination angle of 45° in the optical path. The first hemispherical lens 7-1 and the second hemispherical lens The plane of 7-2 is arranged on both sides of the beam splitter 5 in a vertical state; both ends of the beam splitter 5 and the first hemispherical lens 7-1 and the second hemispherical lens 7-2 are fixed in one body by a rectangular frame 10, The laser diode 3 is placed at the focal point of the first hemispherical lens 7-1, and the beam splitter 5 is placed at the focal point of the second hemispherical lens 7-2.
[0069] Package 2 applied to the light-emitting module (such as Picture 9 Shown), including the laser diode mounting end 2-2, the photodiode mounting end 2-4, and the optical fiber mounting end 2-5. The inside of the package 2 has a cav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com