Stroke amount detecting device
一种检测装置、行程量的技术,应用在测量装置、采用电装置、采用电/磁装置传递传感构件等方向,能够解决磁通量密度改变、不平等、不够等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0047] The stroke amount detection device according to the first embodiment is employed to detect the stroke amount of a traveling object. For example, a stroke amount detection device is employed to detect the stroke amount of a traveling member such as a transmission of a vehicle, an accelerator pedal, or a brake pedal.
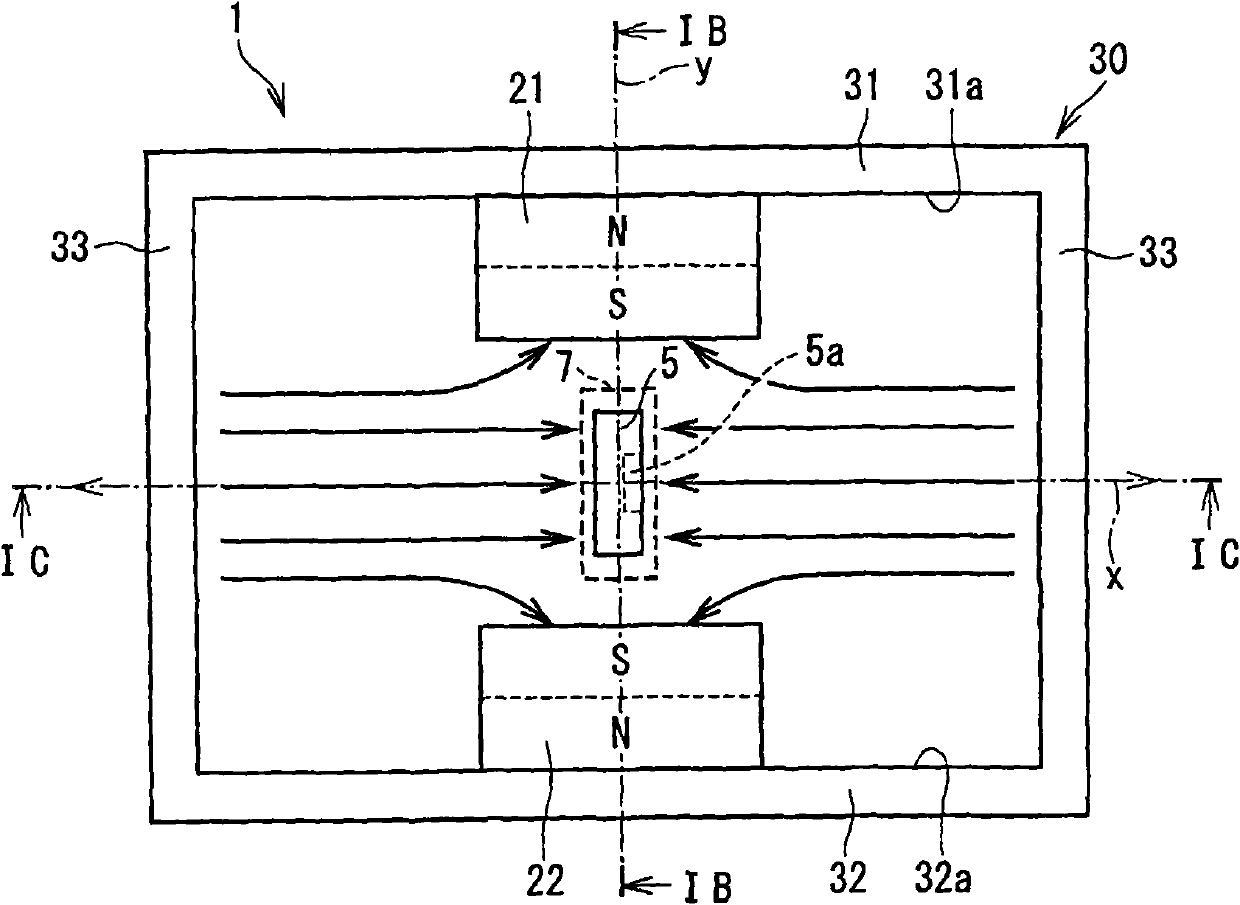
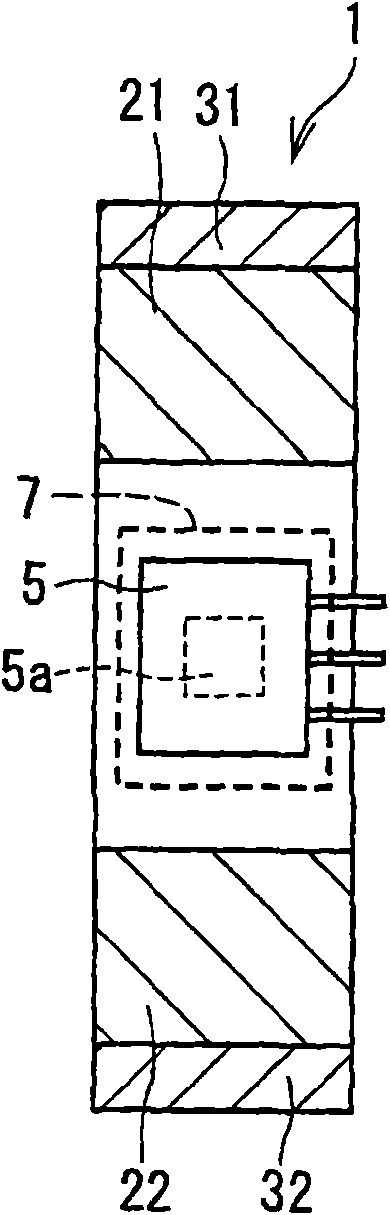
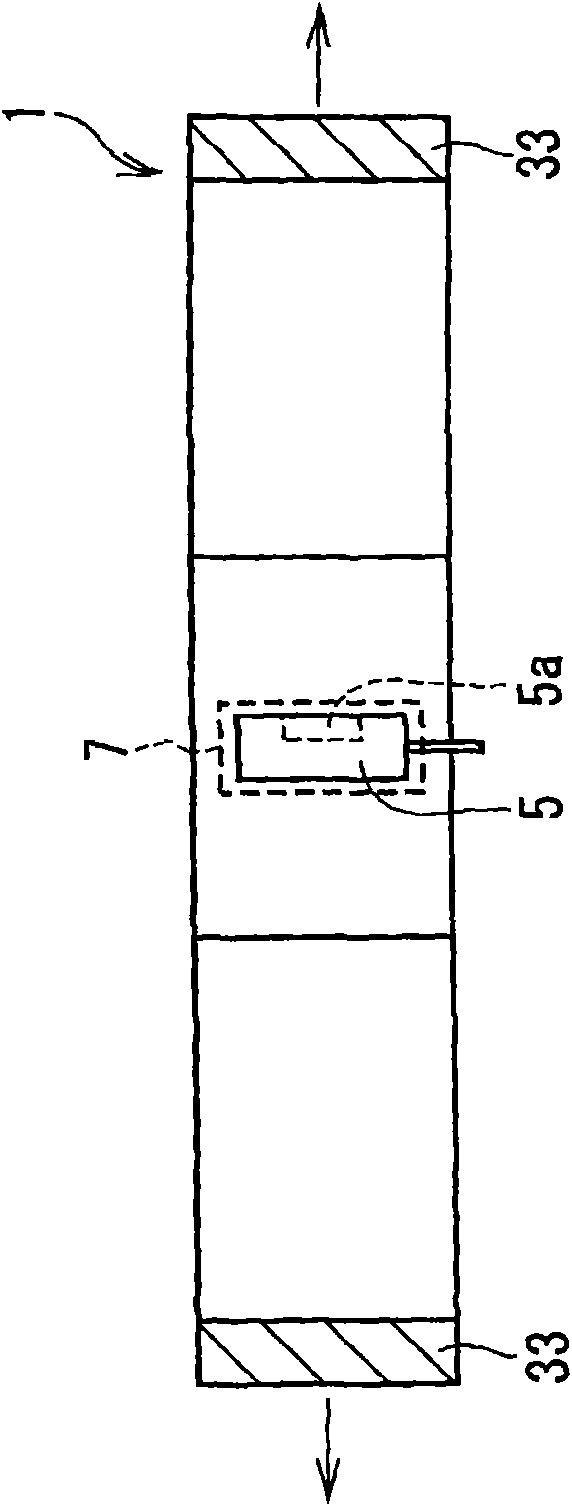
[0048] refer to figure 2 The stroke amount detection device 1 according to the first embodiment generally includes a first magnet 21 and a second magnet 22 as examples of first and second magnetic field generating members and a Hall element 5 as an example of a first sensor element. The Hall element 5 moves relative to the first magnet 21 and the second magnet 22 according to the linear movement of the traveling member 3a of the linear actuator 3 so as to detect the stroke amount.
[0049] The detected stroke amount is sent to an engine control unit (ECU) 10 . The ECU 10 performs feedback control of the linear brake 3 using the detected stroke amount.
...
no. 2 example
[0076] will refer to Figure 5 and 6 The second embodiment will be described.
[0077] refer to Figure 5 , the stroke detection device 1 according to the second embodiment has a first magnet 25 and a second magnet 26 instead of the first magnet 21 and the second magnet 22 of the first embodiment. Each of the first magnet 25 and the second magnet 26 has a concave shape including a thin portion 25a, 26a and a thick portion 25b, 26b at opposite sides of the thin portion 25a, 26a.
[0078] The thin portion 25a is provided at the middle position of the stroke range, that is, in the range including the Y-axis. The thick portion 25b is provided on the opposite side of the thin portion 25a with respect to the stroke direction. The thickness of each of the thick portions 25b is larger than the thickness of the thin portions 25a with respect to the Y direction. Therefore, the distance between the thick portion 25b and the surface and the X-axis is smaller than the distance between...
no. 3 example
[0084] will refer to Figure 7 , 8A and 8B to describe the third embodiment. In the stroke detection device 1 according to the third embodiment, as Figure 7 As shown, the first magnet 21 and the second magnet 22 deviate from the Y axis to the negative side of the travel direction, that is, deviate to Figure 7 in the left side.
[0085] For example, in the case of biasing the travel range of the traveling object toward the negative side from the reference point, the first magnet 21 and the second magnet 22 are disposed on the negative side so as to be adjacent to the center of the travel range. Therefore, since the point where the magnetic flux density is zero is centered, an accurate range can be selectively utilized.
[0086] exist Figure 7 , arrow Le represents a detectable range (detection applicable range) in which the magnetic flux density can be detected by the Hall element 5 and an arrow Lu represents an undetectable range in which the magnetic flux density cann...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com