Vehicle-mounted engine controller
A control device and engine technology, applied in engine control, machine/engine, electrical control, etc., can solve the problems of excessive heat of switching elements, large excitation current, and heavy battery overcurrent burden, and achieve the average supply current and prevent Malfunction and overcurrent burden reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0073] (1) Detailed description of the structure
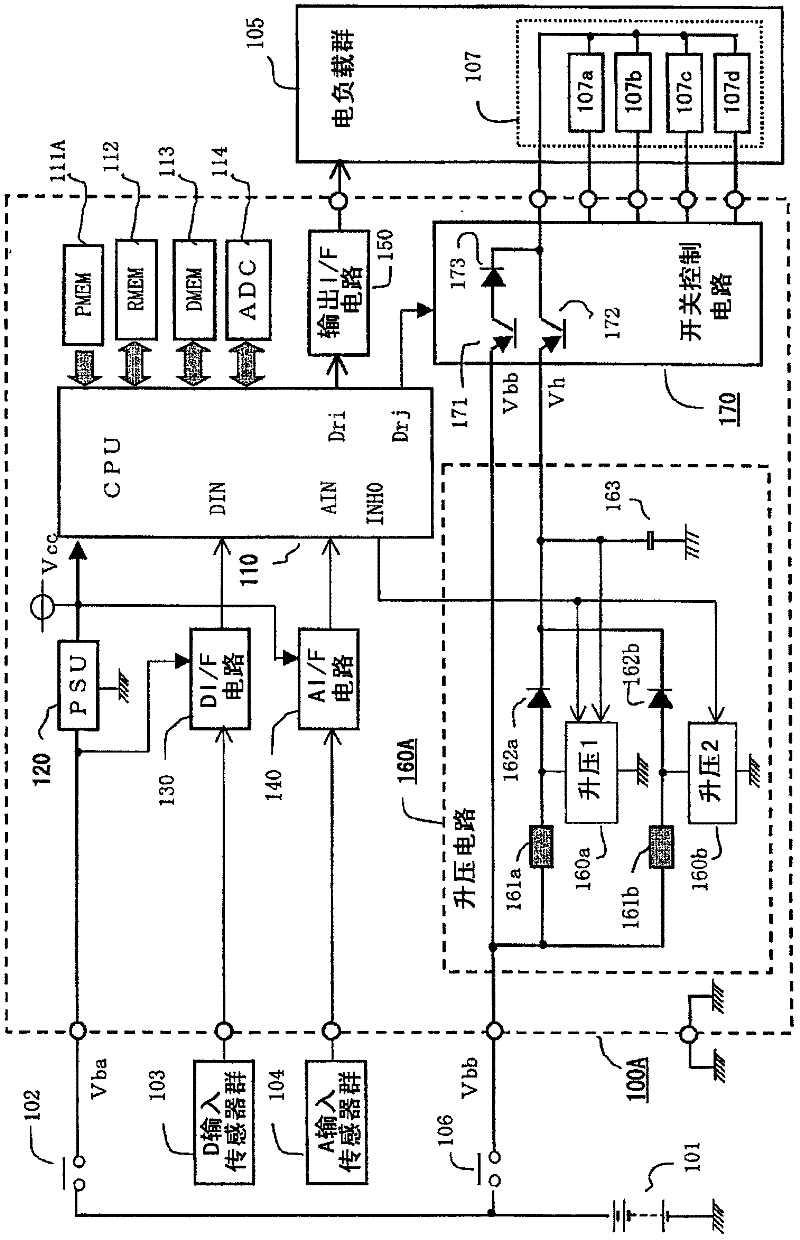
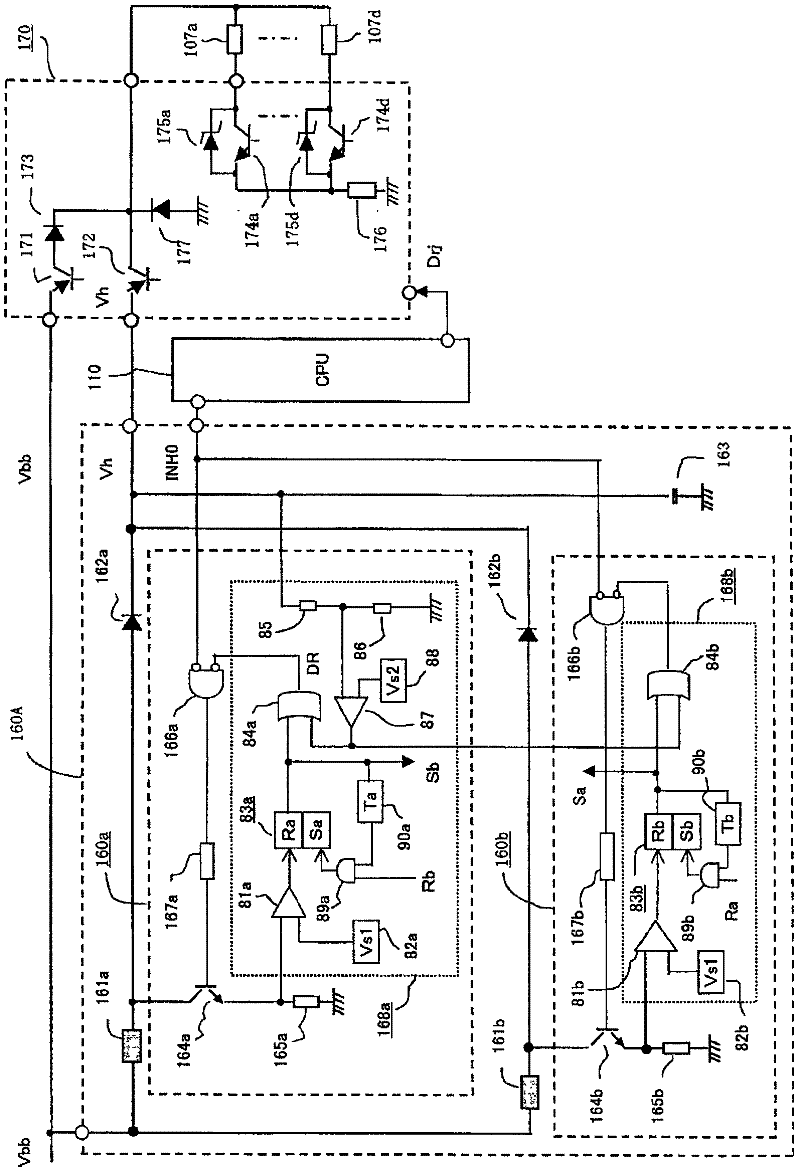
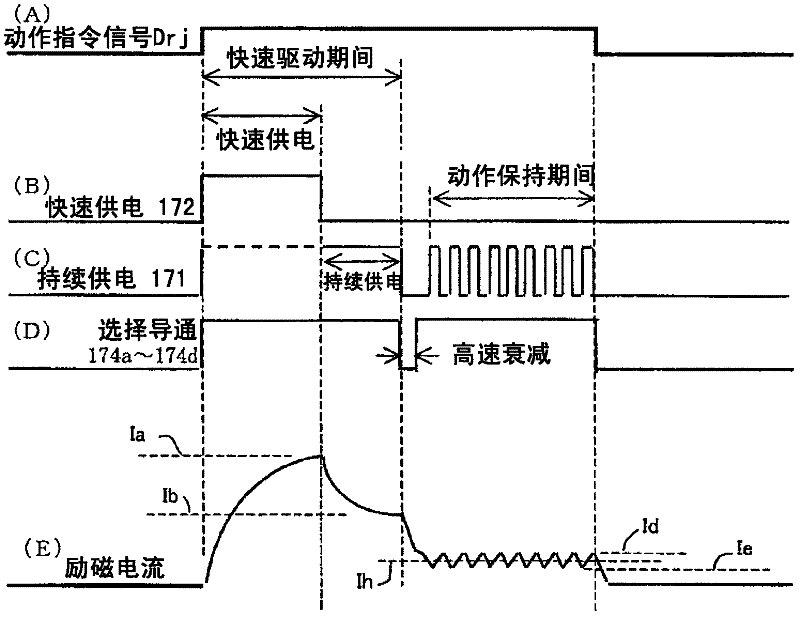
[0074] Hereinafter, the in-vehicle engine control device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described. figure 1 It is a block diagram showing an overall circuit in the vehicle-mounted engine control device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. exist figure 1 Among them, the on-vehicle engine control device 100A is mainly composed of a microprocessor 110, and includes a booster circuit 160A and a switch control circuit for overexcitation control of the electromagnetic coil 107 of the solenoid valve for fuel injection, which is a part of the electric load group 105. circuit 170.
[0075] First, as a component connected to the outside of the vehicle engine control device 100A, the vehicle battery 101 supplies the main power supply voltage Vba to the vehicle engine control device 100A by controlling the power switch 102 . The control power switch 102 is an output contact of an electromagnet...
Embodiment approach 2
[0160] (1) Detailed description of the structure
[0161] Next, an in-vehicle engine control device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. Figure 5It is a block diagram showing the overall circuit of the vehicle-mounted engine control device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In the following description, the same as in Embodiment 1 figure 1 The differences will be explained centering on. In addition, the same code|symbol in each figure shows the same or corresponding part.
[0162] exist Figure 5 Among them, the on-vehicle engine control device 100B is mainly composed of a microprocessor 110, and includes a booster circuit 160B for overexcitation control of the electromagnetic coil 107 of the solenoid valve for fuel injection, which is a part of the electric load group 105, and a switch control unit. circuit 170.
[0163] outside the on-vehicle engine control device 100B, and figure 1 Like the device, the vehicle battery...
Embodiment approach 3
[0233] (1) Detailed description of the structure
[0234] Next, an in-vehicle engine control device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. Figure 8 It is a block diagram showing the overall circuit of the vehicle-mounted engine control device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Below, based on Figure 8 , with the above figure 1 , Figure 5 The difference between the devices will be explained mainly. In addition, the same code|symbol in each figure shows the same or corresponding part.
[0235] exist Figure 8 Among them, the on-vehicle engine control device 100C is mainly composed of a microprocessor 110, and includes a booster circuit 160C for overexcitation control of the electromagnetic coil 107 of the solenoid valve for fuel injection, which is a part of the electric load group 105, and a switch control unit. circuit 170. on the outside of the vehicle engine control device 100C, and figure 1 Like the device, the vehi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com