Shift register circuit and image display apparatus containing the same
A shift register, circuit technology, used in logic circuits, static memory, digital memory information and other directions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
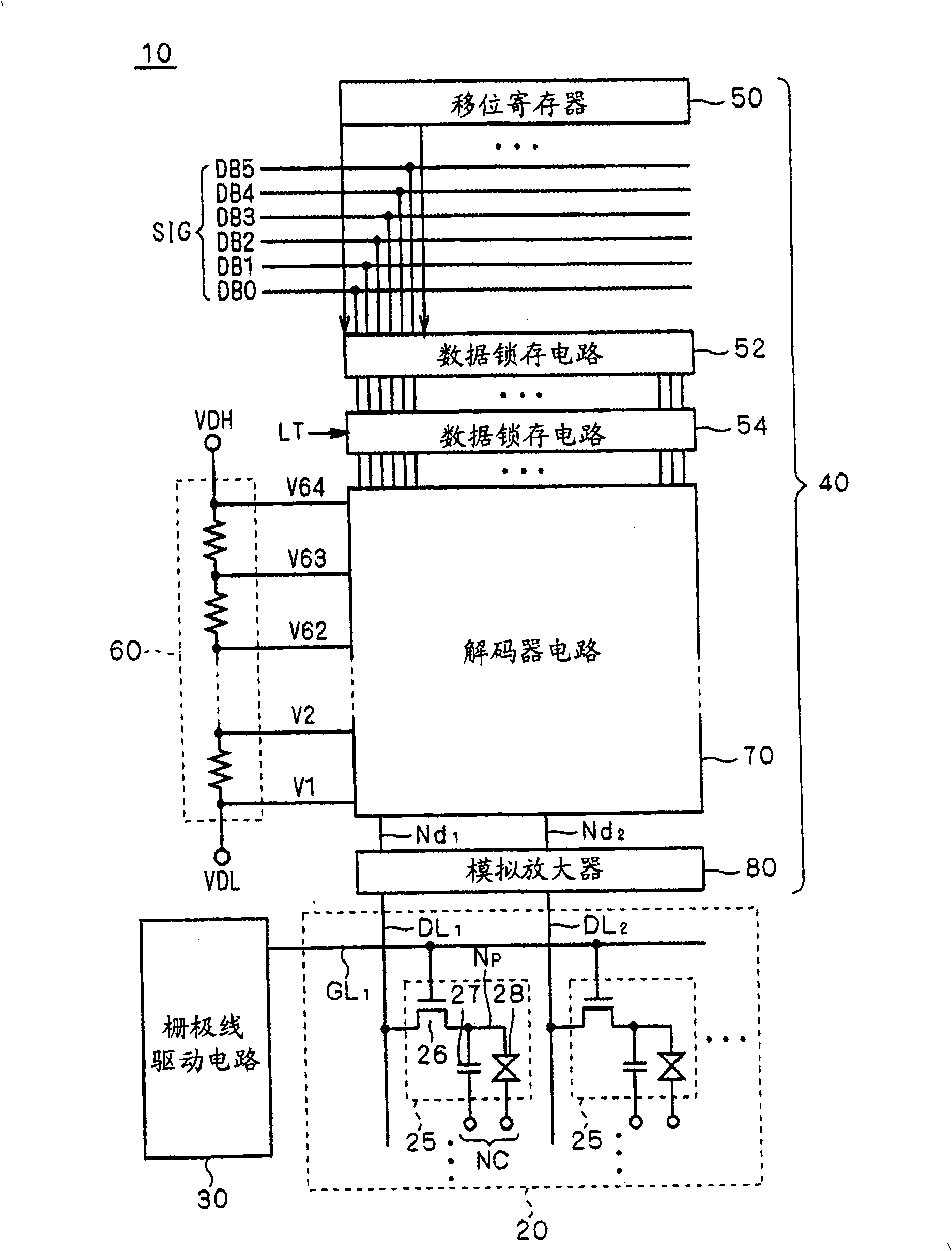
[0070] figure 1 It is a schematic block diagram showing the configuration of the display device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and shows the overall configuration of a liquid crystal display device 10 as a representative example of the display device.
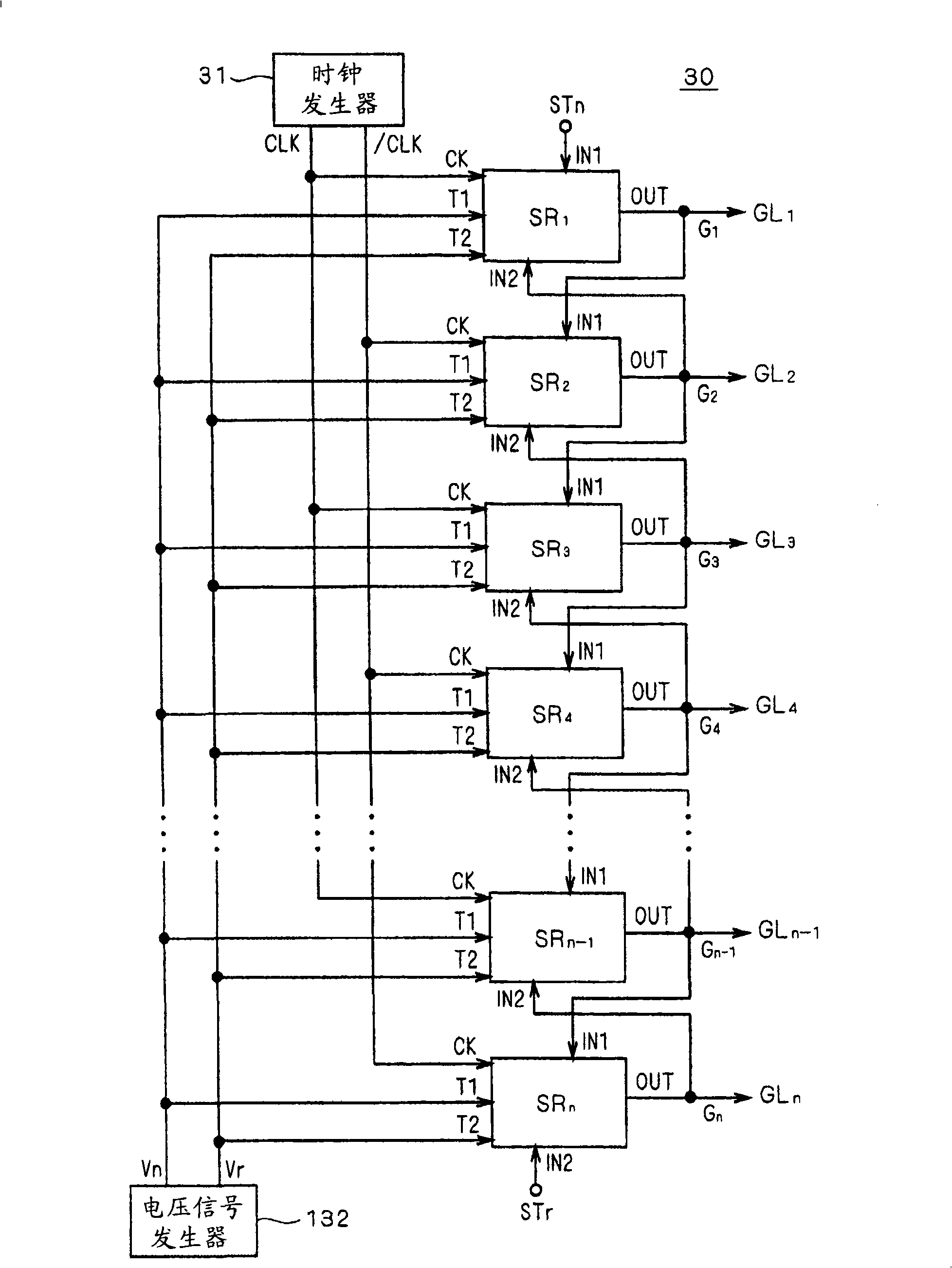
[0071] The liquid crystal display device 10 includes a liquid crystal array unit 20 , a gate line driver circuit (scanning line driver circuit) 30 , and a source driver 40 . As will be apparent from the description below, the bidirectional shift register according to the embodiment of the present invention is mounted on the gate line driver circuit 30 and integrally formed with the liquid crystal array unit 20 .
[0072] The liquid crystal array unit 20 includes a plurality of pixels 25 arranged in a matrix. Gate lines GL are respectively provided in rows of pixels (hereinafter also referred to as "pixel rows") 1 、GL 2 ... (collectively referred to as "gate lines GL"), and in addition, data lines DL are...
Embodiment approach 2
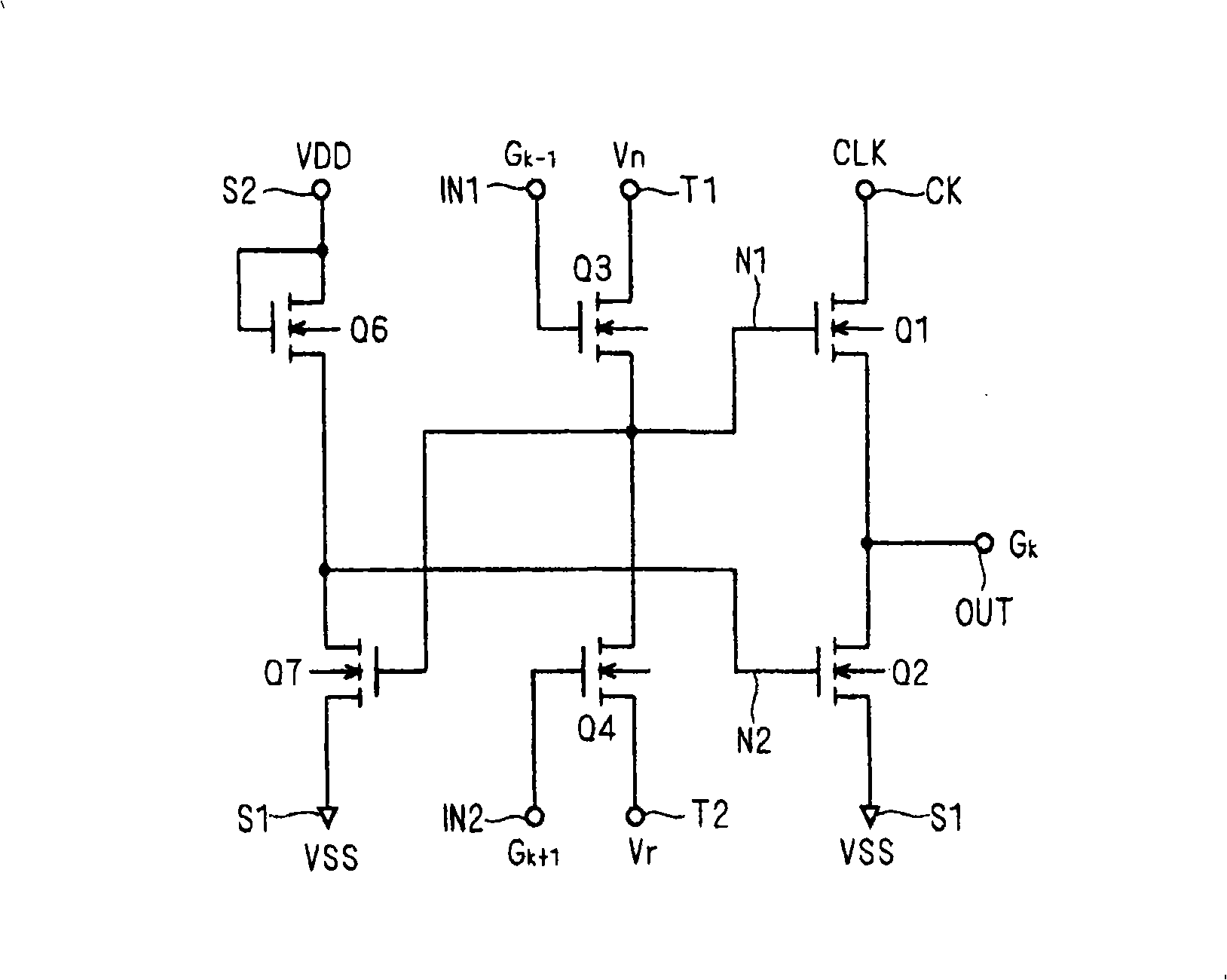
[0172] Here, modified examples of the first pull-down circuit 41 and the second pull-down circuit 42 included in the unit shift register SR of the present invention are shown. However, as described below, regarding the first pull-down circuit 41, since it is basically preferable in Embodiment Mode 1 ( Figure 8 ), therefore, the modification example of the second pull-down circuit 42 will be mainly described below in detail.
[0173] Figure 11 (a) is a circuit diagram of the second pull-down circuit 42 of the second embodiment. exist Figure 11 (a) shows an example in which the clock signal CLK is input to the first clock terminal CK1 and the clock signal / CLK is input to the second clock terminal CK2 (in Figure 12 It is the same in each subsequent circuit diagram).
[0174] In this embodiment, compared to Figure 8 The second pull-down circuit 42 uses transistors Q6B and Q9B instead of the capacitive element C2B. The transistor Q6B is connected between the second cloc...
Embodiment approach 3
[0185] Figure 12 (a) is a circuit diagram of the second pull-down circuit 42 of the third embodiment. In this embodiment, compared to Figure 11 In the circuit of (a), the transistor Q7B is replaced by two transistors Q7Bn and Q7Br. The transistor Q7Bn is connected between the node N4 and the first power supply terminal S1, and its gate is connected to the first input terminal IN1. The transistor Q7Br is connected between the node N4 and the first power supply terminal S1, and its gate is connected to the second input terminal IN2.
[0186] The on-resistance of transistor Q6B is set sufficiently larger than that of transistors Q7Bn and Q7Br, respectively, and the combination of transistors Q6B and Q7Bn and the combination of transistors Q6B and Q7Br constitute a proportional inverter. That is, the on-resistance of the transistors Q7Bn, Q7Br is set sufficiently lower than that of the transistor Q6B. Therefore, in the circuit composed of Q6B, Q7Bn, and Q7Br, assuming that t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com