Coaxial optical fiber-based temperature and stress dual-parameter optical fiber sensor
A fiber optic sensor, coaxial fiber technology, used in thermometers with physical/chemical changes, thermometers, and measurement of force by measuring changes in optical properties of materials when they are stressed, to achieve good compatibility, strong stability, and good The effect of compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
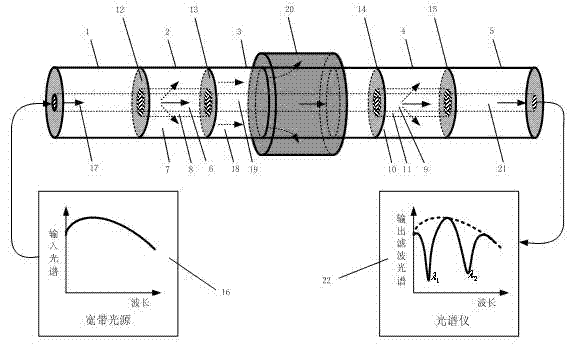
[0021] See figure 1 , This dual-parameter optical fiber sensor for temperature and stress based on coaxial fiber includes single-mode input fiber 1, first coaxial fiber 2, intermediate single-mode fiber 3, second coaxial fiber 4, and single-mode output fiber 5 connected in sequence, It is characterized in that the single-mode input fiber 1, the first coaxial fiber 2 and the intermediate single-mode fiber 3 are sequentially fused by a fiber fusion splicer to form the No. 1 sensing unit with resonant filter transmission spectrum; the intermediate single-mode fiber 3, the second coaxial fiber The optical fiber 4 and the single-mode output optical fiber 5 are sequentially fused by an optical fiber fusion splicer to form the No. 2 sensing unit with resonance filtering transmission spectrum.
Embodiment 2
[0023] See figure 1 This embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, and the specific structure is described in detail as follows.
[0024] See figure 1 The structure of this embodiment consists of five parts: single-mode input fiber 1, first coaxial fiber 2, intermediate single-mode fiber 3, second coaxial fiber 4, and single-mode output fiber 5, of which the first coaxial fiber 2 And the second coaxial fiber 4 have a double-clad structure. In the first coaxial fiber 2, the refractive index of the core 6 and the outer cladding 7 is higher than that of the inner cladding 8. In the second coaxial fiber 4, the core The refractive index of 9 and the outer cladding 10 is higher than that of the inner cladding 11. Although both coaxial fibers have a double-clad structure, their inner cladding dopant materials, inner cladding thickness and refractive index of the inner cladding Values are different, so they have different cladding mode resonant filter spectral wavel...
Embodiment 3
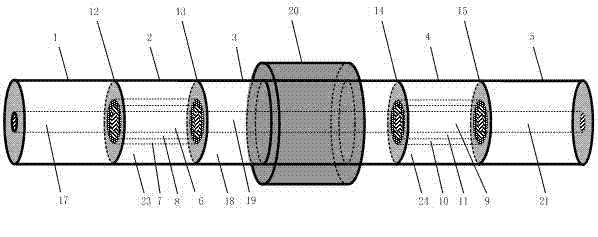
[0026] See figure 2 The structure of this embodiment consists of five parts: single-mode input fiber 1, first coaxial fiber 2, intermediate single-mode fiber 3, second coaxial fiber 4, and single-mode output fiber 5, of which the first coaxial fiber 2 And the second coaxial optical fiber 4 has a three-clad structure. In the first coaxial optical fiber 2, the refractive index of the core 6 and the outer cladding 7 is higher than that of the first cladding 8 and the third cladding 23, and the second In the coaxial optical fiber 4, the refractive index of the core 9 and the outer cladding 10 is higher than the refractive index of the first cladding 11 and the third cladding 24. Although both coaxial fibers have a three-clad structure, they The first cladding and the second cladding doped materials, the thickness of the inner cladding and the refractive index of the inner cladding are different, so they have different cladding mode resonance filter spectral wavelengths (respec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com