Method for obtaining gene information and functional genes from species without genome reference sequence
A reference sequence and genome technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, difficult to eliminate redundant sequences, and impact on animal and plant genome research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Embodiment 1, obtain DGE-tag
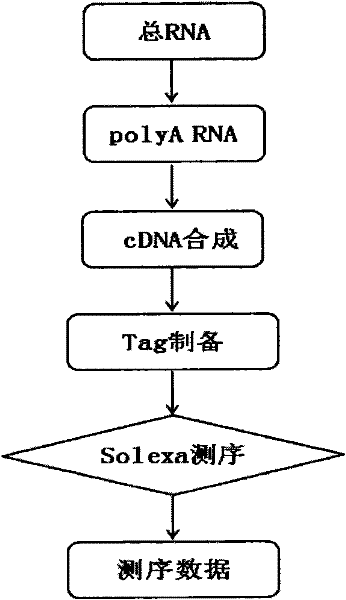
[0100] Taking the DGE-tag analysis of the Asian corn borer as an example, the method steps are as follows, and the concise experimental procedure is shown in figure 1 and figure 2 .
[0101] 1. Extraction of total RNA from Ostrinia officinalis
[0102] Extract by conventional Trizol method, purify by conventional method, and treat with DNase to obtain a Total RNA sample with a concentration ≥ 300ng / ul, a total amount ≥ 6ug, and an OD260 / 280 of 1.8-2.2 (must meet the detection requirements of Agilent 2100).
[0103] 2. Isolation of mRNA and synthesis of cDNA
[0104] The mRNA with polyA was isolated using magnetic beads with oligo-dT, and then the first-strand cDNA was synthesized using random 6-mers and Invitrogen's Superscript II reverse transcriptase kit. cDNA second strand was completed with RNase H (Invitrogen) and DNA polymerase I (New England BioLabs).
[0105] 3. Tag preparation and sequencing
[0106] Utilizing the double-st...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Embodiment 2, DGE-tag analysis
[0112] DGE-tag analysis continues with embodiment 1, and proceeds to the following steps:
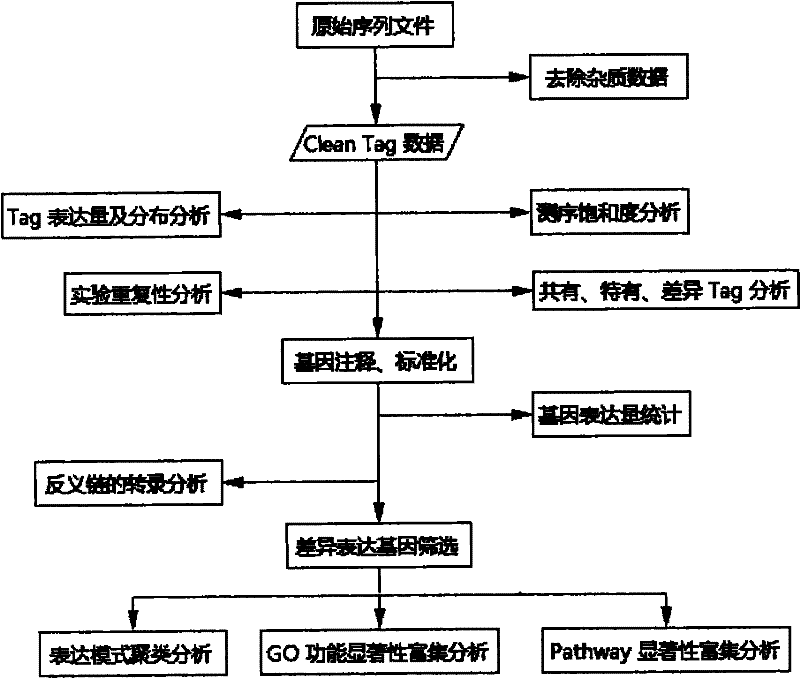
[0113] (c) Annotate the Tag and establish the corresponding relationship between the Tag and the gene: since there is no reference gene data for Ostrinia oleifera, the inventors refer to the RNA-seq data of Ostrinia strigae that was completed at the same time, and use software to retrieve the RNA-seq data for Ostrinia striatus For all CATG sites in the database, a reference label database of CATG+17nt bases is generated. Then compare all Clean Tags with the reference tag database, allow up to one base mismatch, perform gene annotation on the tag (Unambiguous Tags) that is uniquely compared to a gene, and count the number of original Clean Tags corresponding to each gene, and then Standardize the original Clean Tag numbers to obtain standardized gene expression levels, so as to measure gene expression levels more accurately and scientifically. Th...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Example 3, RNA-seq analysis
[0120] For sample processing and sequencing procedures, see image 3 . The specific method is as follows:
[0121] 1. Extraction of Total RNA from Ostrinia cerevisiae
[0122] The conventional Trizol method was used to extract, purify, and treat with DNase to obtain a Total RNA sample with a concentration ≥ 300ng / ul, a total amount ≥ 6ug, and an OD260 / 280 of 1.8-2.2 (which must meet the detection requirements of Agilent 2100).
[0123] 2. mRNA isolation and random interruption
[0124] Use magnetic beads with oligo-dT to separate the mRNA with polyA, and then use ultrasonic waves to randomly interrupt and recover fragments of 200-700bp.
[0125] 3. Synthesis of first and second strands of cDNA
[0126] First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using random 6-mers and Invitrogen's Superscript II reverse transcriptase kit. cDNA second strand was completed with RNase H (Invitrogen) and DNA polymerase I (New England BioLabs).
[0127] 4....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com