Perfusion culture method of mammal cell
A cell culture and mammalian technology, applied in the direction of animal cells, vertebrate cells, artificial cell constructs, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient cell density and vigor, expanded culture scale, low expression level, etc., to achieve good operability and Practicality, the effect of expanding the scale of cultivation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The step-by-step expansion of embodiment 1 cell
[0029] The recovery and expansion of seed cells and the high-density fermentation stage all use serum-free medium.
[0030] Take a cryopreserved seed cell from the liquid nitrogen of the cell bank, which is a recombinant CHO cell highly expressing TNFR: Fc fusion protein, quickly put it into warm water at 37°C for recovery, add 37°C preheated culture medium and blow gently, Centrifuge at 800rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant, add 40mL of medium preheated at 37°C to the pellet, and place in 5% CO 2 Constant temperature incubator culture. Subculture after 72 hours, centrifuge at 800rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant, and add fresh 37°C preheated medium to the pellet to make the cell density reach 2.0×10 5 cells / mL above.
[0031] In the process of cell subculture and expansion, the culture container is enlarged step by step, and after cell expansion in 30mL, 90mL, 300mL, 900mL, 1500mL spinner bottles, when the tot...
Embodiment 25L
[0032] Fermentation culture in embodiment 25L tank
[0033] Serum-free medium is still used in the high-density culture stage of fermentation production to maintain the stability of parameters in each stage of fermentation. During the whole process, open perfusion culture and fermentation are adopted to monitor cell density and glucose consumption. According to the consumption of glucose, the glucose concentration is controlled by continuously adding a certain concentration of glucose to 0.5-3g / L; dissolved oxygen is controlled as oxygen dissolved in the air 50% of the amount.
[0034] In the initial stage of 5L fermenter culture, the culture temperature of engineered cell strains was maintained at 36-37°C; the pH was controlled at pH 7.1-7.2, and CO was added during fermentation 2 and NaHCO 3 To maintain its stability; stirring speed is controlled at 150rpm;
[0035] When the cell density reaches 8×10 6 When cells / mL, the cell growth trend slows down and reaches a plateau...
Embodiment 3
[0037] The comparative test of two kinds of fermentation process control of embodiment 3
[0038] 1. Fermentation control 1
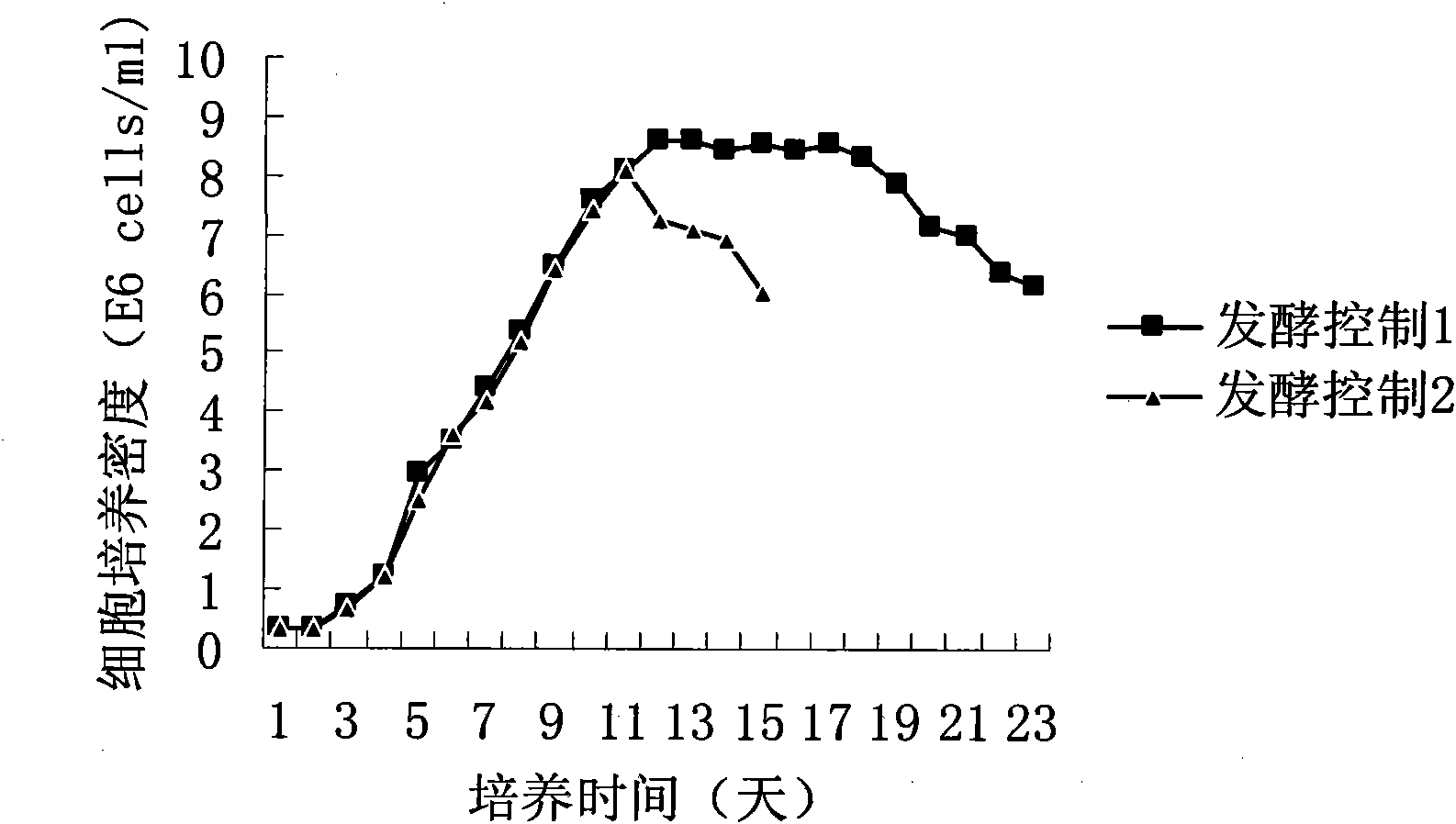
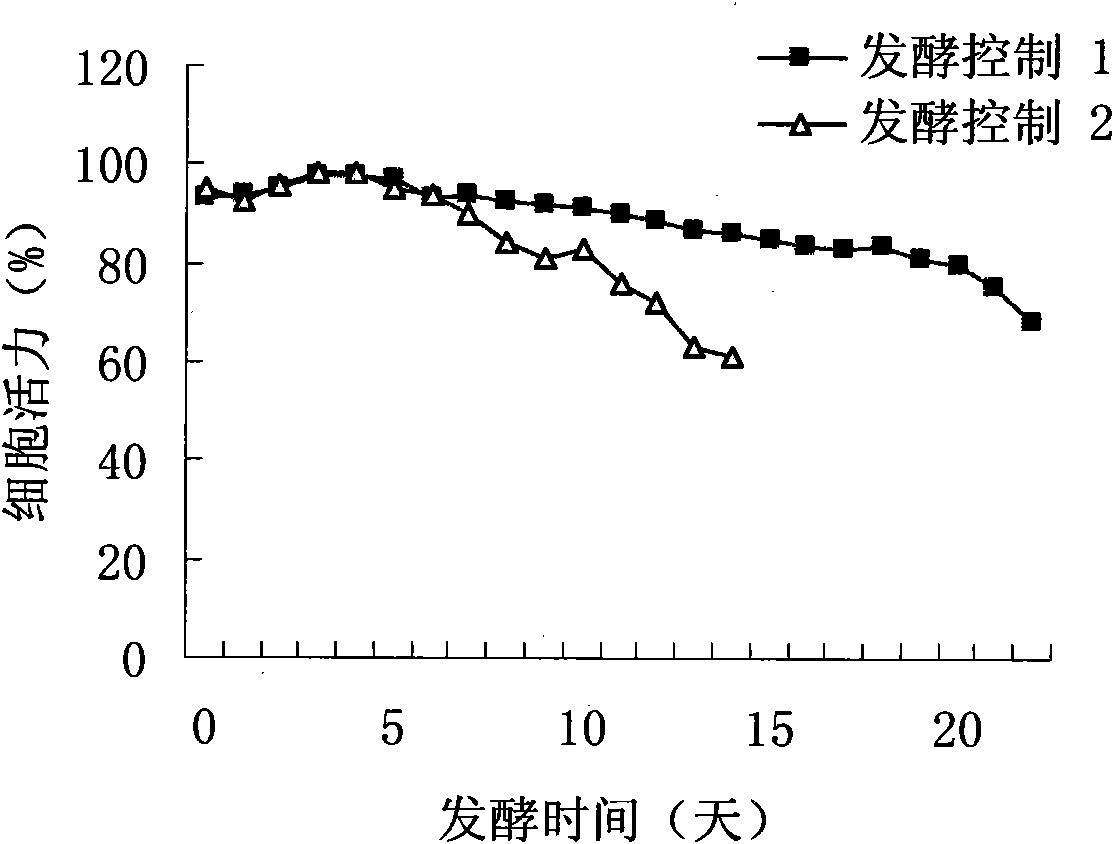
[0039] The fermentation process is controlled to pH 7.1-7.2 in the early stage of fermentation, the stirring speed is 150rpm, the dissolved oxygen is 50%, the temperature is 36-37°C, and the cell density reaches 8×10 6 When the cells / mL reached the stable stage, the pH was lowered to 6.9, the temperature was lowered to 33°C, the stirring speed was reduced to 82rpm, the dissolved oxygen was 50%, and the concentration of glucose was controlled to be 0.5-3g / L.
[0040] 2. Fermentation control 2
[0041] During the entire fermentation process, the pH is controlled to be 7.1-7.2, the stirring speed is 150 rpm, the dissolved oxygen is 50%, the temperature is 36-37° C., and the concentration of glucose is controlled to be 0.5-3 g / L.
[0042] The test results are shown in Table 1. figure 1 and figure 2 . The results show that the present invention has ach...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com