Photovoltaic cell
A photovoltaic cell and battery technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in accurately controlling the thickness of the n-type doped layer, improve open circuit voltage and overall efficiency, reduce doping concentration, and improve compounding. effect of life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
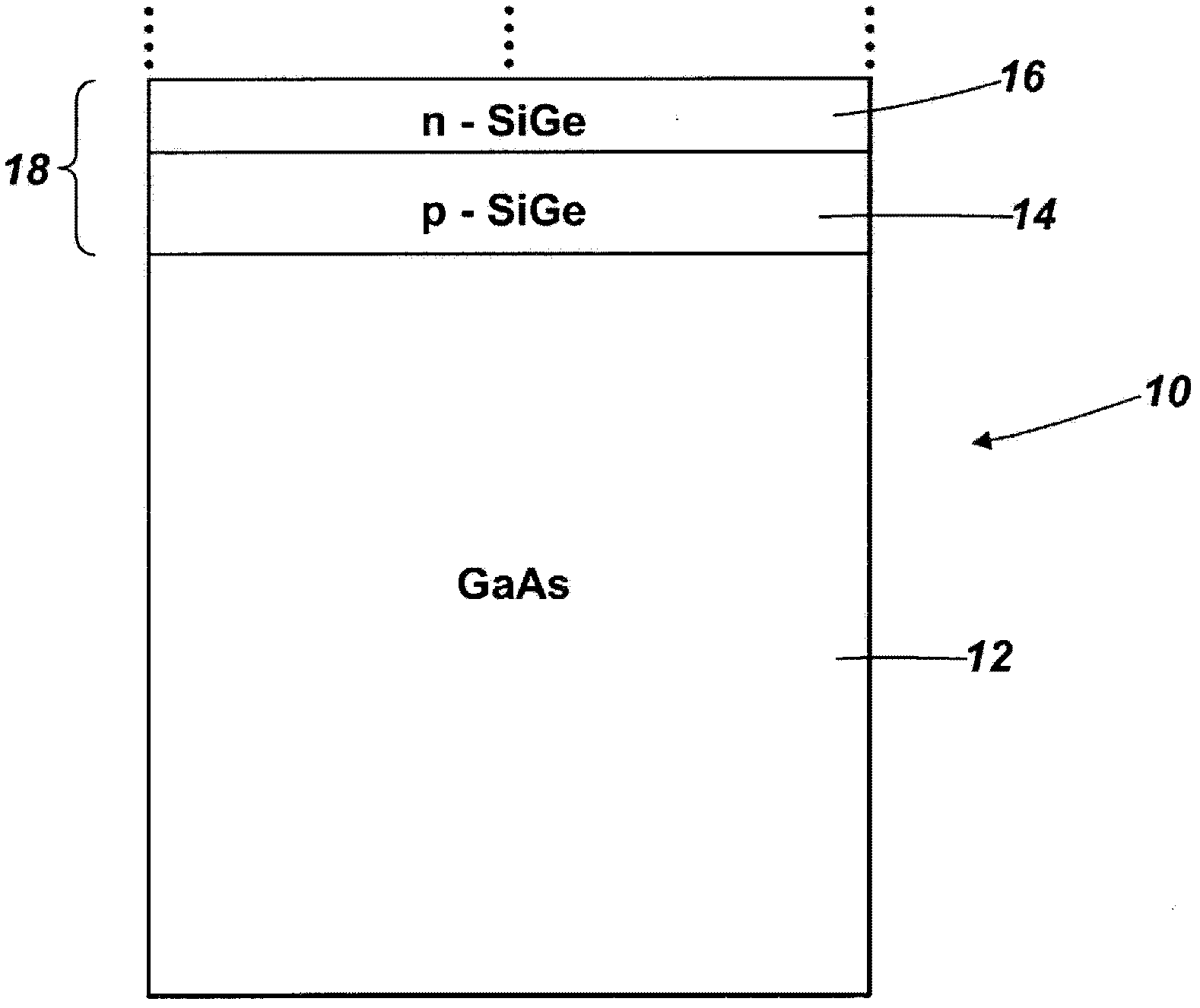
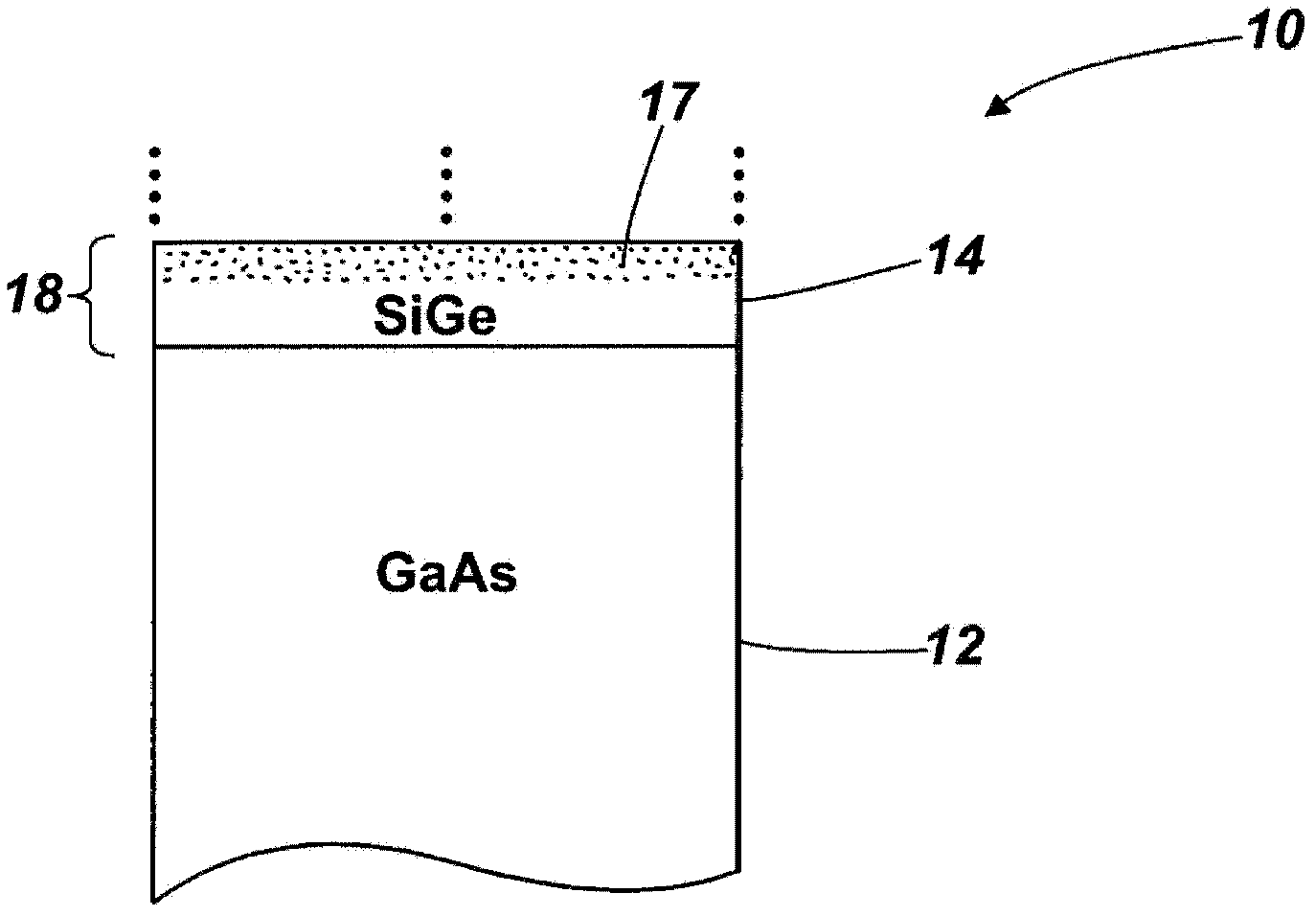
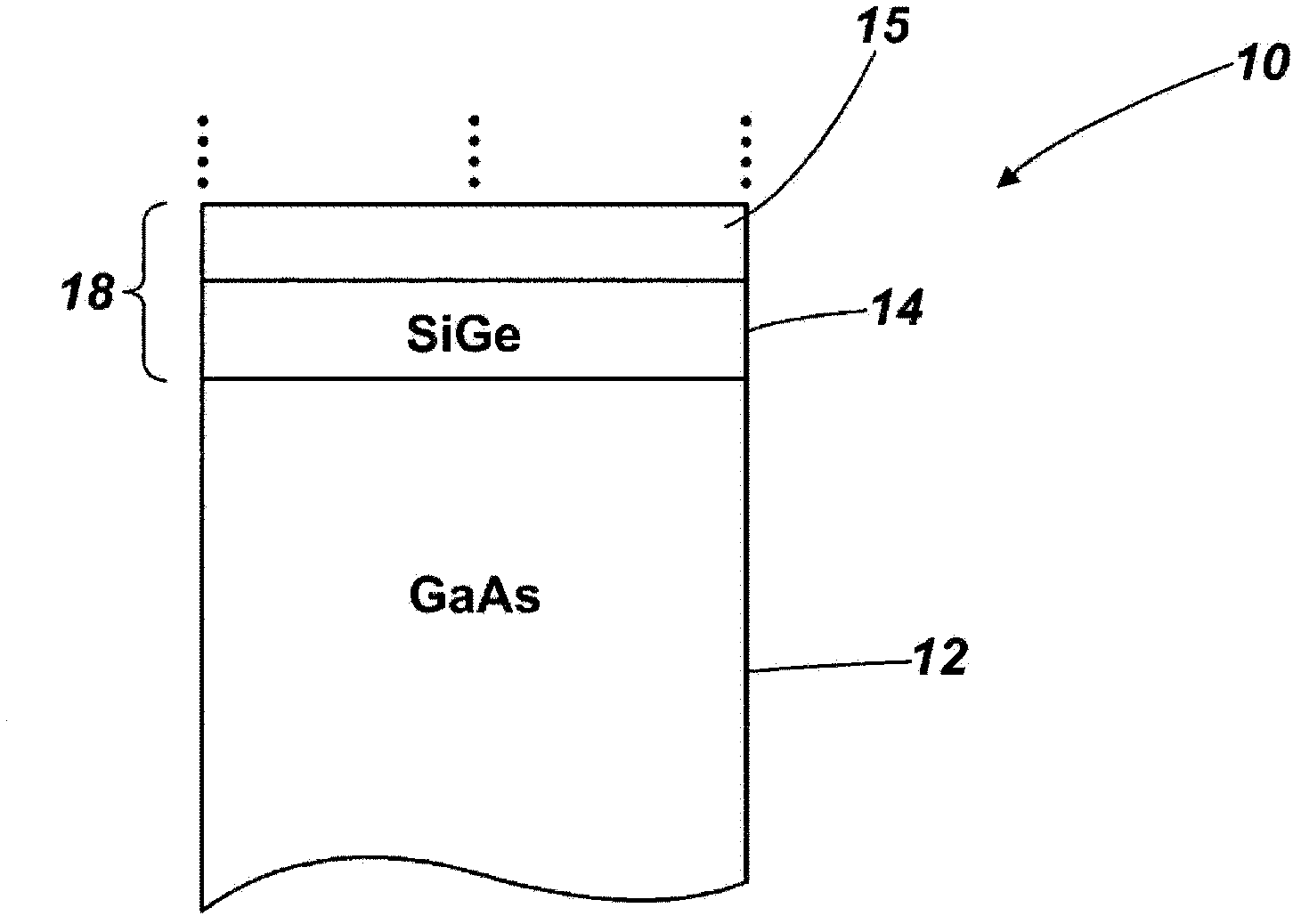
[0033] see Figure 1A , which schematically shows the photovoltaic cell structure 10 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The structure 10 includes a GaAs substrate 12 . On said GaAs substrate there are two continuous first layers 14 , 16 of SiGe material epitaxially grown on the GaAs substrate and monolithic therewith, these layers together forming a first germanium-based photovoltaic junction 18 . The silicon content of the first layer of SiGe is chosen to substantially lattice match the GaAs substrate. For this reason, Si x Ge 1-x The silicon fraction x may be 0-0.04, more preferably 0.01-0.03, still more preferably 0.016-0.02. To form a practical photovoltaic junction, the lower SiGe layer can typically be doped p-type to a concentration of about 5×10 16 cm -3 ~5×10 19 cm -3 , and the thickness is about 1 μm to 2 μm. The upper SiGe layer can typically be n-type doped to a concentration of about 1 x 10 17 cm -3 , and the thickness is about 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com