Laser lap welding method
A lap welding and laser technology, applied in laser welding equipment, welding/welding/cutting items, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reduction of welding length, burn-through, and reduction of laser beam energy density, etc. Effects of burden, improved quality, avoided space and cycle time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
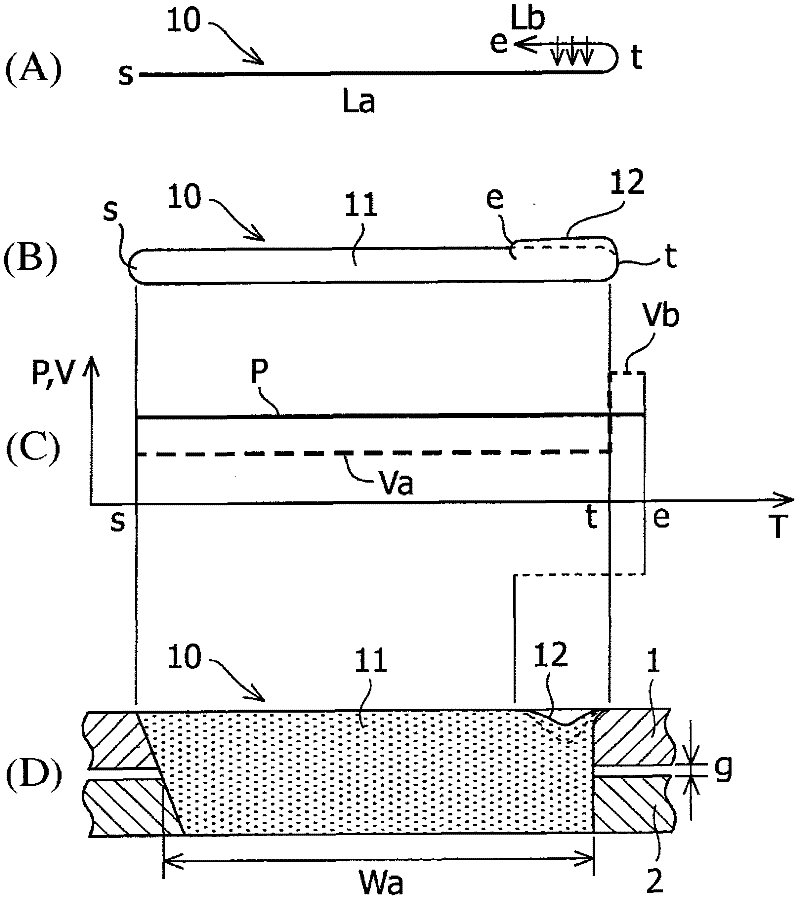
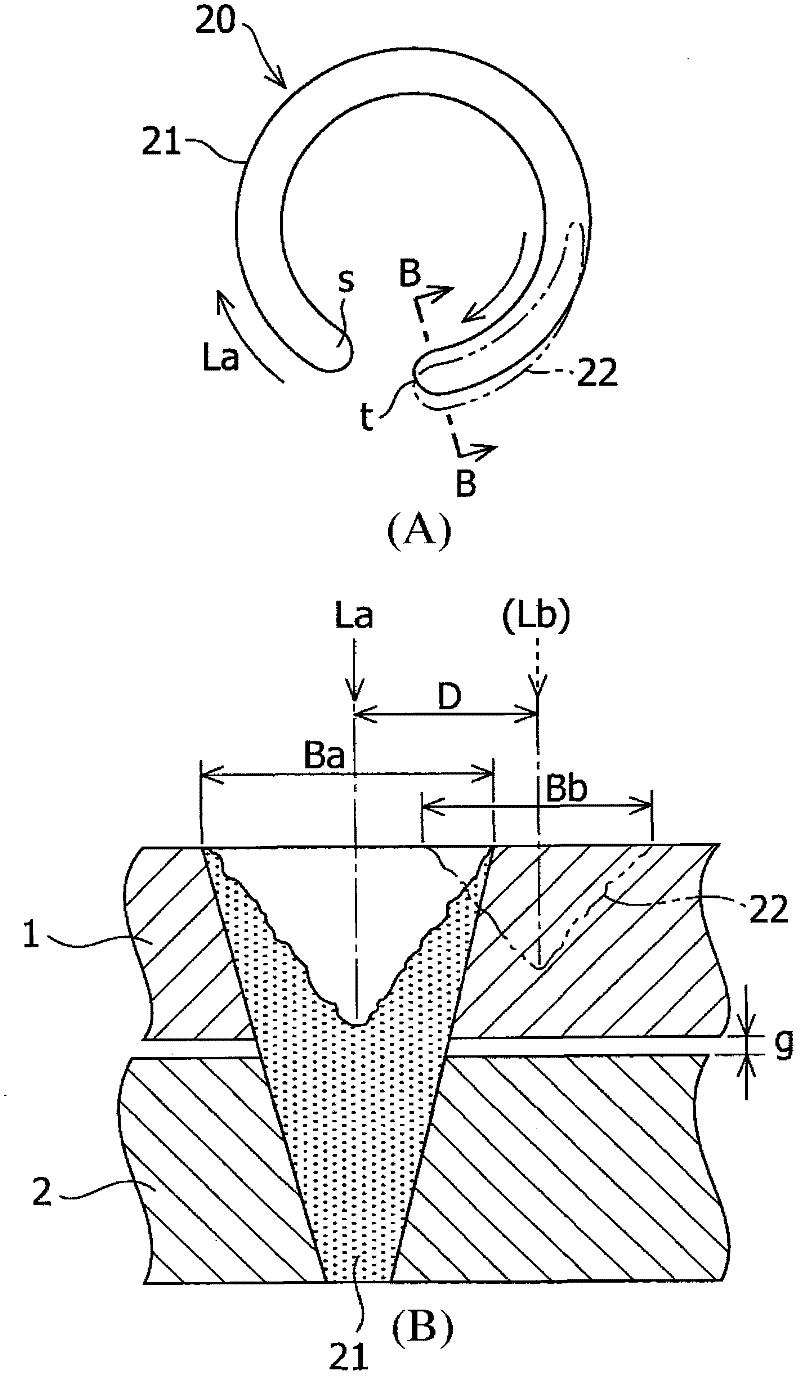
[0036] Similar to the first embodiment, laser scanning Lb in the backward direction is performed at high speed. Therefore, even when the laser output amount and spot diameter in the laser scanning Lb in the backward direction are the same as those in the laser scanning La in the forward direction, a reduction in the laser output amount (power density) is obtained. small effect. Therefore, the bead width Bb of laser scanning Lb in the backward direction is made narrower than the bead width Ba of laser scanning La in the forward direction while the depth of penetration is reduced to be smaller than the thickness of the upper steel plate 1 . When this state is reached, even by terminating the laser scanning Lb in the backward direction at the terminating end e, defects such as indentations are not left.
Embodiment
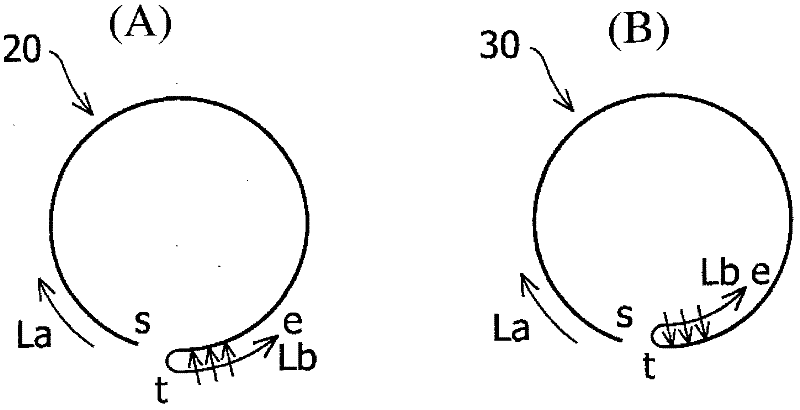
[0038] In order to check the effect of the laser lap welding method according to the present invention, experiments were carried out in the laser lap welding 20 and 30 according to the above-mentioned second embodiment and the third embodiment, while changing the laser scan La along the forward direction and along the The quality of the weld bead was evaluated in each case of the shift amount D between the laser scans Lb in the backward direction, and the scanning speed Vb of the laser scans Lb in the backward direction.
[0039] In the experiment, an optical fiber laser oscillator (with maximum output: 7 kW, diameter of transmission fiber: 0.2 mm) manufactured by IP G Photonics Corporation and a scanning head manufactured by HIGHYAG Laser Technology Corporation (processing focus diameter in focused state : 0.6mm). A non-plated steel sheet (1) with a thickness of 0.65 mm is superimposed on a plated steel sheet (2) with a thickness of 0.8 mm with gaps g=0.1 mm and g=0.2 mm as a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com