Method for realizing off-line reading files in SAN (Storage Area Networking) shared file system
A technology for sharing files and reading files, which is applied in transmission systems, electrical components, and special data processing applications. Guaranteed continuity of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
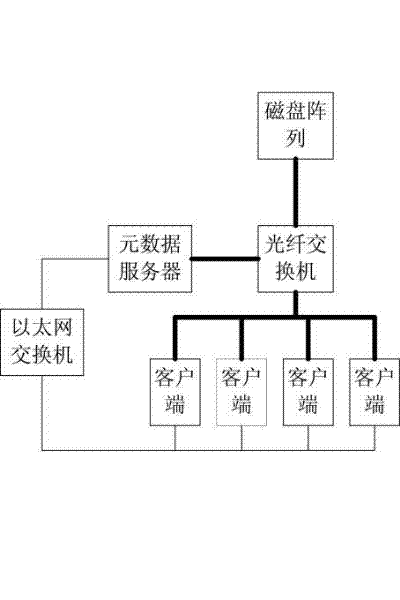
[0023] This embodiment is a method for realizing offline file reading in a SAN shared file system. The hardware system used by the method, such as figure 1 shown. The thick solid line in the figure indicates the SAN network, and the thin solid line indicates the LAN network. This embodiment includes: multiple clients are connected to the metadata server and the disk array through the SAN network for transmitting video files, and the multiple clients are connected to the metadata server through the LAN network for transmitting metadata. The client can be an ordinary PC workstation or a server, which has the ability to connect to a SAN network and can process large files, such as high-definition video files. The SAN network described in this embodiment is an optical fiber network made up of optical fiber switches and optical cables. It is a broadband network with a bandwidth exceeding 1G. It can transmit high-definition video files, and can also use 1000M or 10,000M high-speed...
Embodiment 2
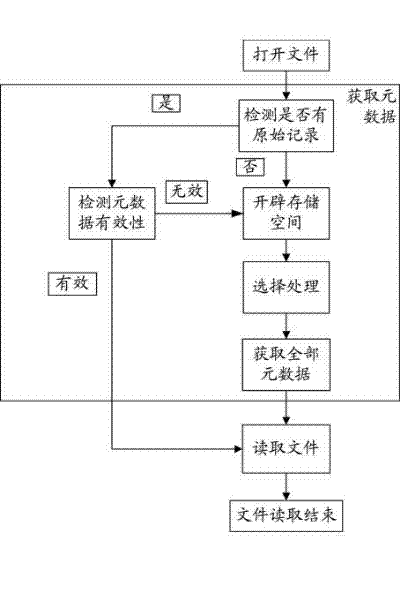
[0046] This embodiment is an improvement of Embodiment 1, and it is a refinement of the steps of reading files in Embodiment 1, such as image 3 shown. This embodiment is performed under the condition that metadata is stored in the client's local memory or hard disk. Although the metadata is stored in the local memory or the hard disk, this embodiment still obtains the metadata in the traditional way, and the locally stored metadata is only used when the communication between the client and the metadata server is not smooth. The sub-steps in the step of reading the file described in this embodiment are as follows:
[0047] 1a. The sub-step of obtaining the metadata segment from the metadata server: it is used for the client to obtain the metadata segment from the metadata server, and if it is successful, enter "initiate a block data request for the file to be read to the disk array to complete the metadata Read the block data corresponding to the segment, read the metadata s...
Embodiment 3
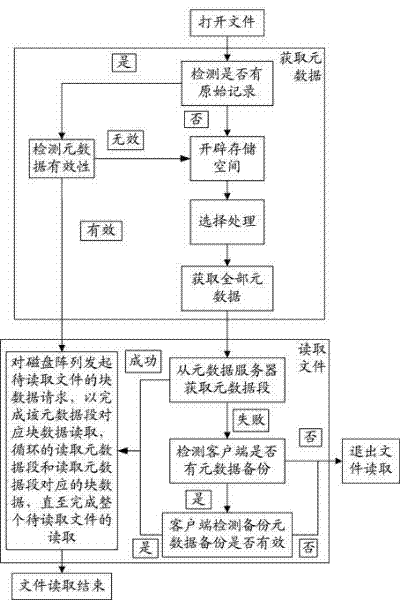
[0054] This embodiment is an improvement of Embodiment 1, and it is a refinement of the steps of reading files in Embodiment 1, such as Figure 4 shown. This embodiment is performed under the condition that metadata is stored in the client's local memory or hard disk. Because the metadata has been stored locally, the local metadata can be used directly. If obtaining metadata locally fails, obtain metadata from the metadata server. The sub-steps in the step of reading the file described in this embodiment are as follows:
[0055] 1b. The sub-step of obtaining the metadata segment from the local memory or the hard disk: it is used for the client to obtain the metadata segment from the local memory or the hard disk. Complete the reading of the block data corresponding to the metadata segment, read the metadata segment and read the block data corresponding to the metadata segment, until the entire file to be read is completed, and if it fails, enter the next step.
[0056] Thi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com