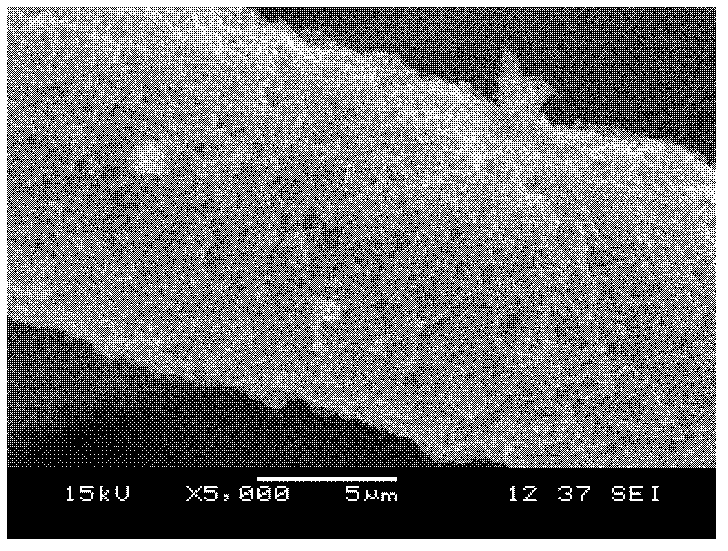
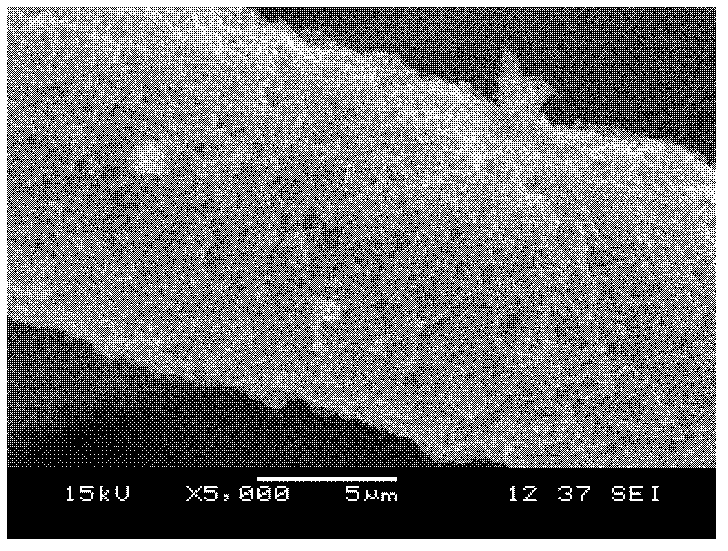
Method for preparing hydroxyapatite bioactive coating
A technology of hydroxyapatite and biological activity, applied in the direction of coating, etc., can solve the problem of poor bonding strength between carbon nanotubes and matrix materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] (1) The carbon fiber prefabricated body is ultrasonically cleaned with acetone, absolute ethanol and distilled water in sequence, and then placed in a vacuum drying oven to dry to obtain sample A;
[0021] (2) Sample A was placed in nitric acid (50% by volume), soaked at 50°C for 10 hours, then ultrasonically cleaned with distilled water and then dried in a vacuum oven to obtain sample B;
[0022] (3) Nickel nitrate and acetone were mixed according to the mass ratio of 1%, and ultrasonically oscillated for 30 minutes to form a uniform solution;
[0023] (4) Place sample B in the solution prepared in step (3), soak for 12 hours at 25 degrees, and then put it into a vacuum drying oven to dry to obtain sample C;
[0024] (5) Place sample C in a chemical vapor deposition furnace, calcinate at 400°C for 30 minutes, then feed in hydrogen with a flow rate of 80L / h for reduction reaction, and the reduction time is 20 minutes; then heat up to 720°C, and feed in propylene (Flow ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) The carbon / carbon composite material was ultrasonically cleaned with acetone, absolute ethanol and distilled water in sequence, and then put into a vacuum drying oven to dry to obtain sample A;
[0030] (2) Sample A was placed in nitric acid (60% by volume), soaked at 60°C for 12 hours, then ultrasonically cleaned with distilled water and then dried in a vacuum oven to obtain sample B;
[0031] (3) Nickel nitrate and acetone were mixed according to a mass ratio of 3%, and ultrasonically oscillated for 60 minutes to form a uniform solution;
[0032] (4) Place sample B in the solution prepared in step (3), soak for 15 hours at 30 degrees, and then put it into a vacuum drying oven to dry to obtain sample C;
[0033] (5) Place sample C in a chemical vapor deposition furnace, calcinate at 450°C for 50 minutes, then feed in hydrogen with a flow rate of 100L / h for reduction reaction, the reduction time is 30 minutes; then heat up to 750°C, and feed in propylene (Flow rate...
Embodiment 3
[0037] (1) The carbon fiber prefabricated body is ultrasonically cleaned with acetone, absolute ethanol and distilled water in sequence, and then placed in a vacuum drying oven to dry to obtain sample A;
[0038] (2) Sample A was placed in nitric acid (55% by volume), soaked at 55°C for 11 hours, then ultrasonically cleaned with distilled water and then dried in a vacuum oven to obtain sample B;
[0039] (3) Nickel nitrate and acetone were mixed according to the mass ratio of 2%, and ultrasonically oscillated for 45 minutes to form a uniform solution;
[0040](4) Place sample B in the solution prepared in step (3), soak for 14 hours at 28 degrees, and then put it into a vacuum drying oven to dry to obtain sample C;
[0041] (5) Place sample C in a chemical vapor deposition furnace, calcinate at 420°C for 40 minutes, then feed in hydrogen with a flow rate of 90L / h for reduction reaction, the reduction time is 25 minutes; then heat up to 730°C, and feed in propylene (Flow rate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com