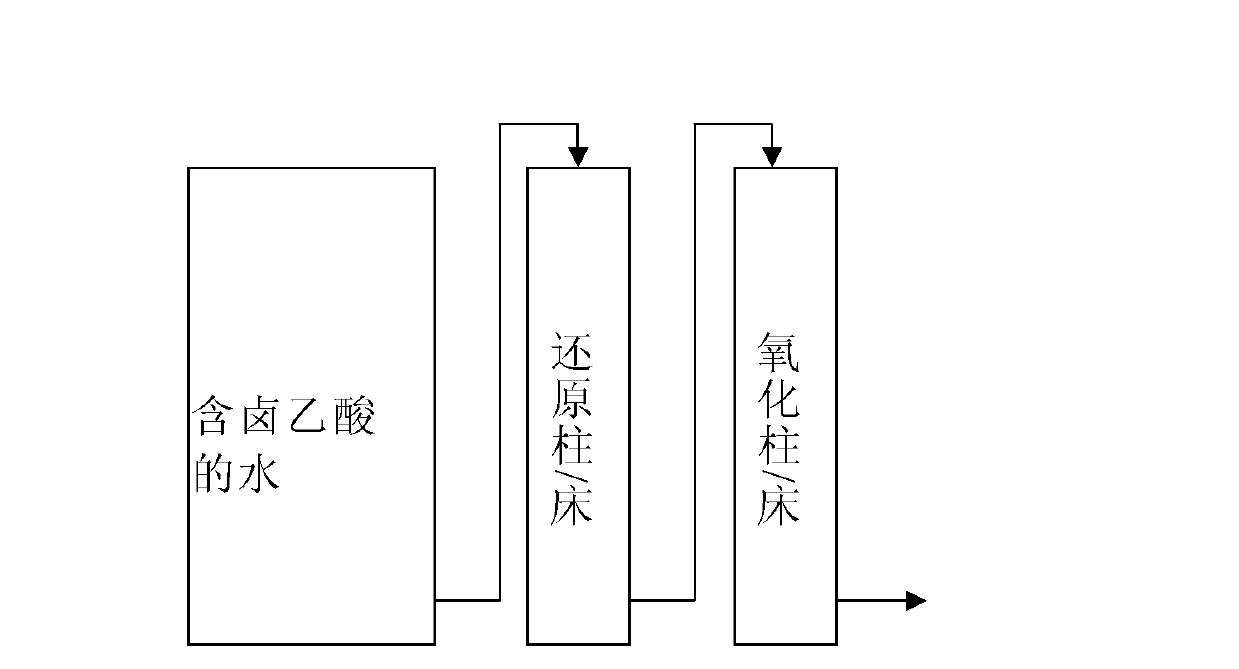
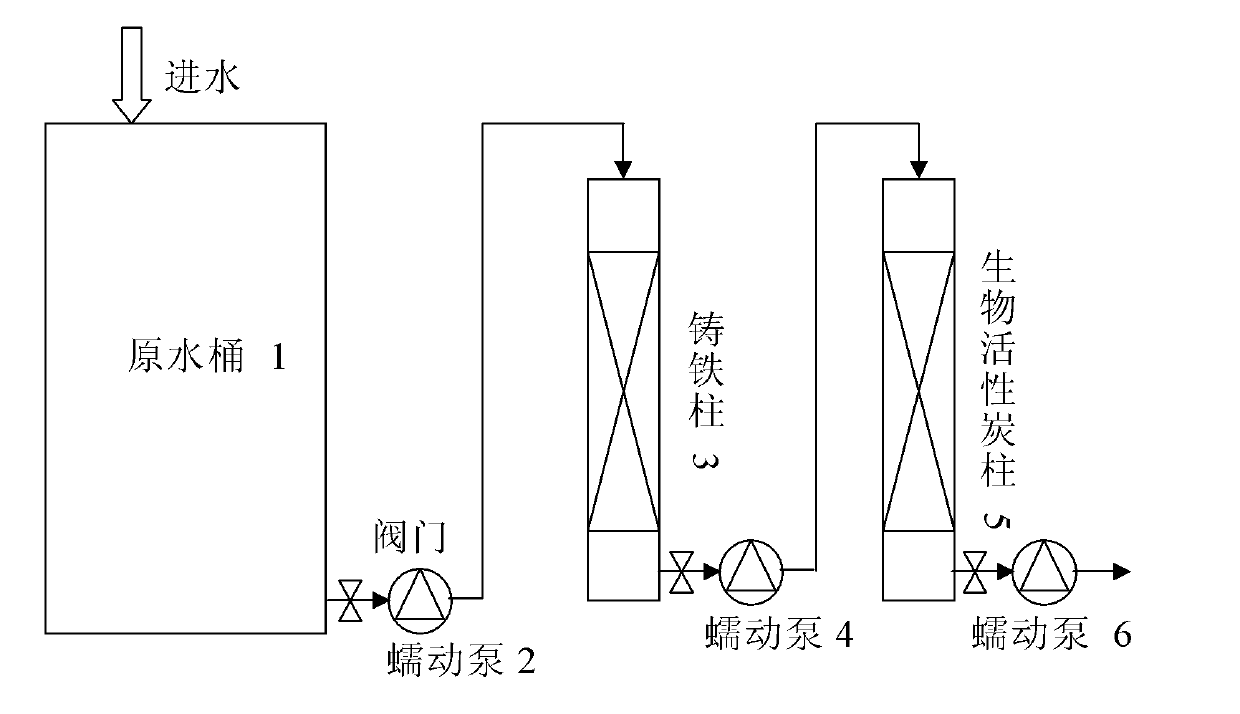
Method for removing haloacetic acids from water
A haloacetic acid, water removal technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as human health threats, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity and mutagenicity, and achieve investment Low cost and operating cost, short hydraulic retention time, small temperature effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
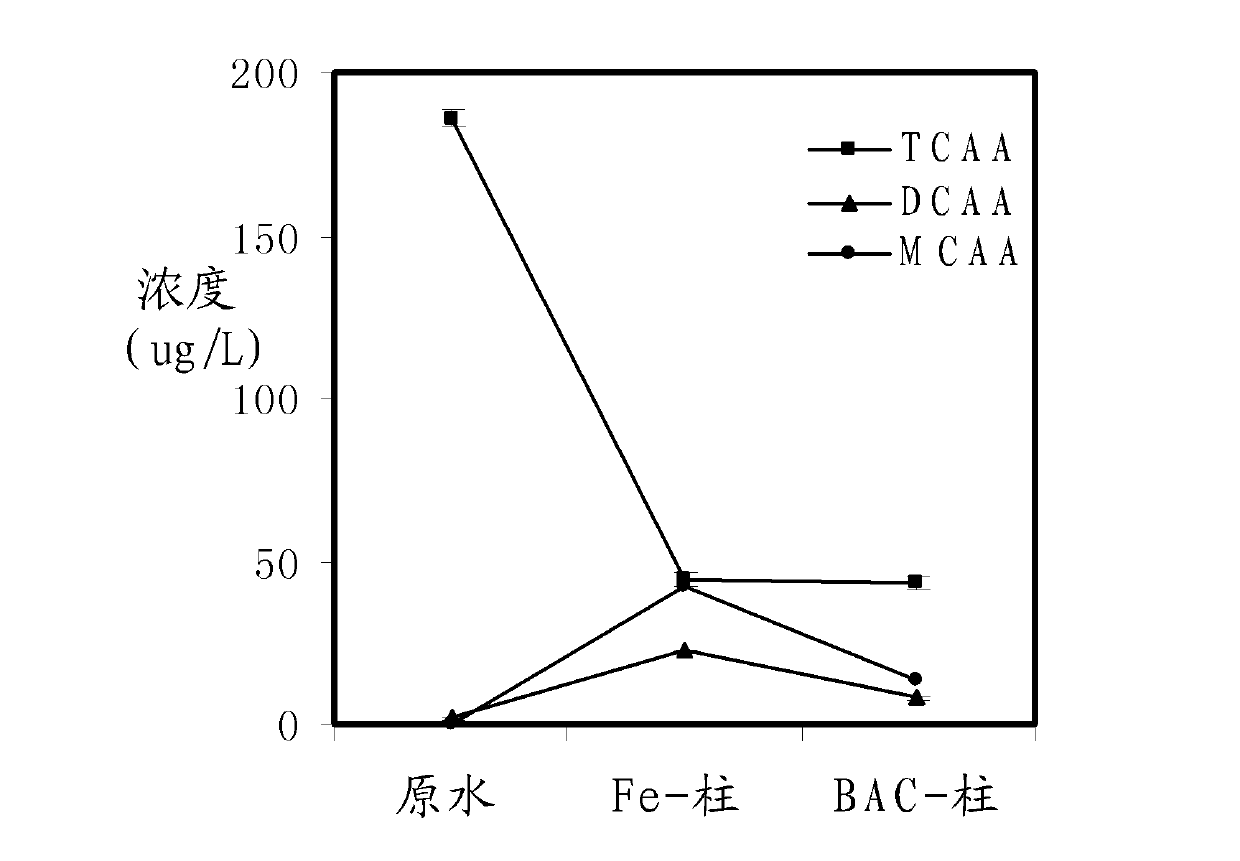
[0050] The average concentration of trichloroacetic acid in the raw water tank is about 185 μg / L; the EBCT of Fe-column and BAC-column is 2.5 minutes; the reaction temperature is 19°C. The average removal effect of nine samples of haloacetic acid under this condition is as follows image 3 .
[0051] image 3 It shows that TCAA in the raw water bucket becomes DCAA and MCAA after passing through the Fe-column, and the concentration of DCAA and MCAA decreases after passing through the BAC-column. Biodegradation occurs in the column. It shows that this method can effectively reduce the concentration of haloacetic acid in water.
Embodiment 2
[0053] The average concentration of trichloroacetic acid in the raw water tank is about 175 μg / L; the EBCT of Fe-column and BAC-column is 4 minutes; the reaction temperature is 15°C. The average removal effect of nine samples of haloacetic acid under this condition is as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0054] Figure 4 It shows that when the EBCT is 4 minutes, most of the TCAA in the raw water bucket is transformed into DCAA and MCAA after passing through the Fe-column. EBCT is beneficial to improve the dehalogenation efficiency of Fe-column to polyhaloacetic acid and the biodegradation effect of BAC-column to low-haloacetic acid, indicating that this method can efficiently treat haloacetic acid in water.
Embodiment 3
[0056] The average concentration of trichloroacetic acid in the raw water tank is about 165 μg / L; the EBCT of Fe-column and BAC-column is 10 minutes; the reaction temperature is 25°C.
[0057] Figure 5 It shows that TCAA in the raw water bucket is almost completely transformed into DCAA and MCAA after passing through the Fe-column, and no haloacetic acid is detected in the effluent after passing through the BAC-column. It can be seen that polyhaloacetic acid is almost completely dehalogenated into less haloacetic acid in the Fe-column , less haloacetic acids are fully biodegraded in the BAC-column. It shows that the method of the present invention can completely and rapidly remove haloacetic acid in water.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com