Relative radiometric correction method for automatically extracting pseudo-invariant features for remote sensing image
A relative radiometric correction and automatic extraction technology, applied in the field of remote sensing image radiometric correction, can solve the problems of strong human-computer interaction, poor data universality, and low robustness, and achieves no manual interaction, strong versatility, and simple processing flow. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
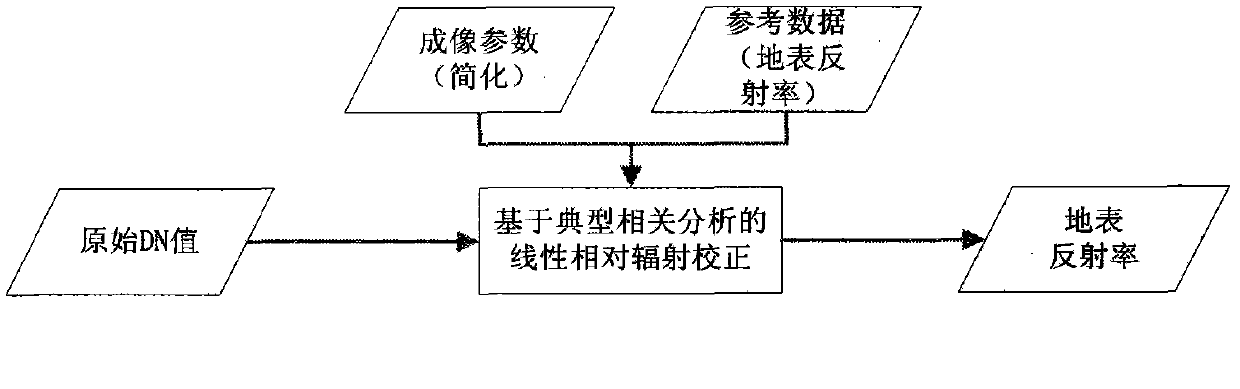
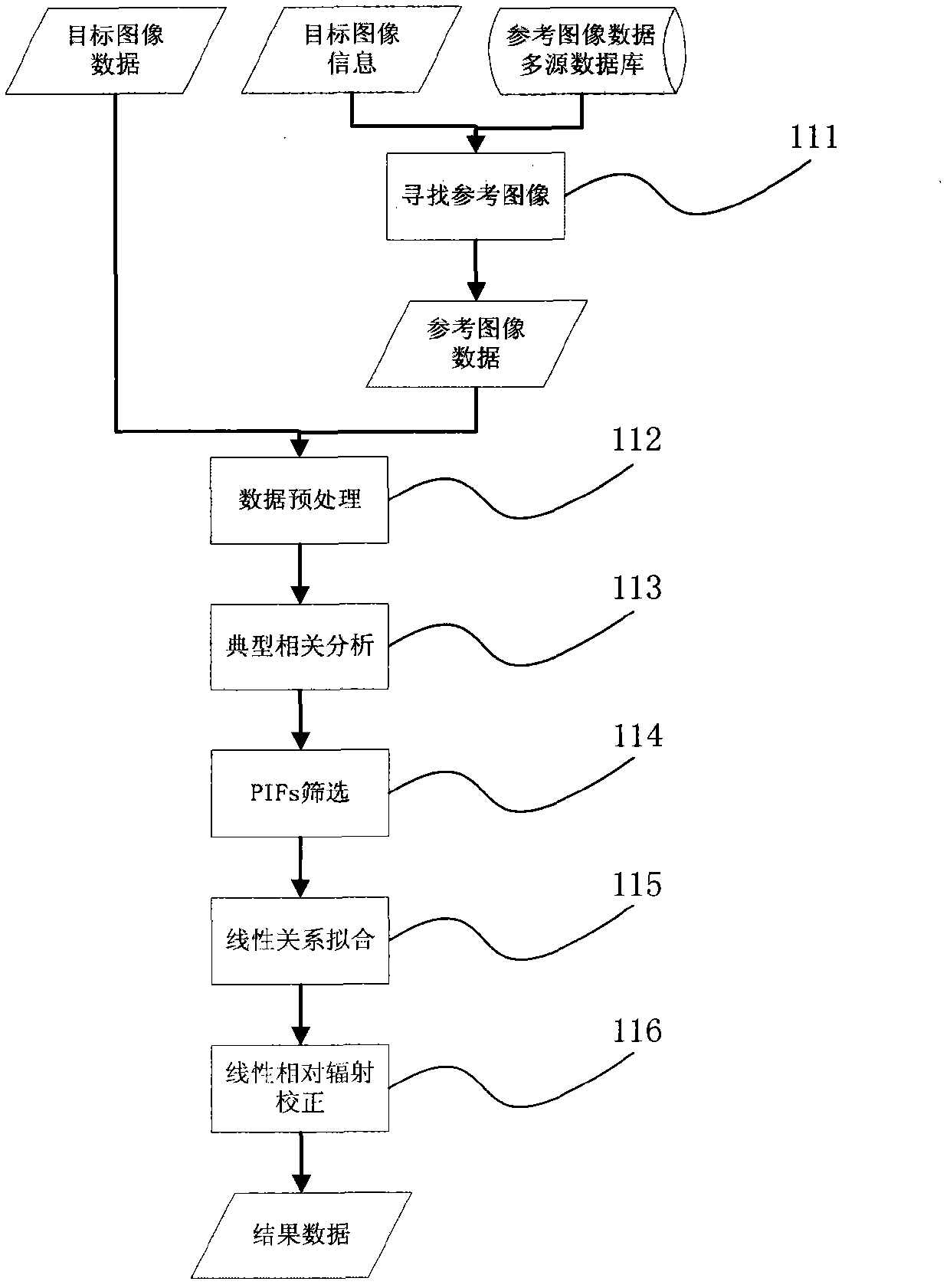
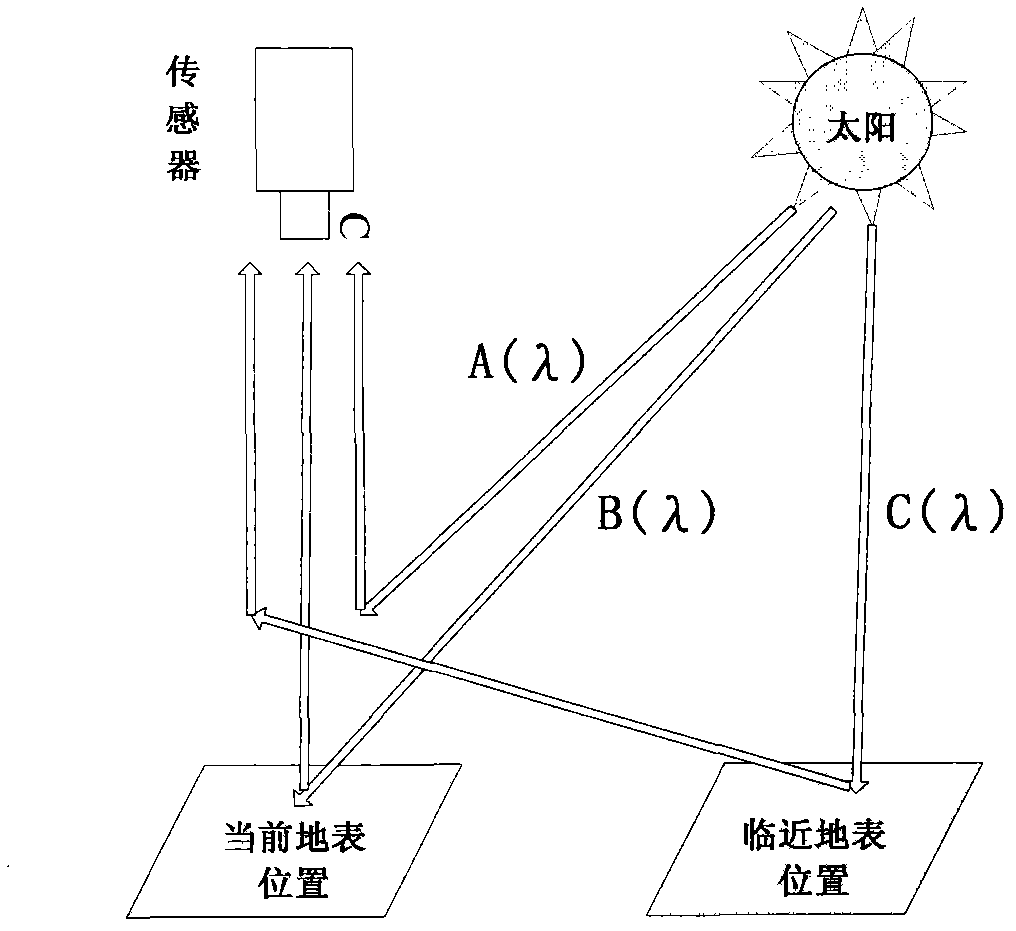
[0030] The idea of this technology is to use linear relative radiometric correction to directly convert the DN value to the surface reflectance. The core assumption is that under certain conditions, there is an approximately linear relationship between the DN value of the PIFs in the target image and the surface reflectance in the reference image. . This assumption is based on the following derivation:
[0031] Generally, the radiometric calibration process of remote sensing images uses a linear formula, such as (1):
[0032] L b =Gain*DN b +Bias (1)
[0033] Among them, Gain and Bias are scaling coefficients. Equation (1) converts the DN value to the apparent radiance L b .
[0034] From the apparent radiance L b Converted to the apparent reflectance ρ, the calculation adopts the formula (2):
[0035] ρ = π * L b * ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com