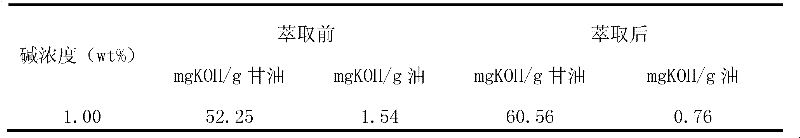Method for removing base catalyst from crude biodiesel
A technology of alkali catalyst and biodiesel, applied in biofuel, fat production, petroleum industry, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the cost of refining process, difficult to popularize and apply, and high cost of adsorbent production, so as to avoid the problem of waste water, avoid alcoholysis, Yield-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Embodiment 1: The removal method of the alkali catalyst in this crude biodiesel, the steps are as follows: using glycerol as the extractant to remove the alkali catalyst in the crude biodiesel, single-stage extraction of glycerol, the extraction temperature is 60-150 ° C, and the operating pressure is At normal pressure, the mass ratio of crude biodiesel to glycerin is between 10-1. The alkali catalyst dissolved in the glycerol phase is separated by cooling and crystallization, the crystallization temperature is 0°C-20°C, and the crystallization time is 1h-12h, and the separated glycerin and alkali catalyst are recycled.
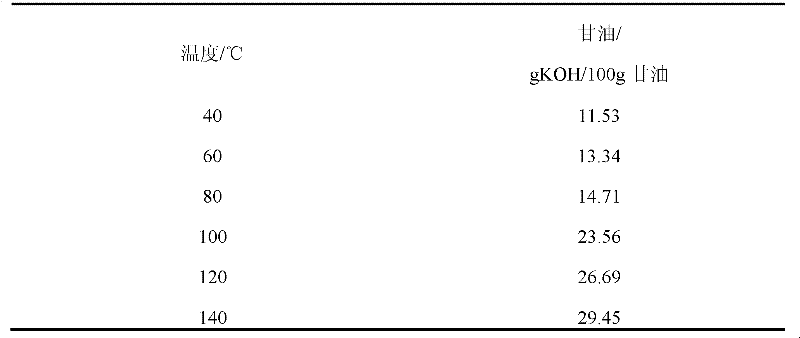
[0014] In order to illustrate the solubility of the alkali catalyst in glycerin, the solubility of the alkali catalyst KOH in glycerol is used to illustrate.
[0015] Solubility of KOH in glycerol at different temperatures in table 1
[0016]
[0017] It can be seen from Table 1 that the alkali catalyst KOH is easily soluble in glycerol, and glyce...
Embodiment 2
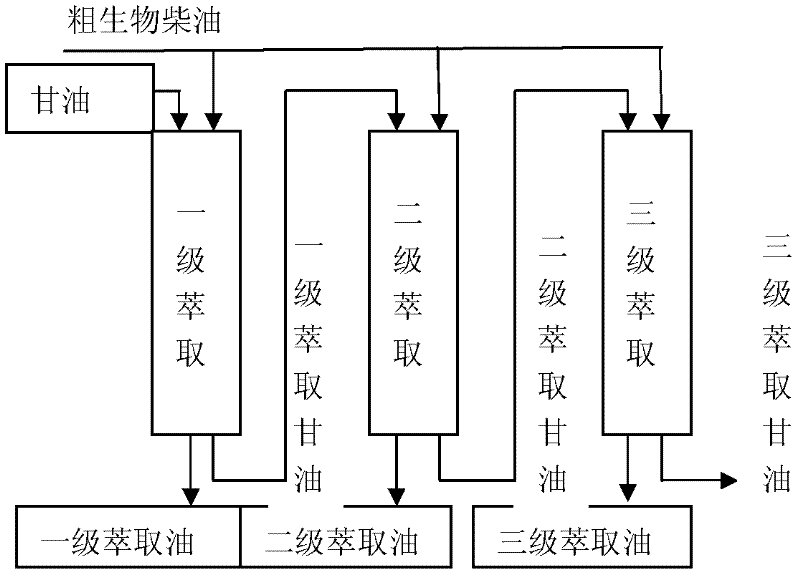
[0023] Embodiment 2: Utilize refined biodiesel by-product glycerin to extract crude biodiesel medium alkali catalyst, alkali catalyst is an example with KOH, figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the process of extracting crude biodiesel KOH from refined glycerin.
[0024] To illustrate the effect of glycerol extraction, crude biodiesel (3.74mgKOH / g oil) was figure 1 The method shown is three-stage extraction, the extraction temperature is 100°C, the mass ratio of crude biodiesel to glycerin is between 10-1, fresh glycerin is used for the first-stage extraction, first-grade glycerin is used for the second-stage extraction, and second-grade glycerin is used for the third-stage. The extraction effect is shown in Table 3.
[0025] Table 3 KOH effect of refined glycerin extraction crude biodiesel
[0026]
[0027] It can be seen from Table 3 that the KOH content in the crude biodiesel can be greatly reduced by three-stage extraction of glycerol, and the KOH content in the oil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com