Method for extracting valuable metals and refining zinc sulphate monohydrate from zinc-containing waste material
A valuable metal, zinc sulfate technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of complex leachate removal industry, high equipment cost and energy consumption, large process energy consumption, etc., and achieves high recovery rate, convenient operation and process simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The technical scheme of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and through specific embodiments:
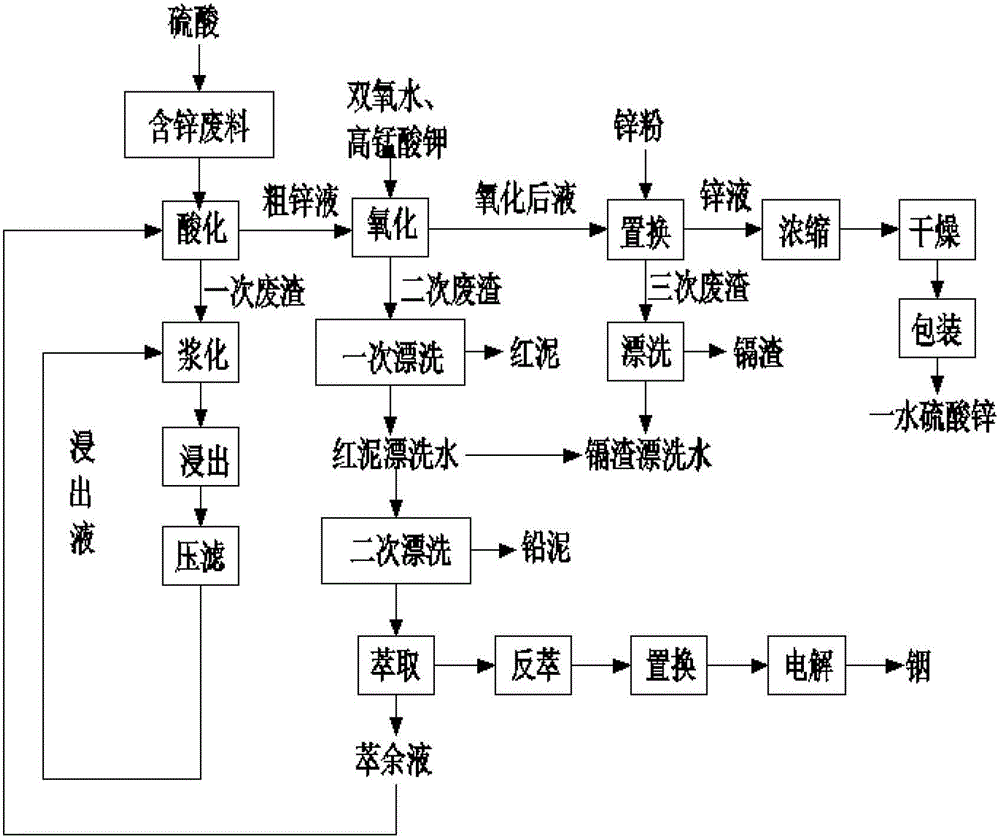
[0018] Please refer to figure 1 , a method for extracting valuable metals and refining zinc sulfate monohydrate from zinc-containing waste provided by the present invention, including refining zinc sulfate monohydrate and extracting valuable metals such as cadmium, lead and indium, wherein the The process of extracting zinc sulfate monohydrate includes steps such as acidification, oxidation, zinc replacement, concentration, drying and packaging; the process of extracting cadmium includes steps such as acidification, oxidation, replacement, and rinsing of cadmium slag; the process of extracting lead includes acidification , oxidation, primary rinsing, secondary rinsing and other steps; the process of extracting indium includes acidification, oxidation, primary rinsing, secondary rinsing, extraction, stripping, ind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com