Lens heat effect measuring system and measuring method
A measurement system and thermal effect technology, applied in the field of photolithography, can solve the problems of thinner graphics lines, invisible lines, high sensor cost, etc., and achieve the effect of high process applicability and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
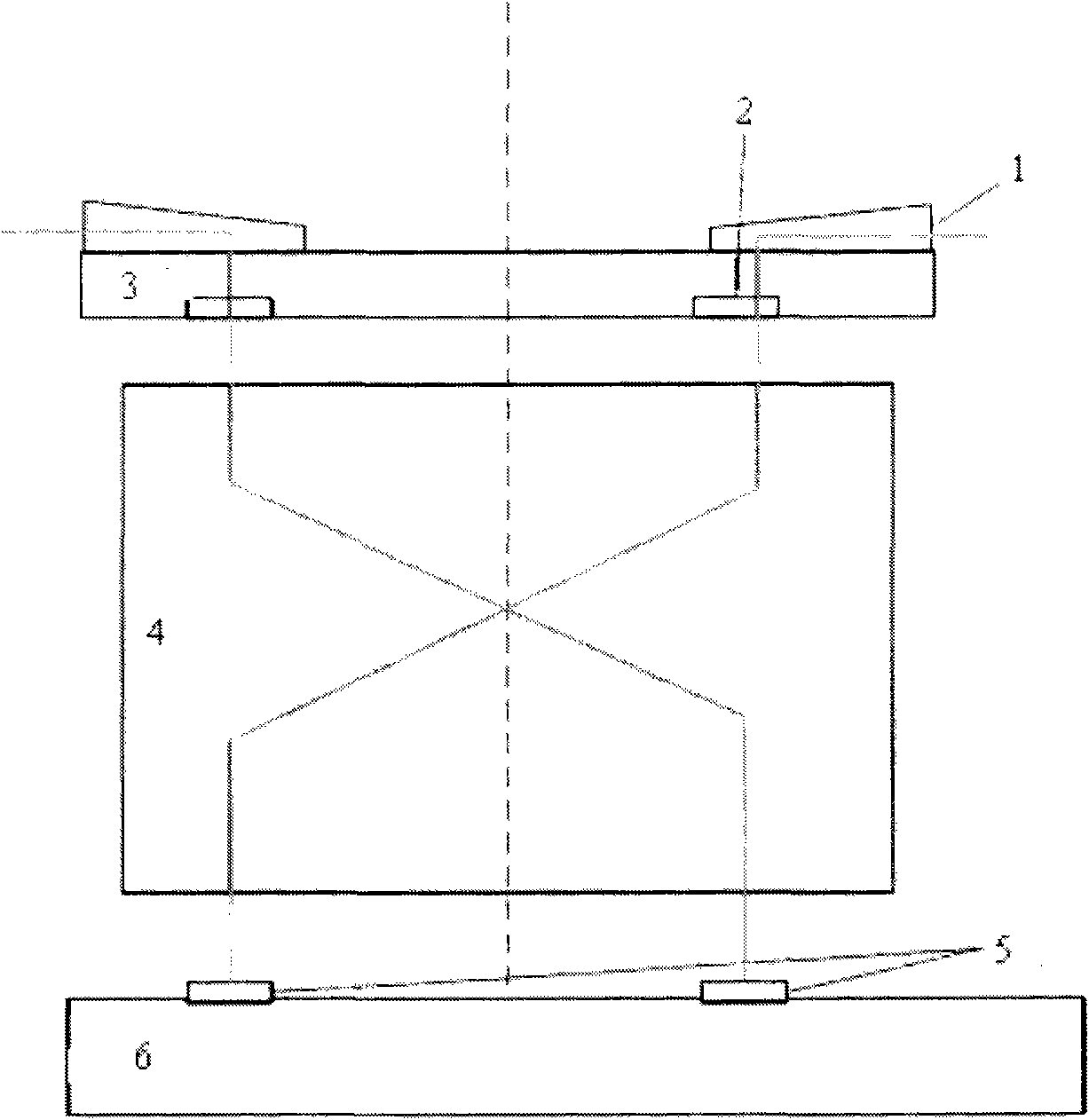
[0039] The structure diagram of the thermal effect measurement system used in the method for measuring the thermal effect of the lens by using the machine vision system according to the present invention is as follows figure 1 As shown, the equipment includes: a mask table reference plate 1 , a mask / mark on the mask table 2 , a mask 3 , a projection objective lens 4 , a machine vision system (MVS) 5 and a workpiece table 6 .
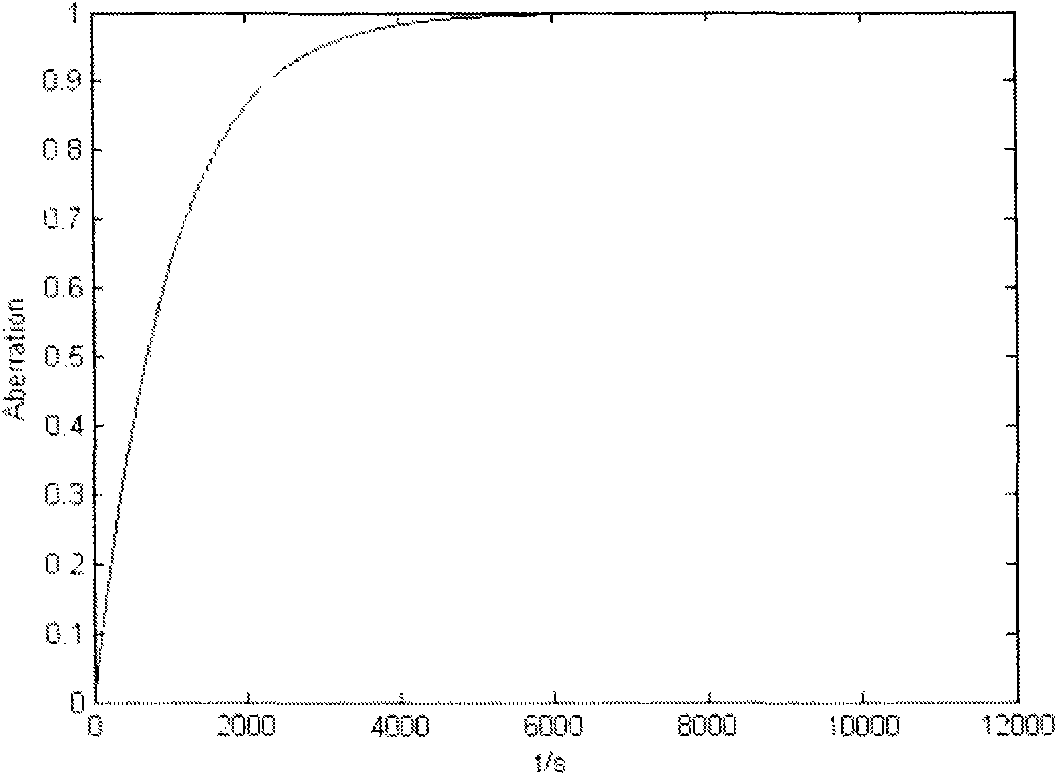
[0040] The basic method of using this equipment to test the thermal effect is: project the mark 2 on the mask / mask stage onto the workpiece stage 6 through the projection objective lens 4, measure the change of the position of the mark with time by the MVS5 on the workpiece stage 6, and collect the time And position information until the thermal equilibrium state (it takes several hours), find out the relationship between time and image quality parameter changes through mathematical methods, that is, the thermal effect scaling factor and time constant.
...
no. 2 example
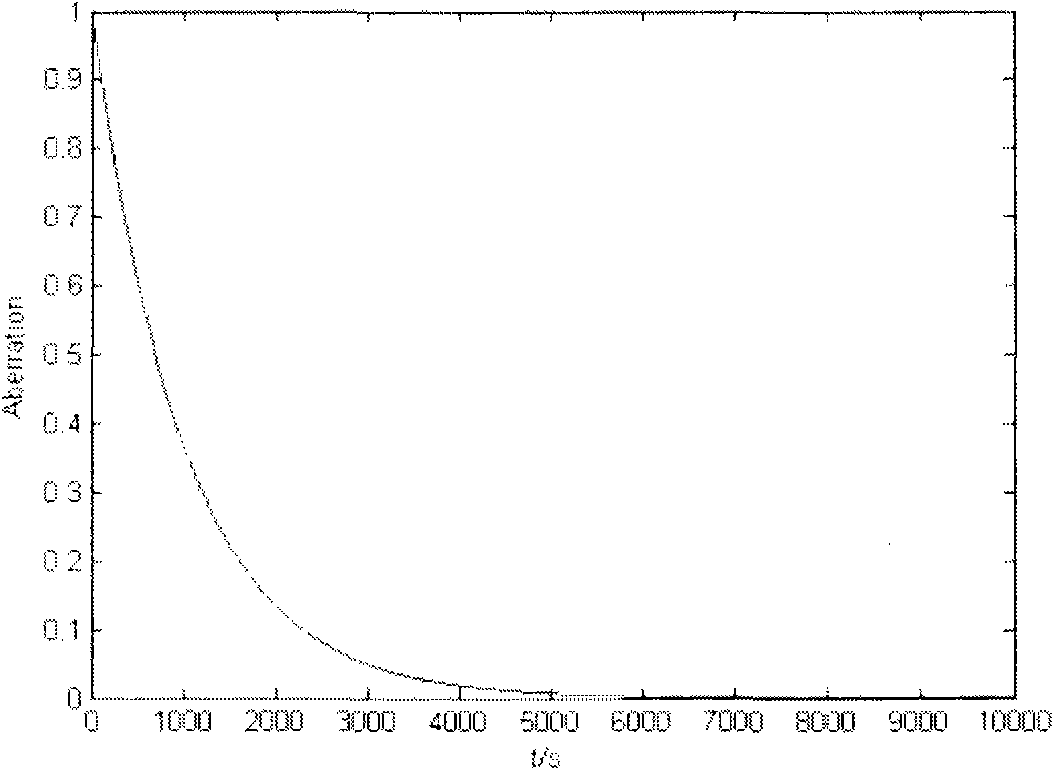
[0063] In this embodiment, the test of the descending curve is carried out. Such as image 3 As shown, where the horizontal axis represents the test time, and the vertical axis represents the image quality change (normalized). The thermal effect curve changes rapidly in the initial stage of measurement, and basically reaches saturation after about 5000s. Since the thermal effect scaling factor and time constant of the lens have the same effect on the rising curve and the falling curve, the falling curve can also be used to test the thermal effect, and the rising and falling curves can be used to verify each other.
[0064] This test consists of the following steps (since this method is used for a drop curve, it requires the lens to be "hot" at the beginning):
[0065] Use the strategy of first tightening and then loosening to select the test sampling time point;
[0066] Check the status of subsystems: whether MVS, mask / mask table reference plate, workpiece table, etc. are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com