Method for extracting tungsten from tungsten mineral by using soda and adopting high-pressure leaching process
A high-pressure leaching and soda technology, which is applied in the field of extracting tungsten from tungsten minerals by soda high-pressure leaching, can solve the problems of high temperature and pressure of soda pressure cooking, large soda excess coefficient, and waste of heat energy, etc., and achieve high decomposition rate and stable decomposition rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
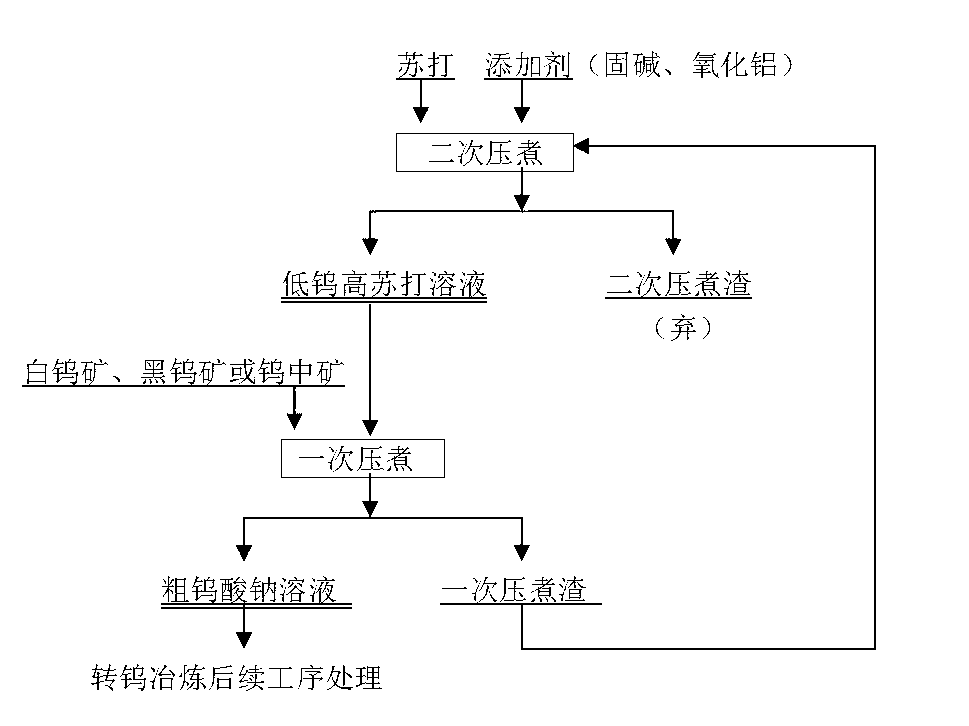
[0015] Example 1 Secondary pressure cooking of scheelite concentrate primary pressure cooking slag. Take scheelite concentrate for primary pressure cooking, add 116g of soda, the excess coefficient is 2.1, mix with 13g of solid alkali, 12g of alumina and 1200ml of water, the liquid-solid ratio is 4:1; Pressure cook for 4.0 hours. Afterwards, the pressure was reduced and the material was filtered, and the slag of the second pressure cooking was sampled and analyzed. The slag contained tungsten: 0.48%, and it was discarded and piled up; 3 : 14.47g / l; leaching rate of tungsten ore: 99.44%.
[0016] Scheelite concentrate is pressure-cooked once. Measure the secondary pressure cooking filtrate, add 250g scheelite fine powder to mix and adjust the slurry, control the liquid-solid ratio to 5:1, and leaching for 4.0 hours at a temperature of 230°C and a pressure of 2.5MPa. Afterwards, the pressure is reduced and the material is filtered, and the residue is transferred to the second...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Example 2 Secondary pressure cooking of scheelite middle ore primary pressure cooking slag. Take tungsten middling ore for one pressure cooking slag, add 146g soda, excess coefficient 2.5, mix with 13g solid alkali, 12g alumina and 1200ml water, liquid-solid ratio 3:1; Cook for 4.0 hours. Afterwards, the pressure is reduced and the material is filtered, and the slag of the second pressure cooking is sampled and analyzed. The slag contains tungsten: 0.36%, and it is discarded and piled up; 3 : 53.30g / l; leaching rate of tungsten ore: 99.35%.
[0018] Scheelite middlings are pressure-cooked once. Measure the filtrate of the secondary pressure cooking, add 345g of tungsten medium ore fine powder to mix and adjust the slurry, control the liquid-solid ratio of 3:1, and leach for 4.0 hours at a temperature of 180°C and a pressure of 0.9MPa. Afterwards, the pressure is reduced and the material is filtered, and the slag is transferred to the secondary pressure cooking ingred...
Embodiment 3
[0019] Example 3 Secondary pressure cooking of scheelite middle ore primary pressure cooking slag. Take scheelite middle ore pressure-cooked slag once, add 147g soda, the excess coefficient is 2.5, mix with 12g solid alkali, 6.5g alumina and 1100ml water, the liquid-solid ratio is 3:1; Sub-pressure cook for 2.0 hours. Afterwards, the pressure was reduced and the material was filtered, and the slag was sampled and analyzed for the second time. The slag contained tungsten: 0.11%, and it was discarded and piled up; 3 : 40.41g / l; leaching rate of tungsten ore: 99.79%.
[0020] Scheelite middlings are pressure-cooked once. Measure the filtrate of the secondary pressure cooking, add 345g of scheelite medium ore fine powder to mix and adjust the slurry, control the liquid-solid ratio of 3:1, and leach for 2.0 hours at a temperature of 230°C and a pressure of 2.4MPa. Afterwards, the pressure is reduced and the material is filtered, and the residue is transferred to the secondary pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com