Power semiconductor device having plurality of switching elements connected in parallel
A semiconductor and power technology, applied in the field of power semiconductor devices, can solve problems such as inability to apply, turn-off loss without considering turn-on loss, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing switching loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0054] [Structure of Power Semiconductor Device 200 ]
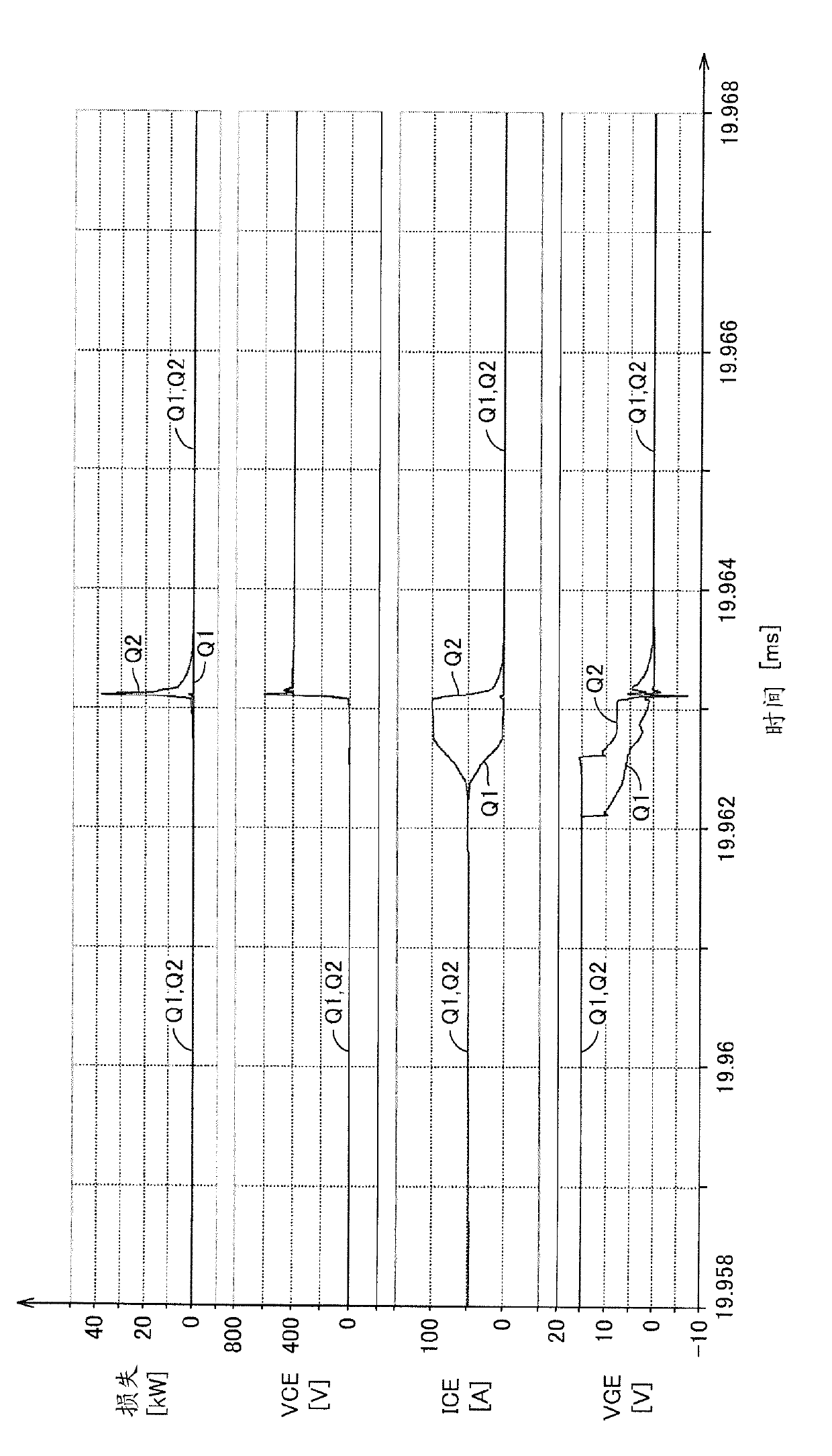
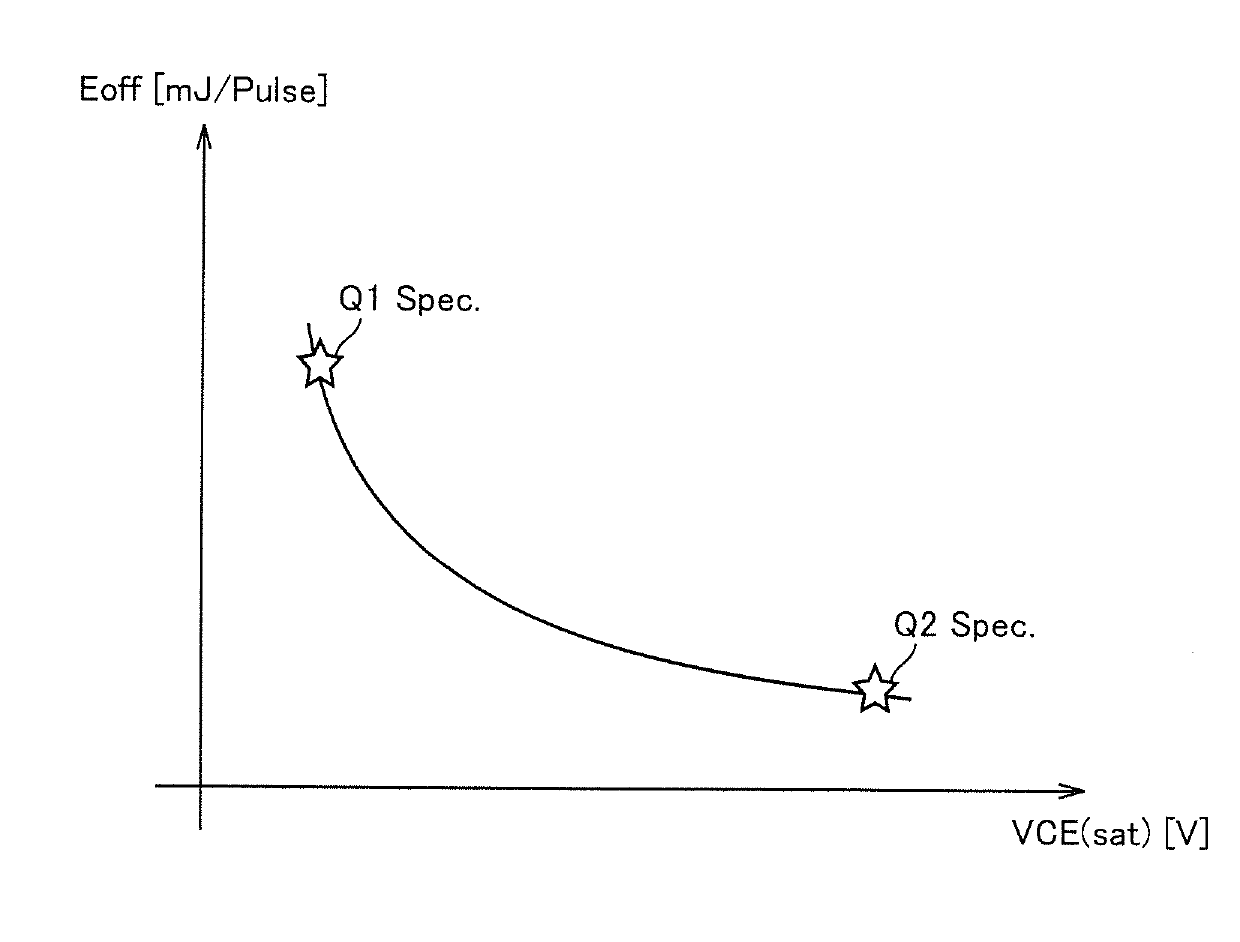
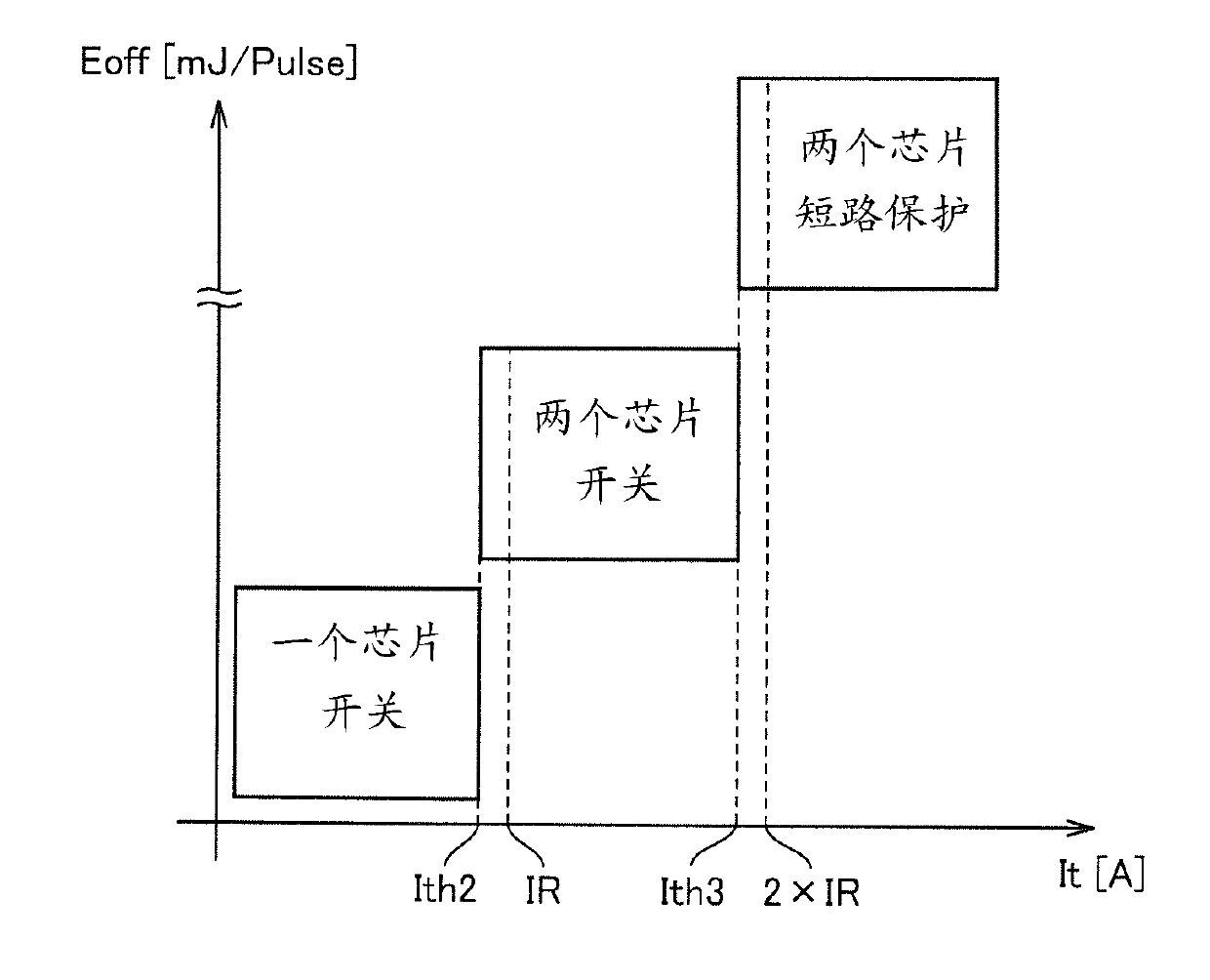
[0055] figure 1 It is a configuration diagram of the power semiconductor device 200 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. refer to figure 1 The power semiconductor device 200 includes the power semiconductor elements Q1 and Q2 connected in parallel between the high voltage node HV and the ground node GND, and the drive control unit 100 . exist figure 1 In the above, IGBTs are exemplified as power semiconductor elements Q1 and Q2 , but other semiconductor elements such as power MOSFETs and bipolar transistors may also be used. Hereinafter, the power semiconductor elements Q1 and Q2 are also referred to as IGBT Q1 and Q2, respectively. The high-voltage node HV to which the collectors of IGBT Q1 and Q2 are connected is connected to an electric device to be controlled, and a high voltage is applied thereto.
[0056] Drive control unit 100 switches IGBT Q1 and Q2 into an on state or an off state according to...
Embodiment approach 2
[0115] Figure 17 It is a circuit diagram showing the configuration of the power semiconductor device 201 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Shown in Embodiment 2 figure 1 An example of the specific structure of the drive control unit 100. Figure 17 The drive control unit 101 includes: integrated circuit (IC: Integrated Circuit) 5 for control; power supply V1 for drive; resistance elements R14, R15, R23, R24; N-type MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor: metal oxide semiconductor) transistors Q11, Q22, Q33, Q44.
[0116] The integrated circuit 5 includes: an input terminal IN for receiving the driving signal DS; and output terminals OUT1, OUT2, OUT3, and OUT4 for outputting control signals corresponding to the driving signal DS to the gates of the transistors Q11, Q22, Q33, and Q44, respectively. The drains of the transistors Q11 and Q33 are connected to the power supply node 9 to which a driving voltage is supplied from the driving power supply V1. The sources ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0127] Figure 19 It is a circuit diagram showing the configuration of the power semiconductor device 202 according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Shown in Embodiment 3 figure 1 An example of the specific structure of the drive control unit 100. Figure 19 The drive control unit 102 includes: integrated circuit (IC) 5a for control; power supply V1 for drive; resistance elements R14, R15, R23, R24; N-type MOS transistors Q11, Q22, Q33, Q44 for driving IGBTQ1, Q2 ; Delay circuits DLY1, DLY2.
[0128] The integrated circuit 5a includes: an input terminal IN for receiving the drive signal DS; for outputting a control signal corresponding to the drive signal DS to the gate of the transistor Q11 and an output terminal OUT1 of the delay circuit DLY1; for outputting a control signal corresponding to the drive signal DS The control signal is output to the gate of the transistor Q22 and the output terminal OUT2 of the delay circuit DLY2. The drains of the transistors Q11 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com