Method for increasing plant folate content by using synergistic effect of transferred soybean genes of GTPCHI and ADCS
A synergistic, genetic technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
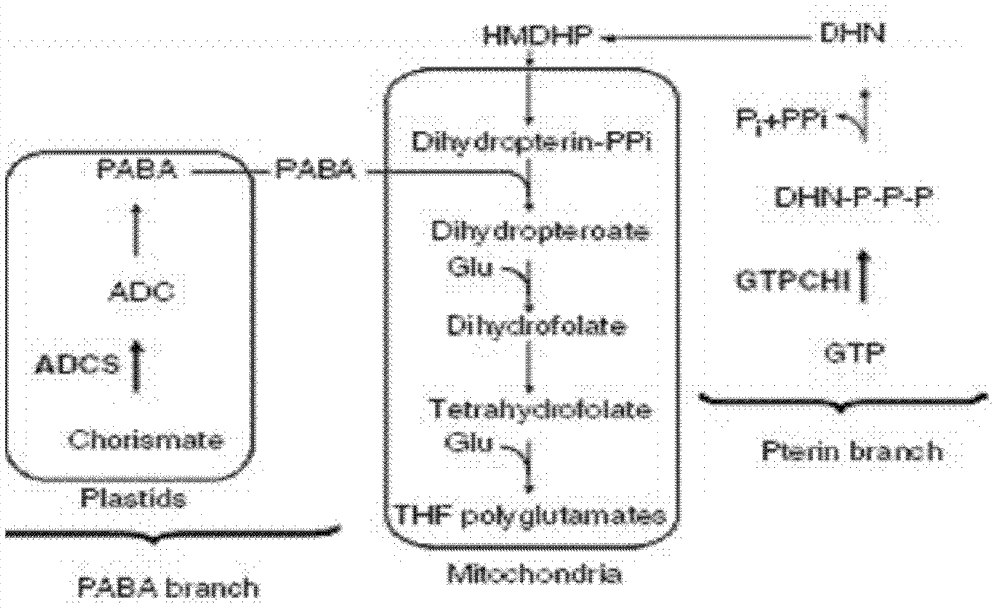
[0032] 1. Obtain the EST sequence of the soybean GTPCHI gene
[0033] Since the GTPCHI genes from different species should have a certain degree of homology, or there are conserved structural domains. To this end, the CDS sequence of the GTPCHI gene of Arabidopsis was compared with the EST sequence of soybean on NCBI to obtain the EST sequence of the GTPCHI gene of soybean.
[0034] 2. PCR amplification to obtain the GmGTPCHI gene fragment and its sequence analysis
[0035] 100 mg of soybean leaves were taken, and total RNA was extracted by Trizol method. After being treated with DNase I, the purity and concentration of RNA were detected, and 1 μg was used to obtain cDNA with the reverse transcription kit First strand cDNA systhesis (purchased from Fermentas). Primers were designed using the EST sequence of soybean GTPCHI gene as a template, and soybean cDNA was used as a template for amplification. A band of about 700 bp was obtained, which was sequenced as the fragment seq...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 1. Obtain the EST sequence of soybean ADCS gene
[0044] The CDS sequence of ADCS gene of Arabidopsis was compared with the EST sequence of soybean on NCBI to obtain the EST sequence of soybean GTPCHI gene.
[0045] 2. PCR amplification to obtain the GmADCS gene fragment and its sequence analysis
[0046] 100 mg of soybean leaves were taken, and total RNA was extracted by Trizol method. After being treated with DNase I, the purity and concentration of RNA were detected, and 1 μg was used to obtain cDNA with the reverse transcription kit First strand cDNA systhesis (purchased from Fermentas). Primers were designed using the EST sequence of soybean ADCS gene as a template, and soybean cDNA was used as a template to amplify. A band of about 1300bp was obtained. After the fragment was recovered, it was connected to the p-EASY-T1 vector, and 8 positive clones were picked for sequencing and compared with 3'EST. It was found that the sequencing results of 6 clones were consis...
Embodiment 3
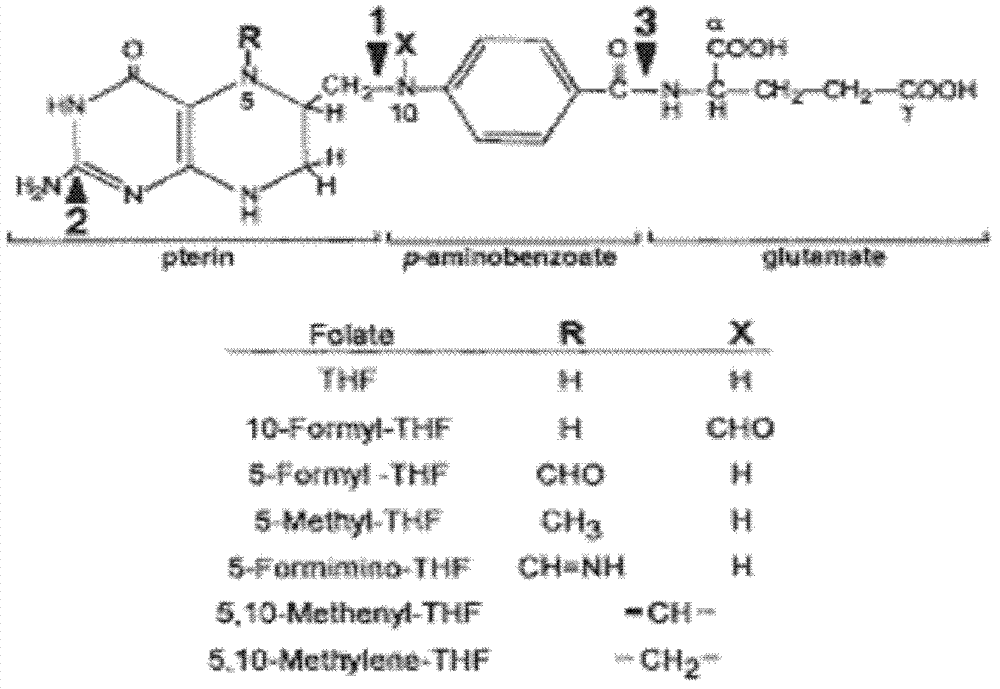
[0054] The CDS sequences of soybean GmGTPCHI and GmADCS were respectively constructed into plant overexpression vectors, both of which were driven by cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter. Among them, the CDS sequence of soybean GmGTPCHI was recombined into pH2GW7 through the Gateway system, and the CDS sequence of soybean folic acid synthesis key enzyme gene GmADCS was constructed between the restriction sites Nco I and Pml I of the plant overexpression vector pCAMBIA1302 to obtain the recombinant expression vector pCAMBIA1302- GmADCS. Wild-type Arabidopsis was infected by Agrobacterium-mediated floral staining.
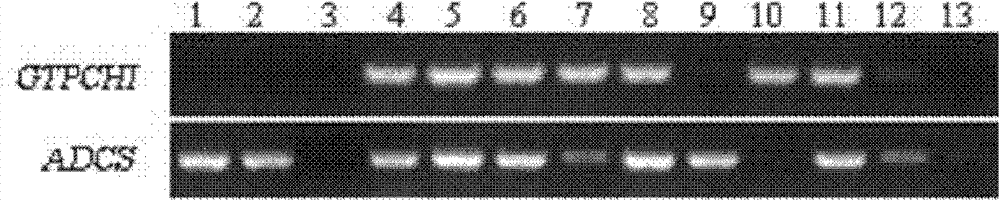
[0055] Transfer the acquired T to GmGTPCHI 0 Generation-positive Arabidopsis plants G1-G4 were used as male parents, and T0-generation positive Arabidopsis plants A1-5 obtained into GmADCS were used as female parents, and the following hybrid combinations were carried out: G1xA1, G1xA2, G2xA3, G2xA4, G3xA2, G4xA5, and seed pods after hybridization were harv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com