Vinyl chloride monomer polymerization reaction system reaction termination method
A vinyl chloride monomer and polymerization reaction technology, which is applied in the field of reaction termination of vinyl chloride monomer polymerization reaction system, can solve the problems of insignificant improvement of thermal stability of resin, low efficiency of polymerization termination, and limited improvement of thermal stability performance, etc., to achieve Excellent thermal stability effect, rapid polymerization termination effect, scientific and reasonable termination method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
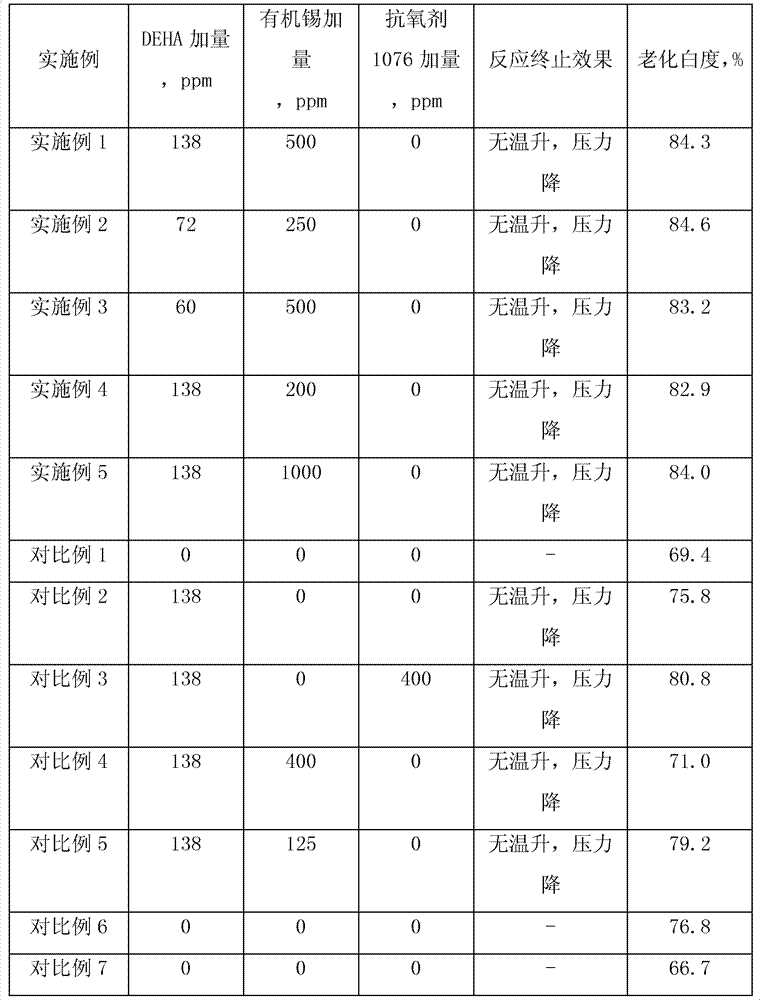
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The polymerization reaction was carried out in a stainless steel reactor with a volume of 5 L equipped with two-layer flat paddles.
[0041] The polymerization formula is as follows:
[0042] raw material name
Dosage / kg
VCM
1.45
DW
2.10
PVA(I)
0.0002
E50
0.00028
PVA(II)
0.00046
TAPP
0.0006
TBPND
0.0003
NG
0.00018
NaOH
0.000065
DEHA
0.0002
OE-Sn
0.00725(500ppm)
[0043] Note:
[0044] VCM: vinyl chloride monomer.
[0045] DW: desalinated water.
[0046] PVA (I): polyvinyl alcohol, alcoholysis degree 80% (mole fraction), viscosity 48mPa.s (measured at 20°C, 4% concentration).
[0047] PVA(II): polyvinyl alcohol, alcoholysis degree 45% (mole fraction), viscosity 90mPa.s (measured at 25°C, 35% concentration).
[0048] E50: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, with a methoxy substitution degree of 25%, a hydroxyprop...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Adopt the polymerization reactor identical with embodiment 1, used formula is as follows:
[0060] raw material name
Dosage / kg
VCM
1.53
DW
1.82
PVA(I)
0.00061
E50
0.00106
PVA(II)
0.00019
ACPND
0.00026
EHP
0.00078
NaOH
0.000048
DEHA
0.00011
OE-Sn
0.00382(250ppm)
[0061] Note:
[0062] VCM: vinyl chloride monomer.
[0063] DW: desalinated water.
[0064] PVA (I): polyvinyl alcohol, alcoholysis degree 80% (mole fraction), viscosity 48mPa.s (measured at 20°C, 4% concentration).
[0065] PVA(II): polyvinyl alcohol, alcoholysis degree 45% (mole fraction), viscosity 90mPa.s (measured at 25°C, 35% concentration).
[0066] E50: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, with a methoxy substitution degree of 25%, a hydroxypropyl substitution degree of 11.5%, and a viscosity of 50 mPa.s (measured at 20° C. at a concentration of 2%).
[006...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Adopt the polymerization reactor identical with embodiment 1, used formula is as follows:
[0077] raw material name
Dosage / kg
VCM
1.45
DW
2.10
PVA(I)
0.00026
E50
0.00039
LE
0.00026
NG
0.00141
NaOH
0.000145
DEHA
0.000087
OE-Sn
0.00725(500ppm)
[0078] Note:
[0079] VCM: vinyl chloride monomer.
[0080] DW: desalinated water.
[0081] PVA (I): polyvinyl alcohol, alcoholysis degree 80% (mole fraction), viscosity 48mPa.s (measured at 20°C, 4% concentration).
[0082] E50: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, with a methoxy substitution degree of 25%, a hydroxypropyl substitution degree of 11.5%, and a viscosity of 50 mPa.s (measured at 20° C. at a concentration of 2%).
[0083] LE: azobisisoheptanonitrile.
[0084] NG: 2-mercaptoethanol.
[0085] NaOH: sodium hydroxide.
[0086] DEHA: Diethylhydroxylamine.
[0087] Polymerization condi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com