Forced shearing flying shear and forced shearing method thereof
A control method and technology of flying shears, which are applied in the direction of shearing devices, devices for shearing forming blanks, and shearing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the production of steel bars, failure to automatically shear, and leakage of cooling bed, etc., so as to reduce artificial The effect of working, simple structure, and reducing labor intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
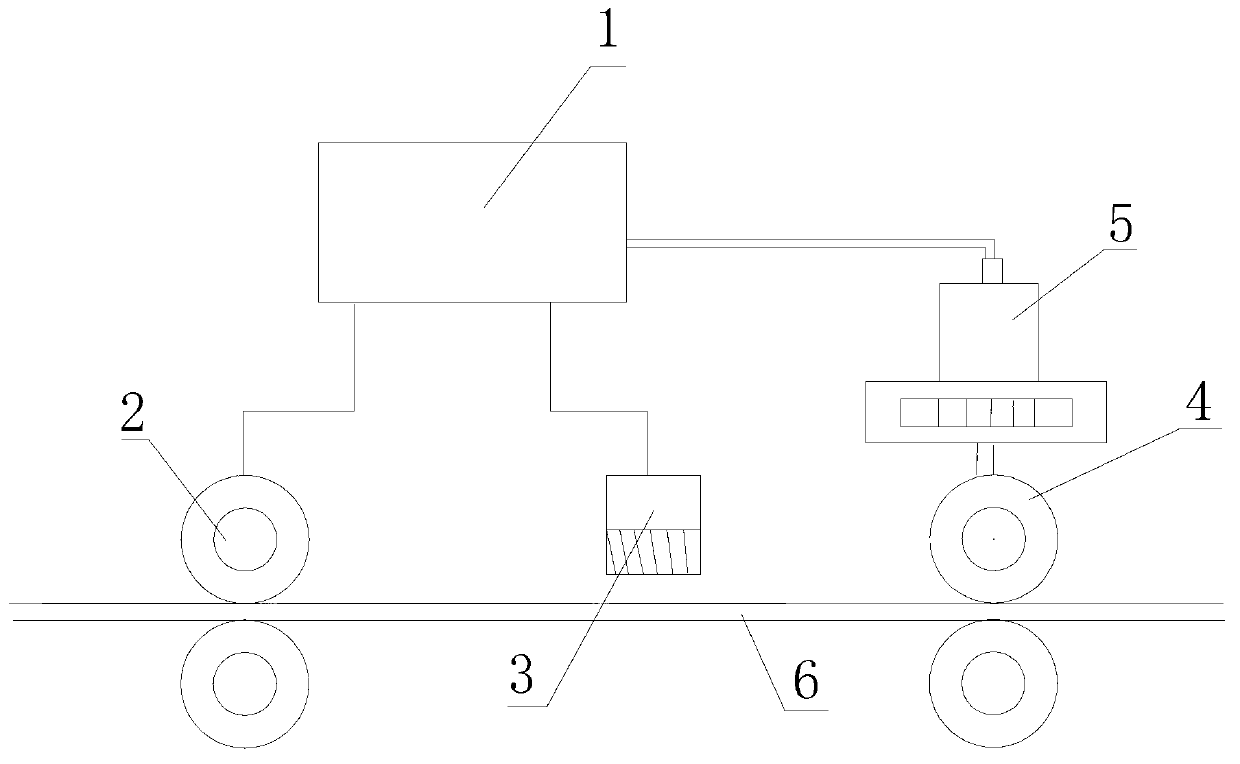
[0029] The forced shear flying shear of the present embodiment has a structure such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a DC motor 5, a reduction box, a flying shear body 4 and a scanning thermal detection device 3. The scanning thermal detection device 3 is aligned with the head of the rolled piece 6 on the finished product frame 2, and the scanning thermal detection device 3 The signal output end of the T400 process board 1 is connected to the signal input end of the T400 process board 1, the output end of the T400 process board 1 is connected to the controlled end of the flying shear body 4, and a positioning proximity switch is provided at the cutting edge of the flying shear body 4. In order to accurately locate the flying shear body, the signal output terminal of the positioning proximity switch is connected to the signal input terminal of the T400 process board 1, and the DC motor 5 is connected to the speed regulating device and the encoder. The speed regulating device ca...
Embodiment 2
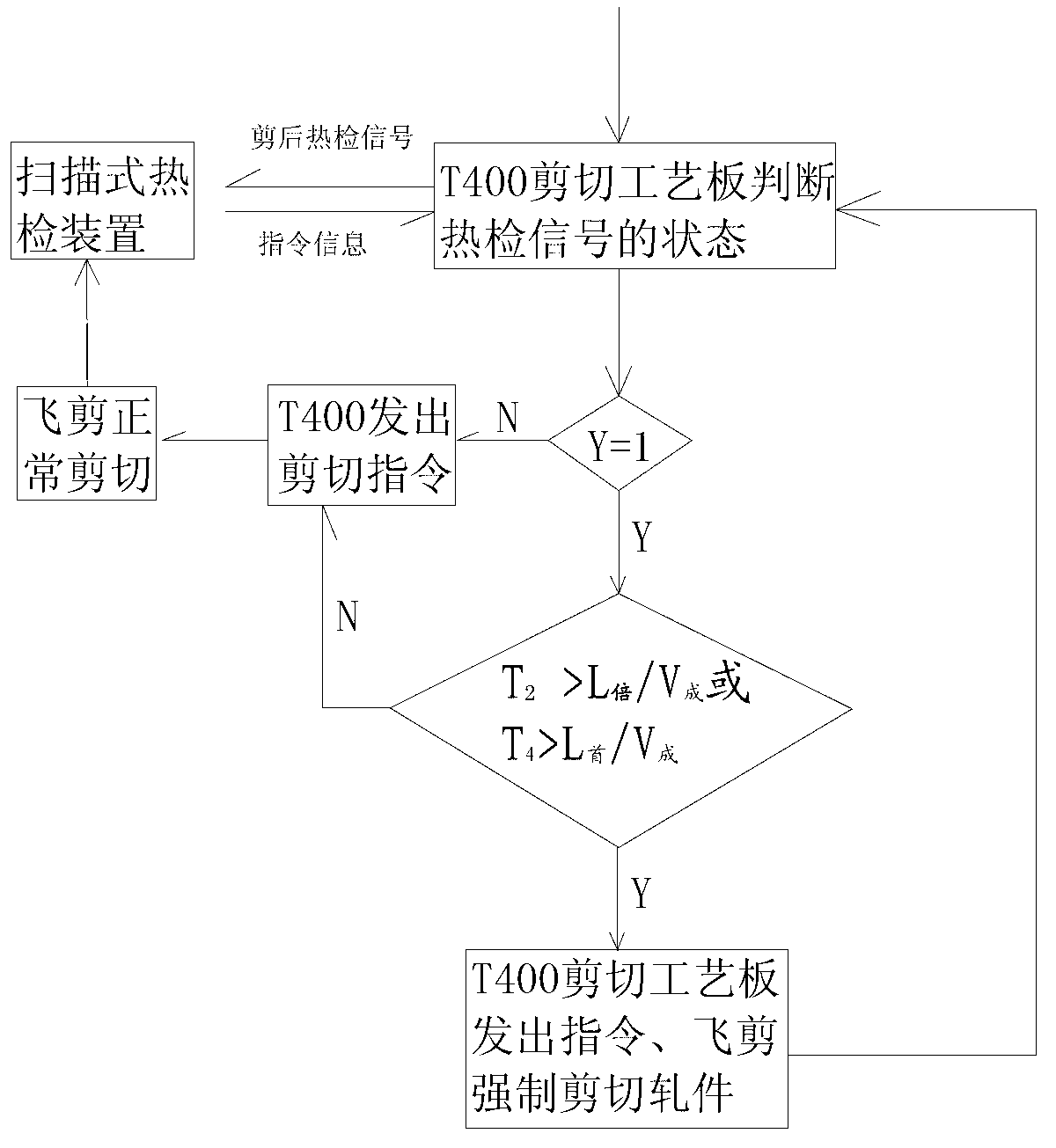
[0032] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the T400 process board judges the time T, when "T≤L 倍 / V 成 ", the T400 process board sends a cutting command to the controlled end of the flying shear, and controls the flying shear to perform normal shearing on the rolled piece. After the operation is completed, it returns to the normal shearing state, enters step 1, and starts the next cycle. Among them, L 倍 Set to 96.30m, V 成 is 7 m / s.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the scanning thermal detection device conducts thermal detection on the rolled piece to obtain the signal Y, and transmits the signal Y to the T400 process board, and the T400 process board judges that "Y=0", The T400 process board sends a delayed cutting command to the controlled end of the flying shear, and the flying shear is delayed for a certain time T 1 Finally, normal shearing is carried out on the rolled piece, and the operation is completed, and the next cycle is entered. where T 1 =(L 倍 -L 45 ) / V 成 , L 倍 95.20 meters, L 45 for 45m, V 成 is 6 m / s.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com