Method for quantitatively detecting microvolt T-wave alternans
A quantitative detection method and detection method technology, applied in the field of biomedical signal processing, can solve problems such as easy to cause false detection and missed detection, large amount of calculation, and high complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be noted that the following description is only for explaining the present invention and not limiting its content.
[0054] A quantitative detection method for microvolt-level T wave alternation, comprising the following steps:
[0055] (1) Obtain ECG data and perform ECG signal preprocessing:
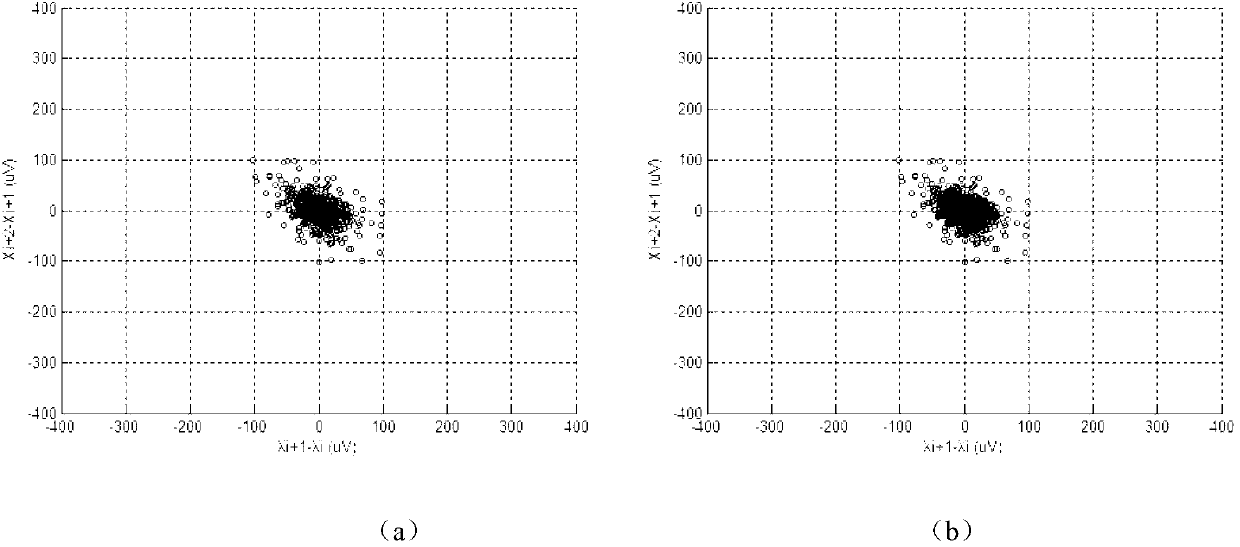
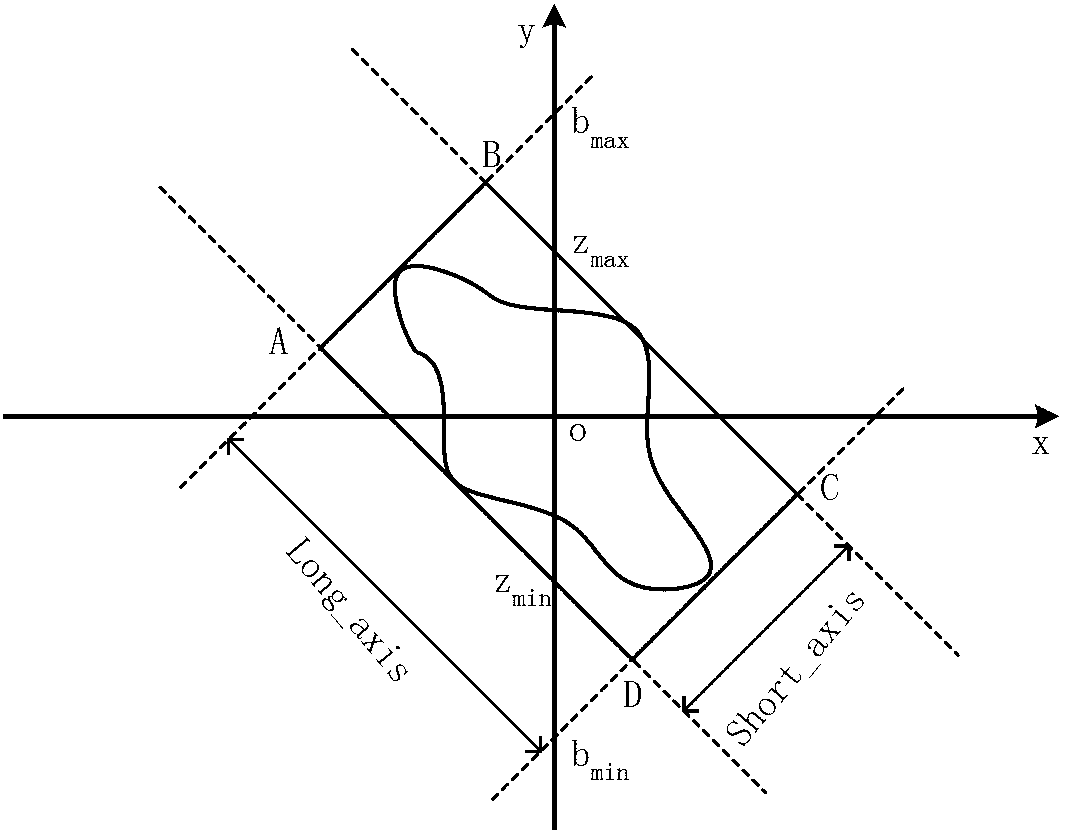
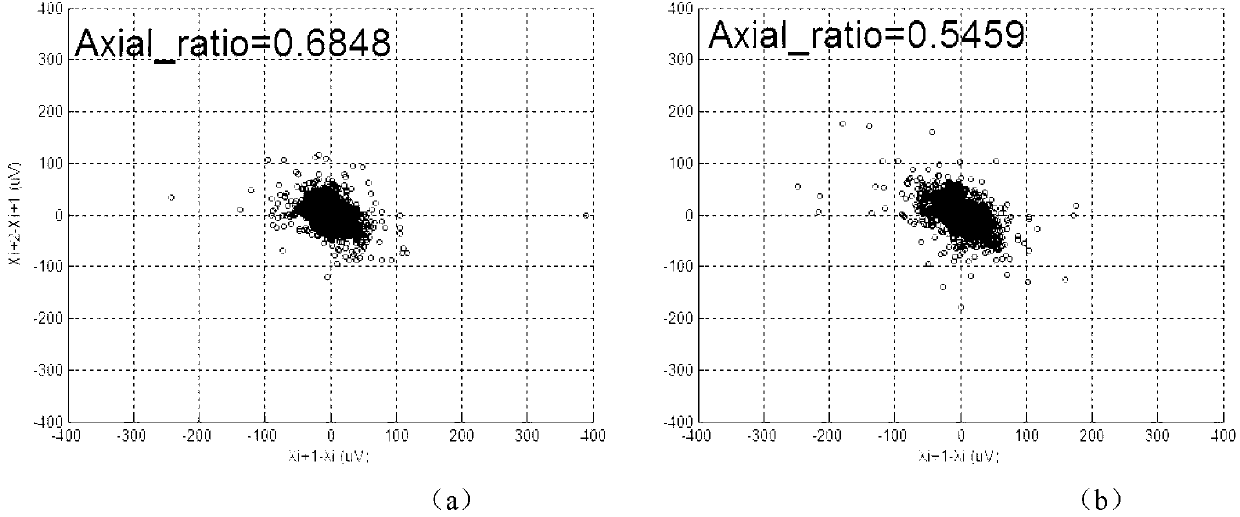
[0056] First, through a simple integer coefficient 50Hz notch filter, a zero-phase digital filter, combined with wavelet decomposition and reconstruction theory and an improved threshold algorithm to remove electrocardiographic noise such as power frequency and its harmonic interference, baseline drift, and myoelectric interference, a clean ECG signal; then use the second-order differential Marr wavelet with accurate positioning and easy calculation, apply the multi-hole algorithm to calibrate the QRS wave group in ECG, and then search for the maximum va...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com