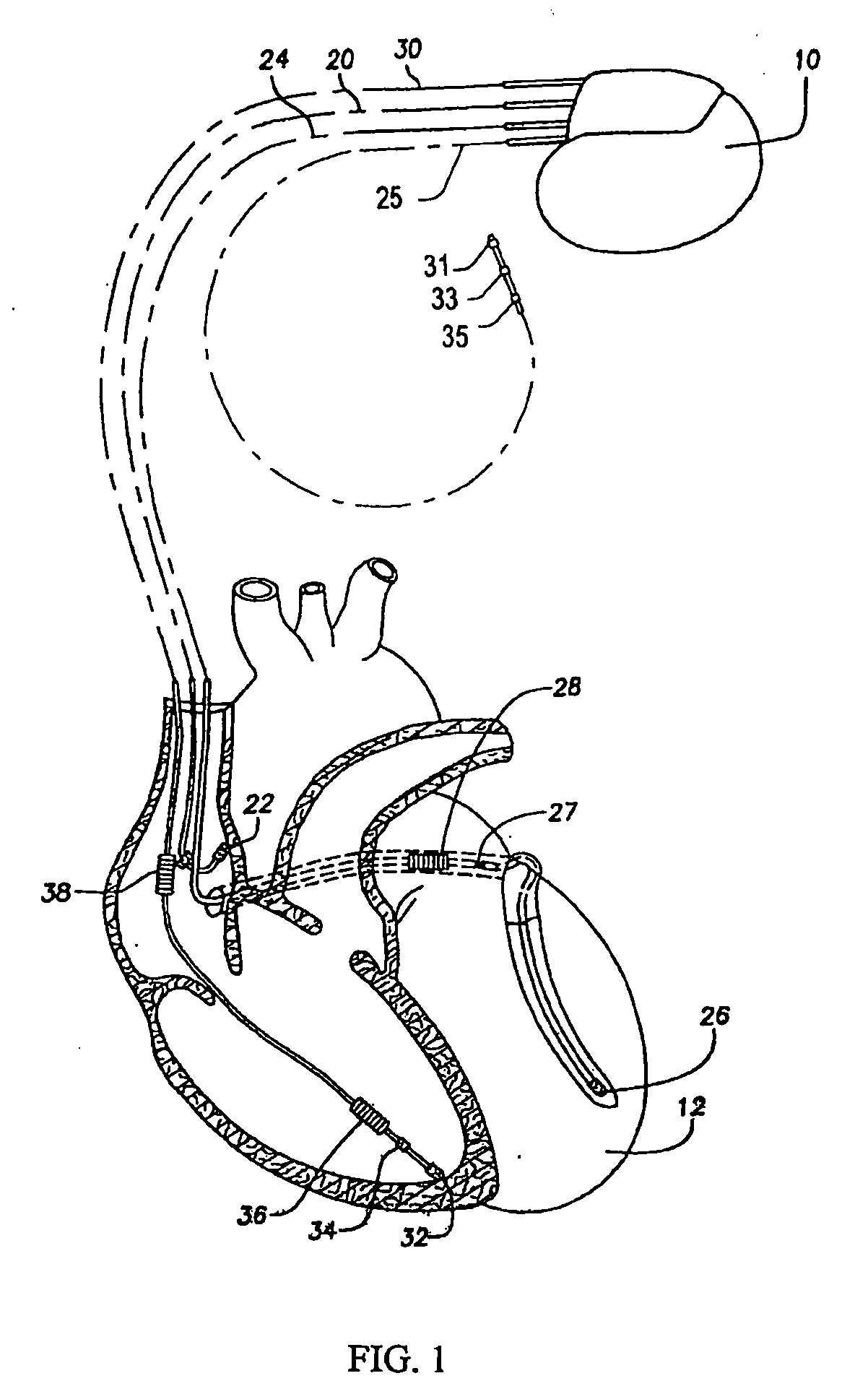
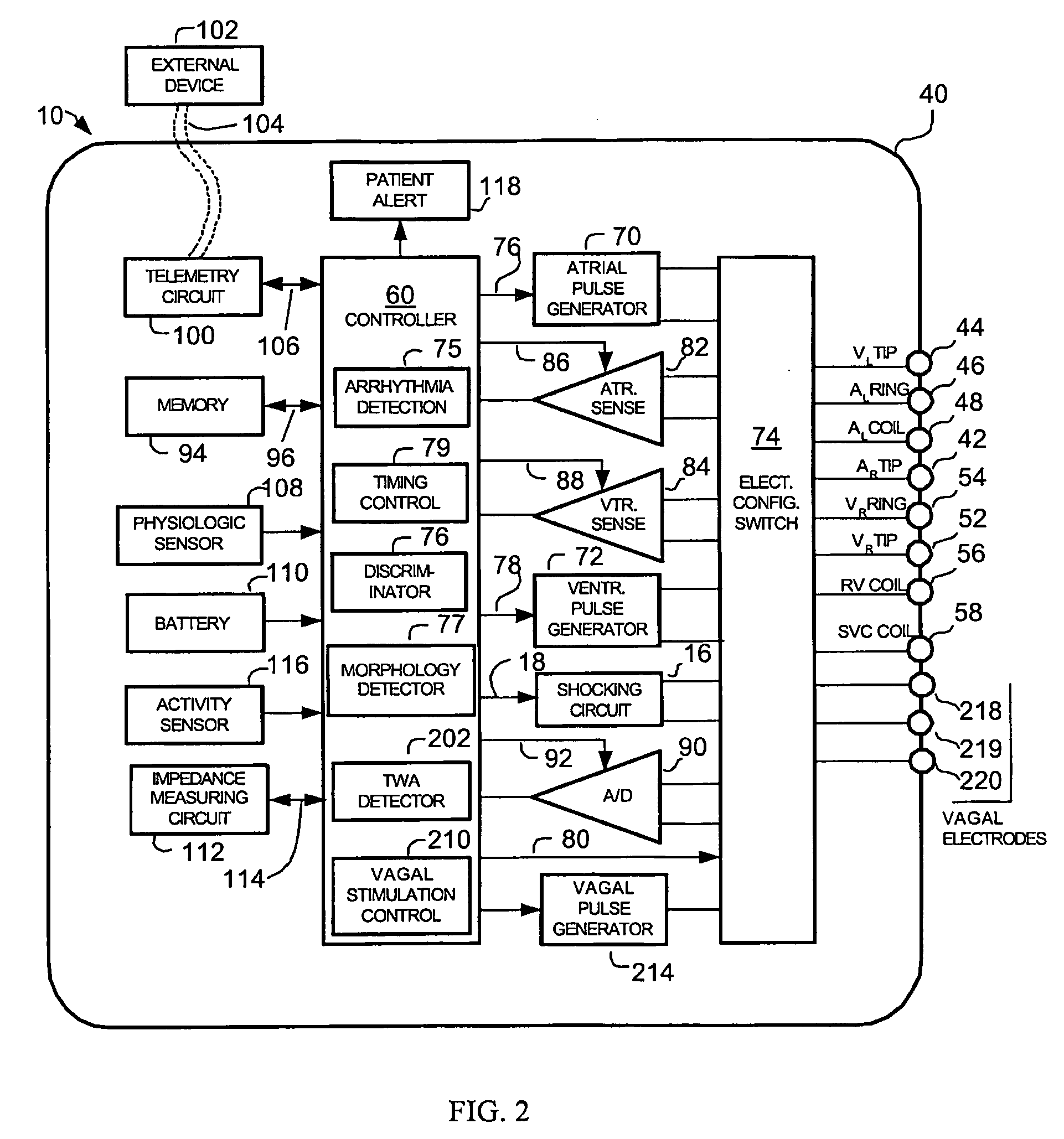
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Flattened T wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
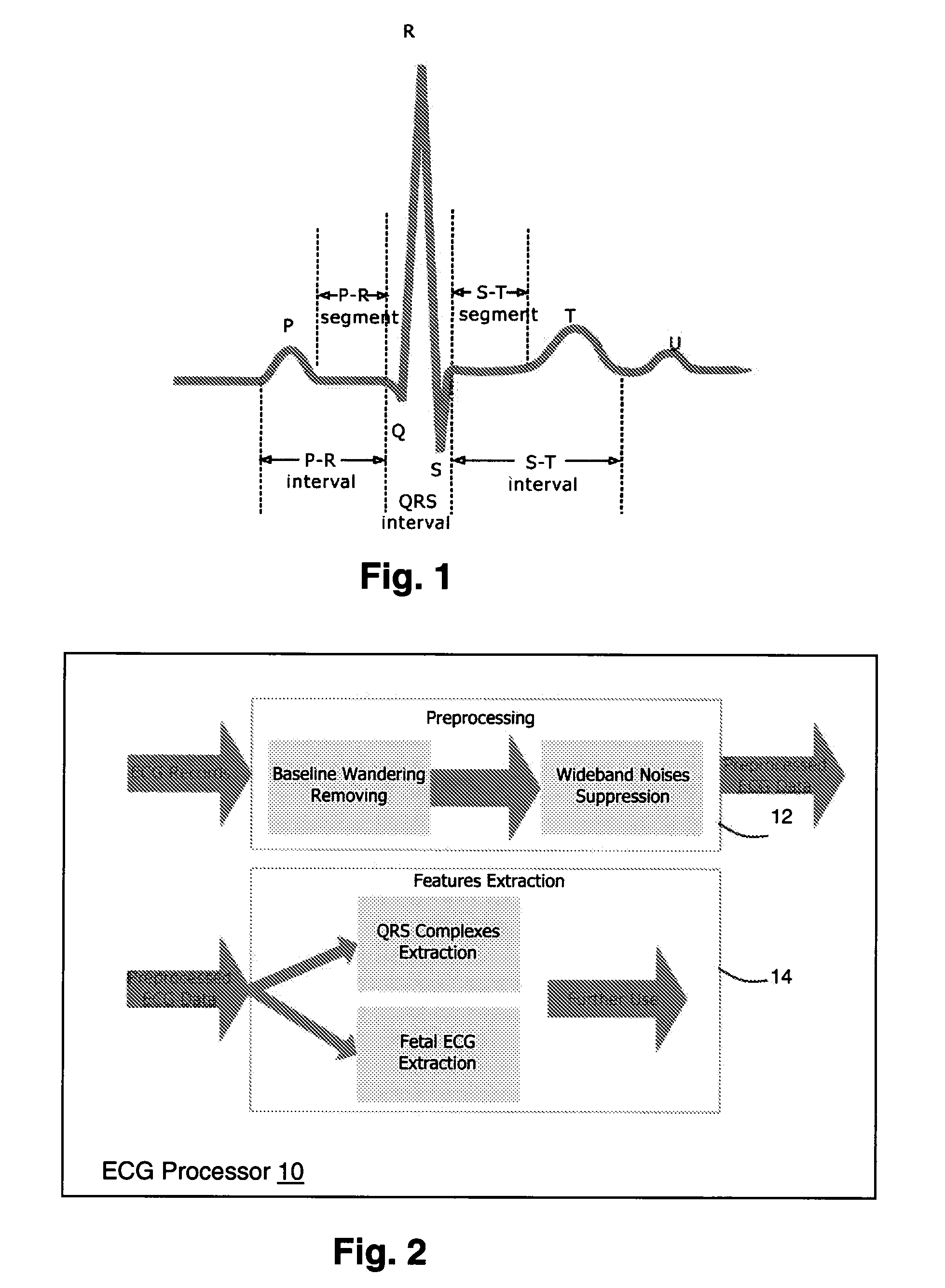
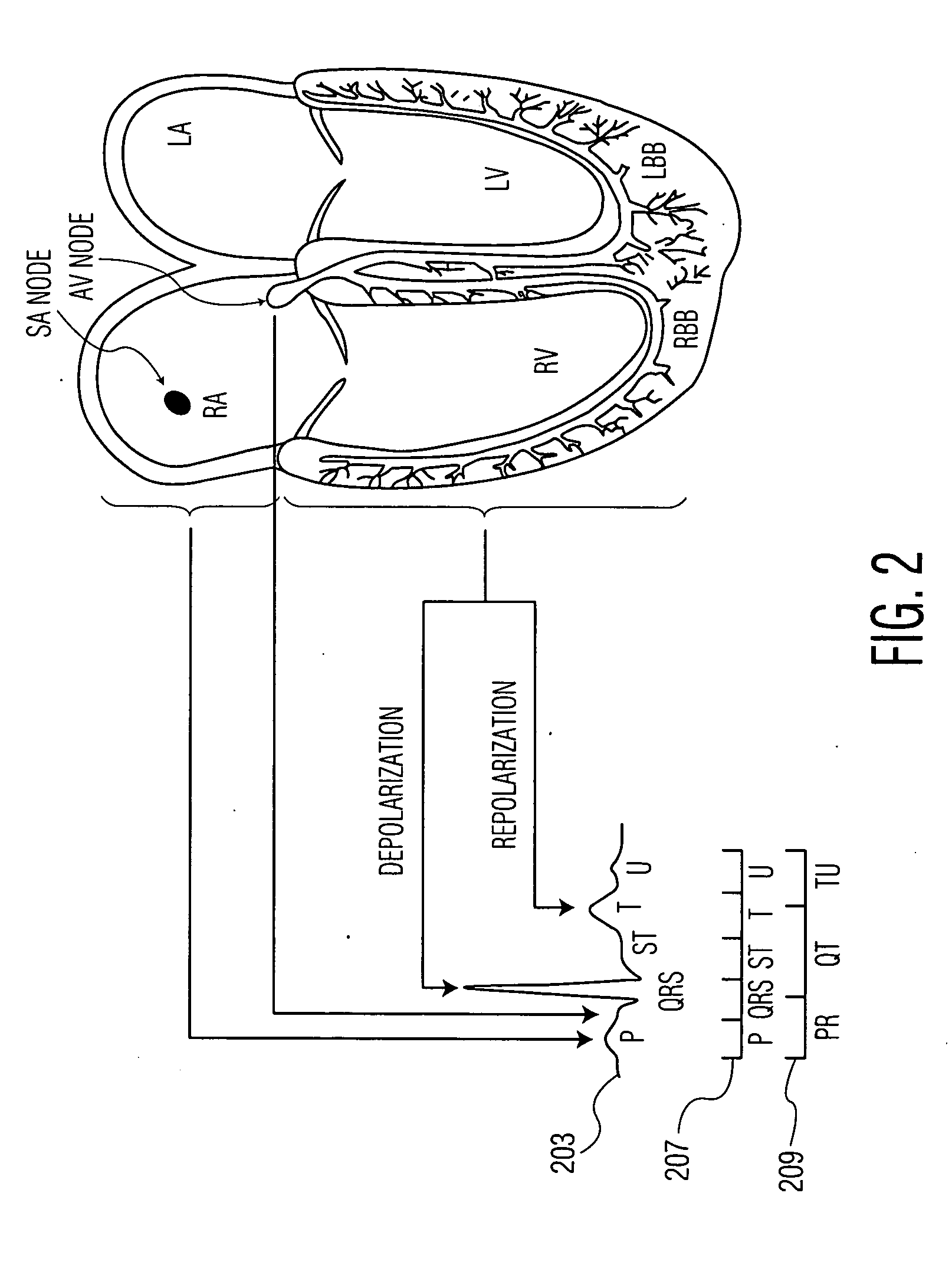
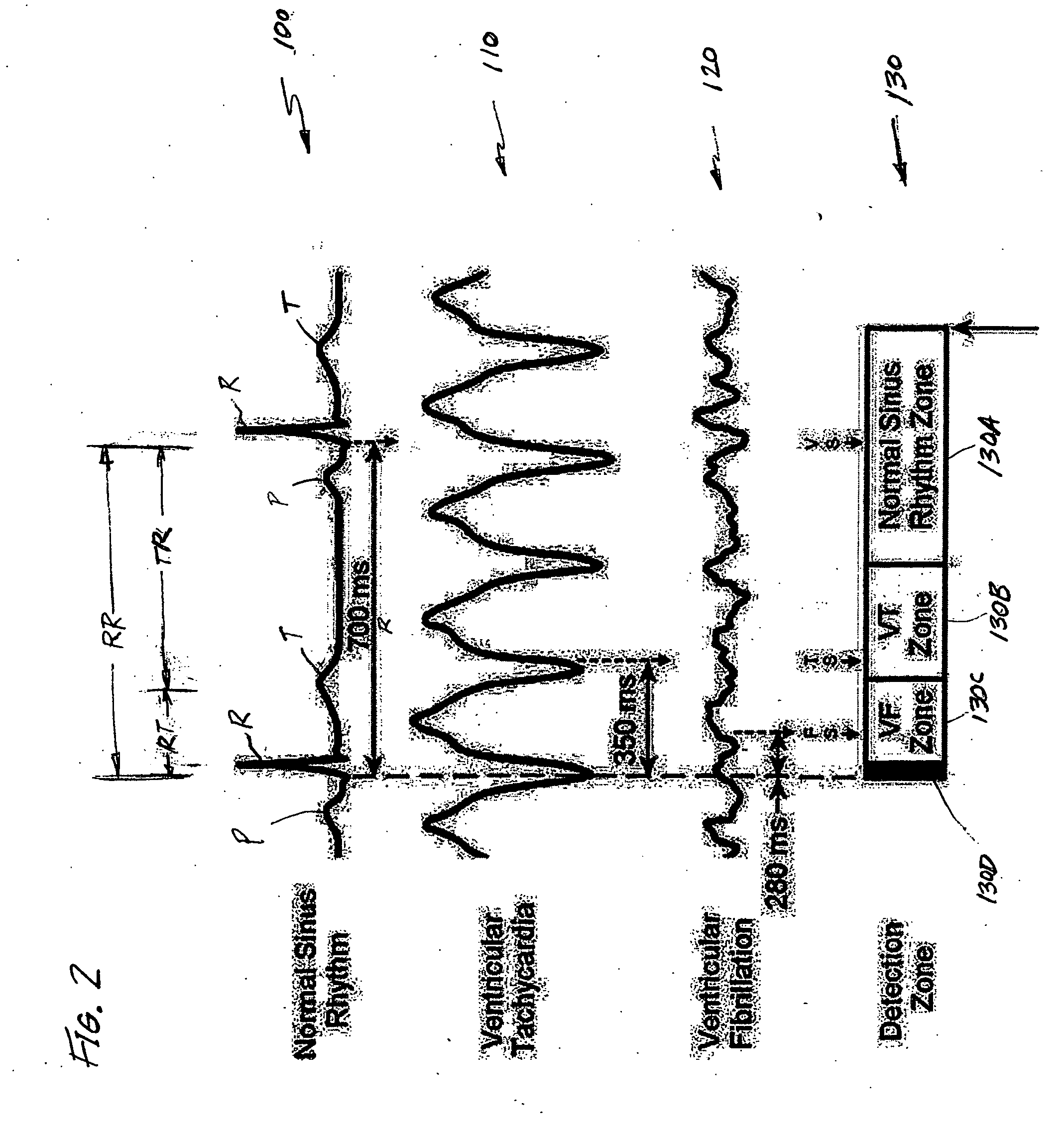
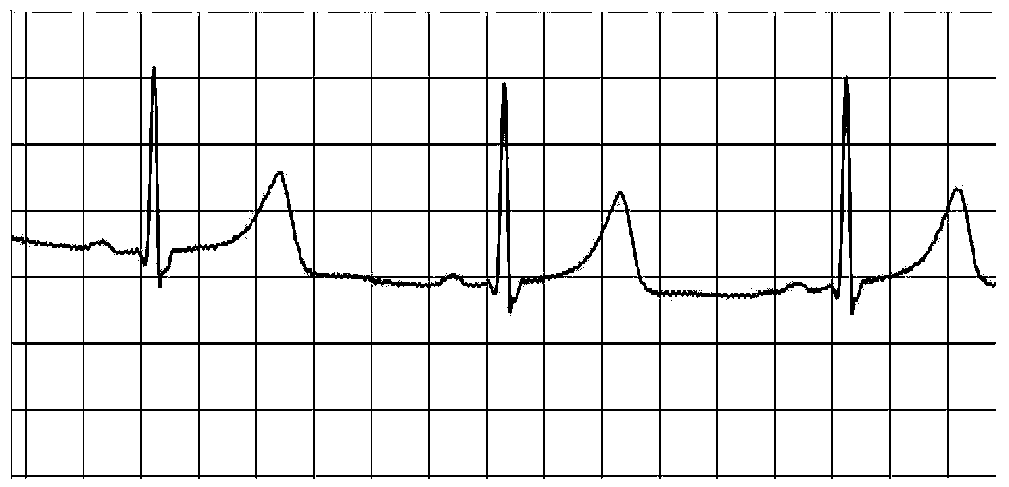
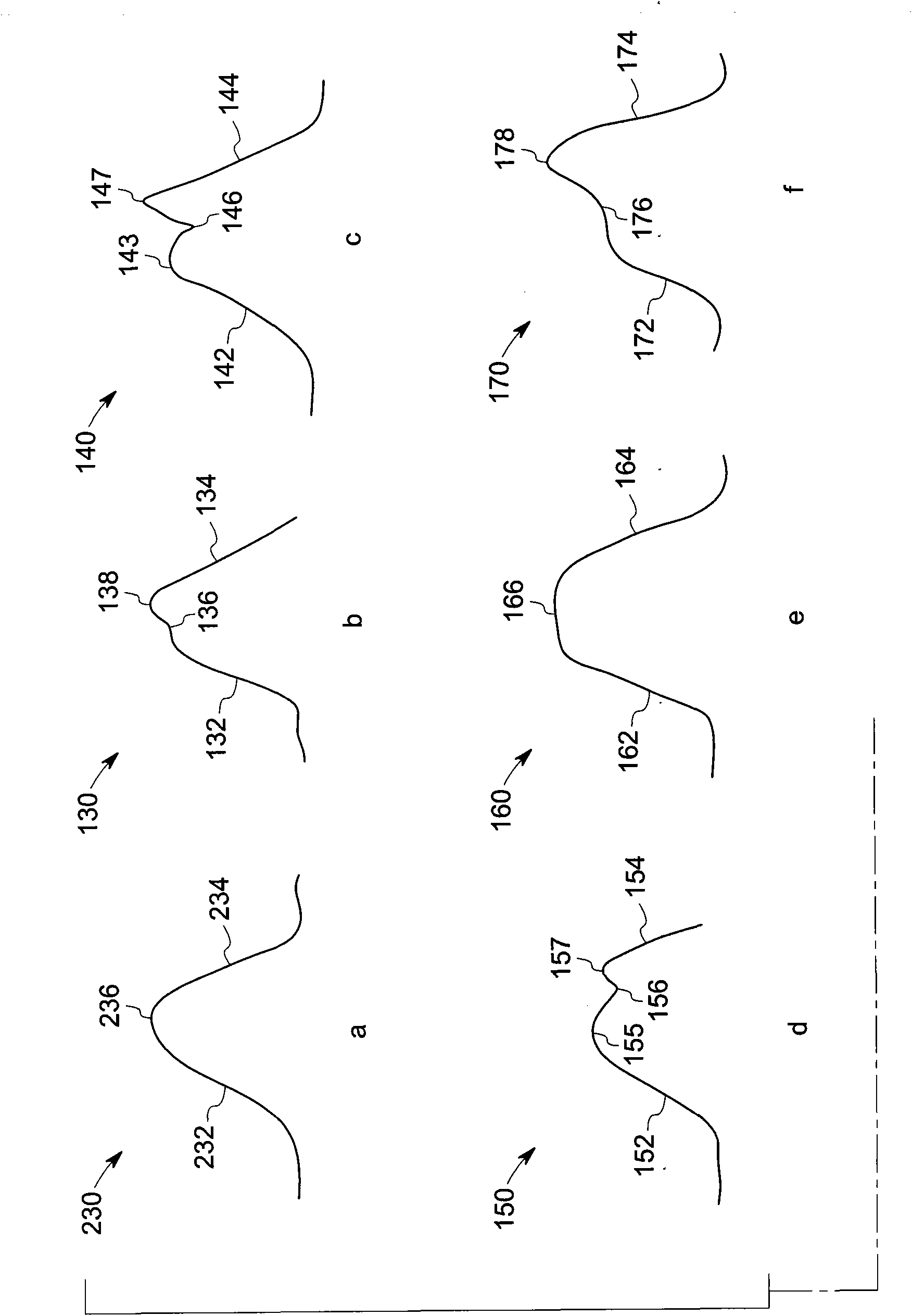
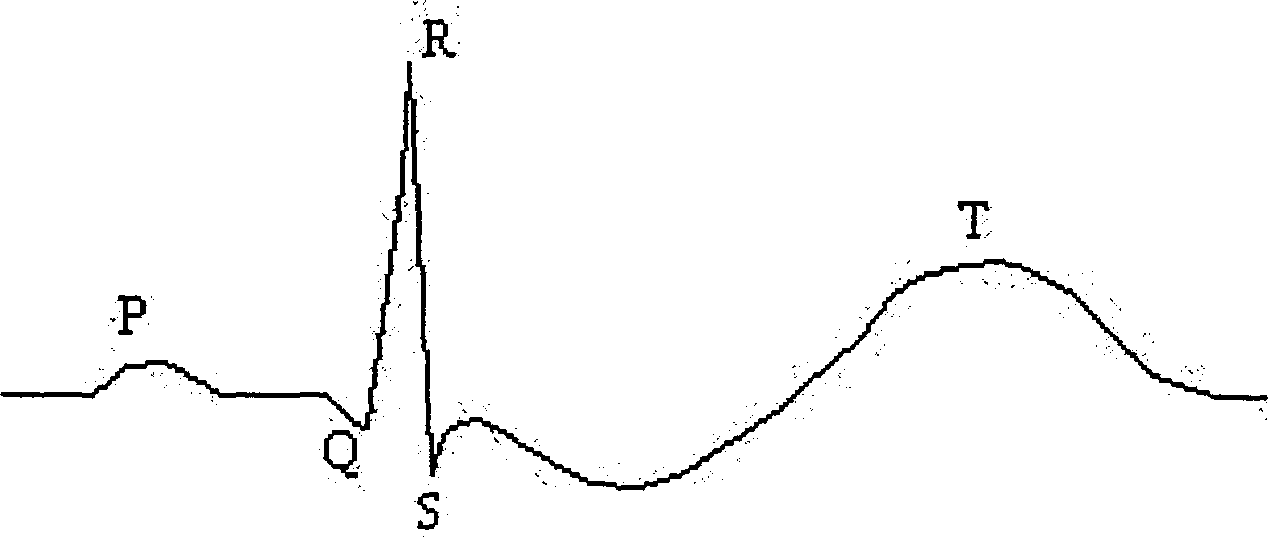
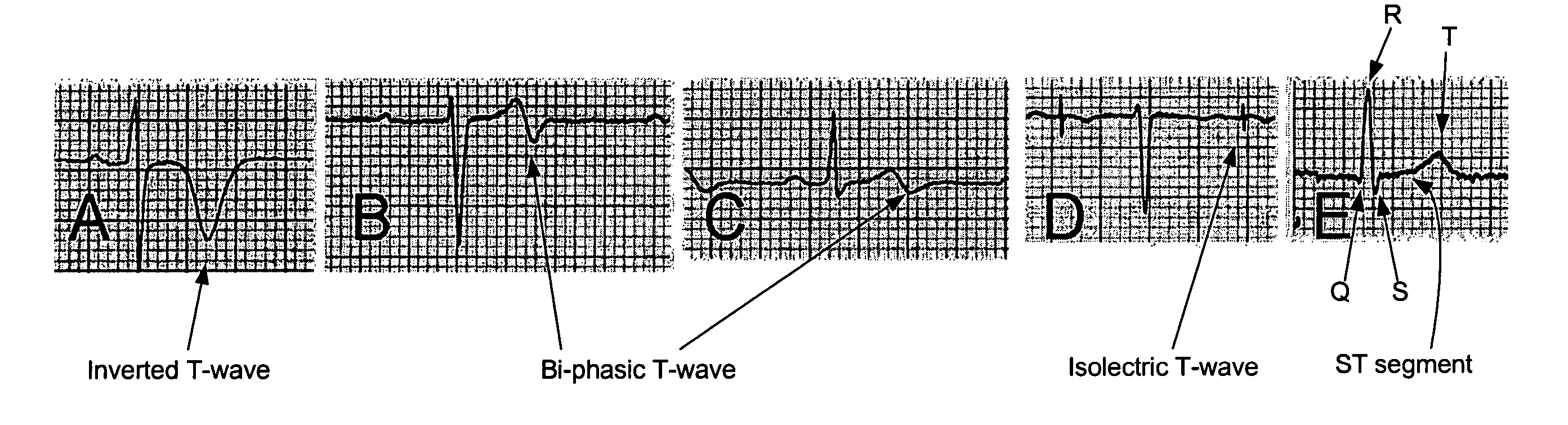
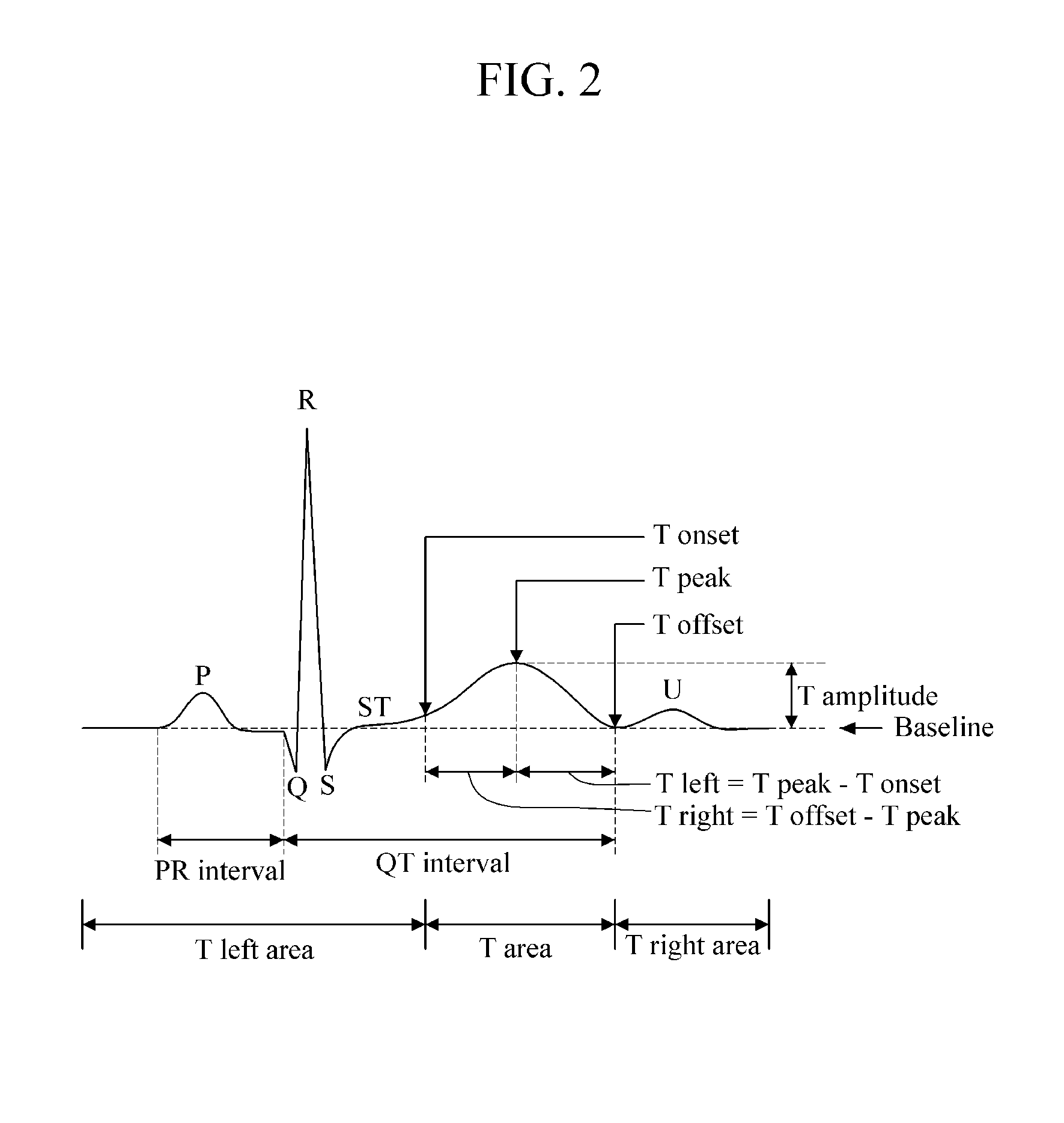
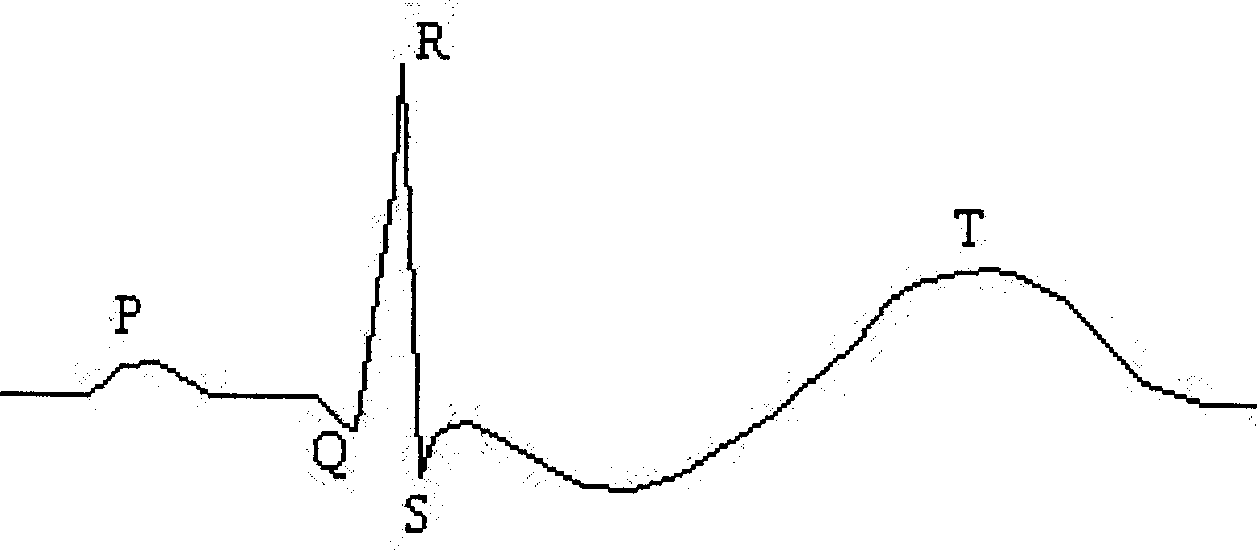
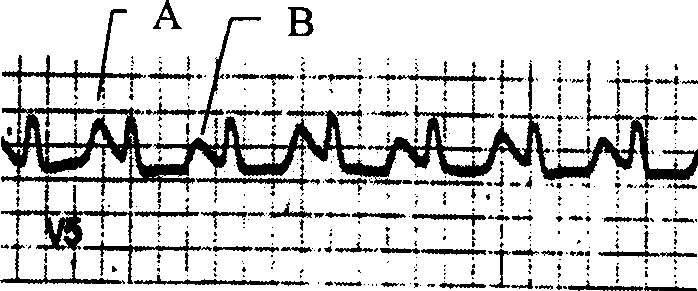
T wave is considered flat when the wave varies from -1.0 mm to + 1.0 mm in height. Hypokalemia or digitalis therapy can cause flattened T wave with a prominent U wave. As hypokalemia progressively worsens, T wave becomes more flatten while U wave becomes more prominent, with progressively deeper ST segment depression.
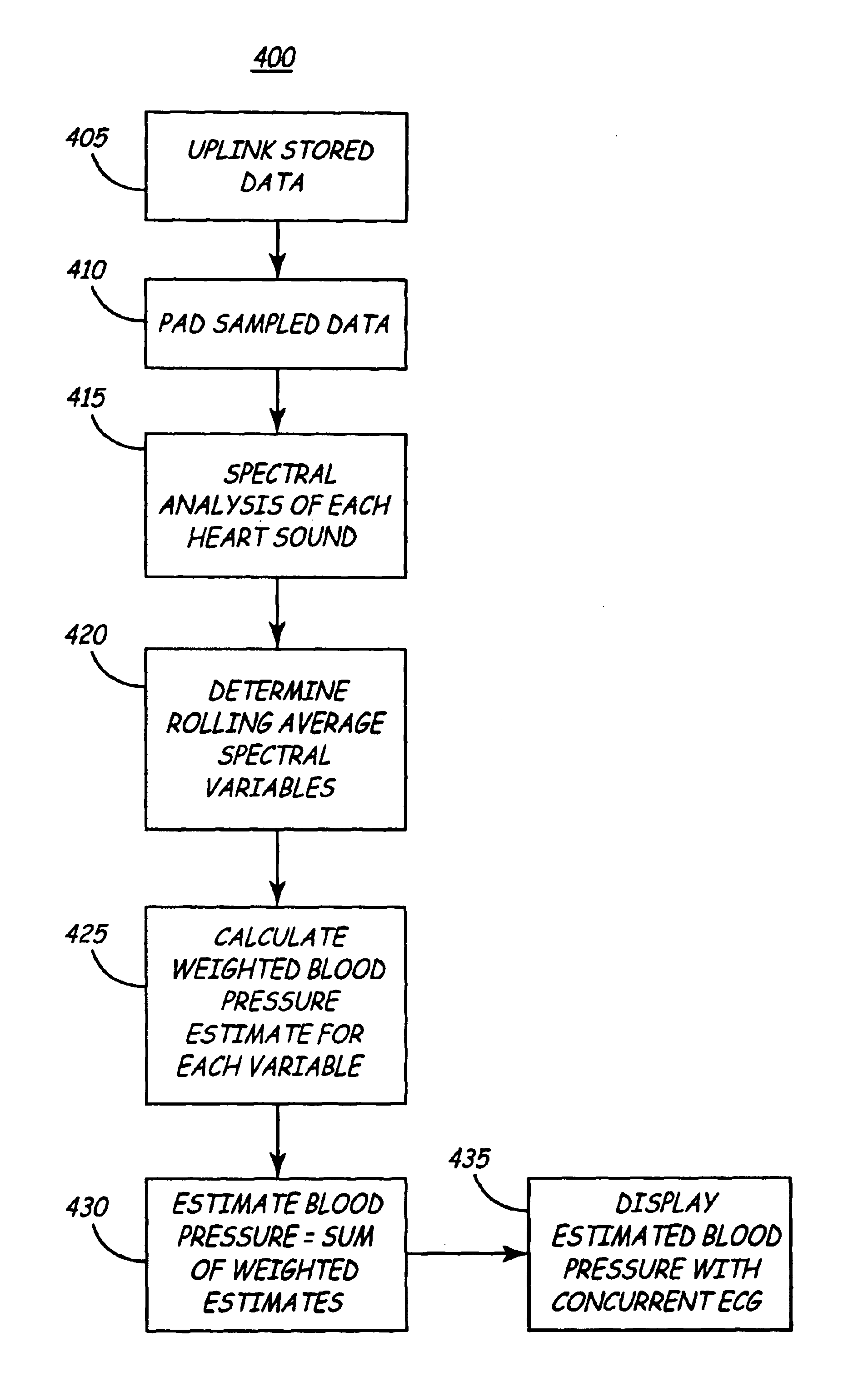
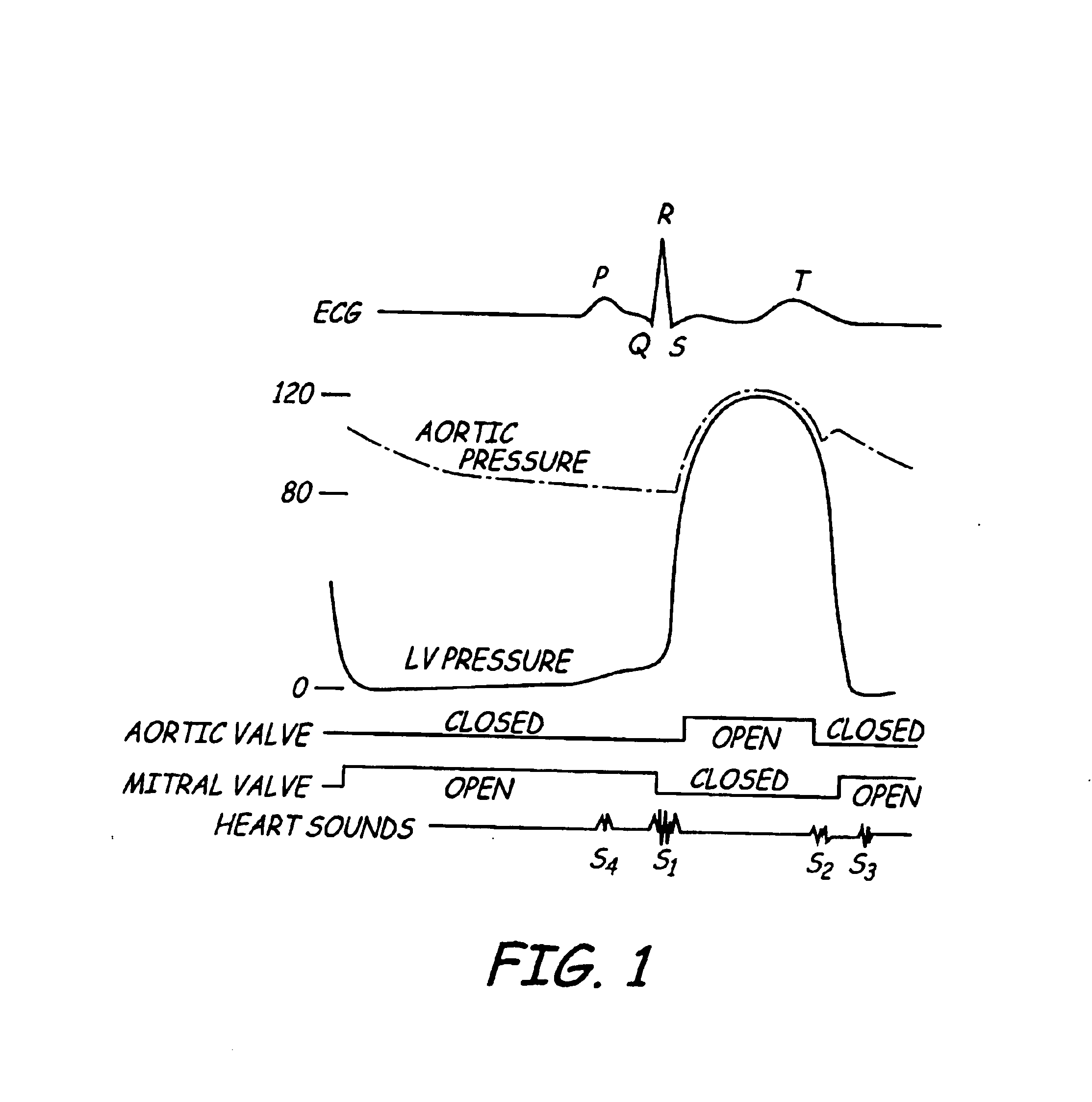
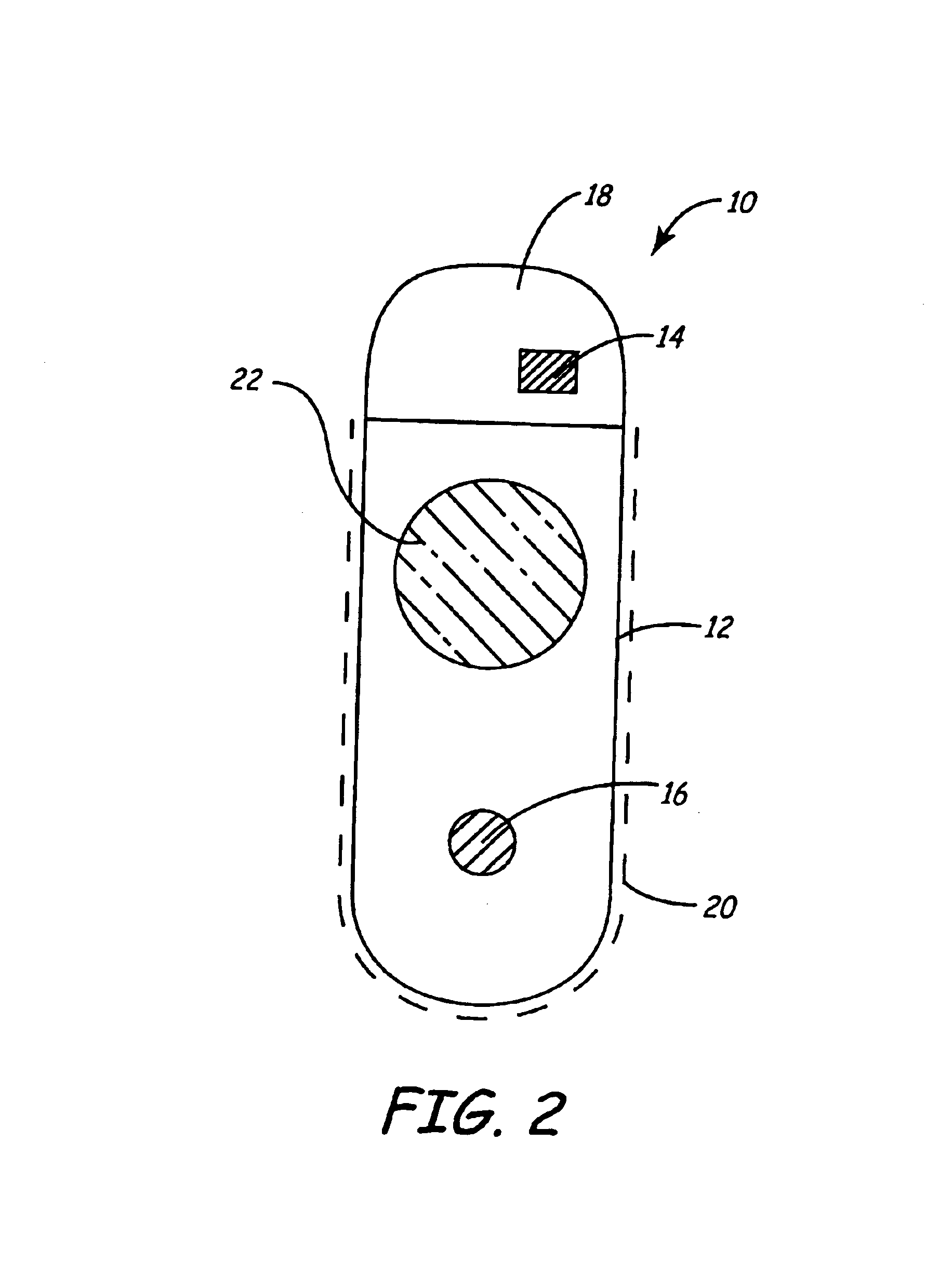
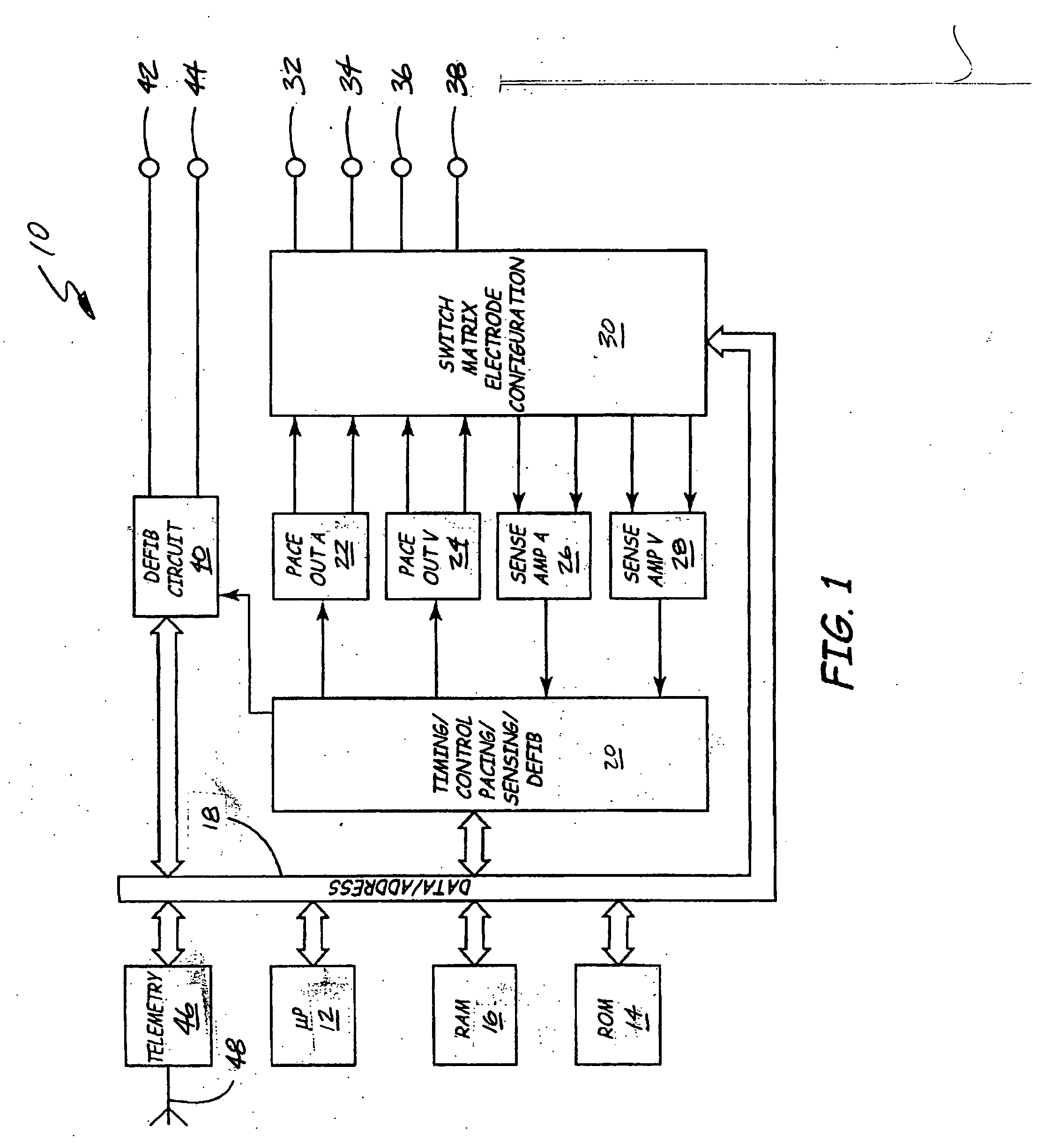
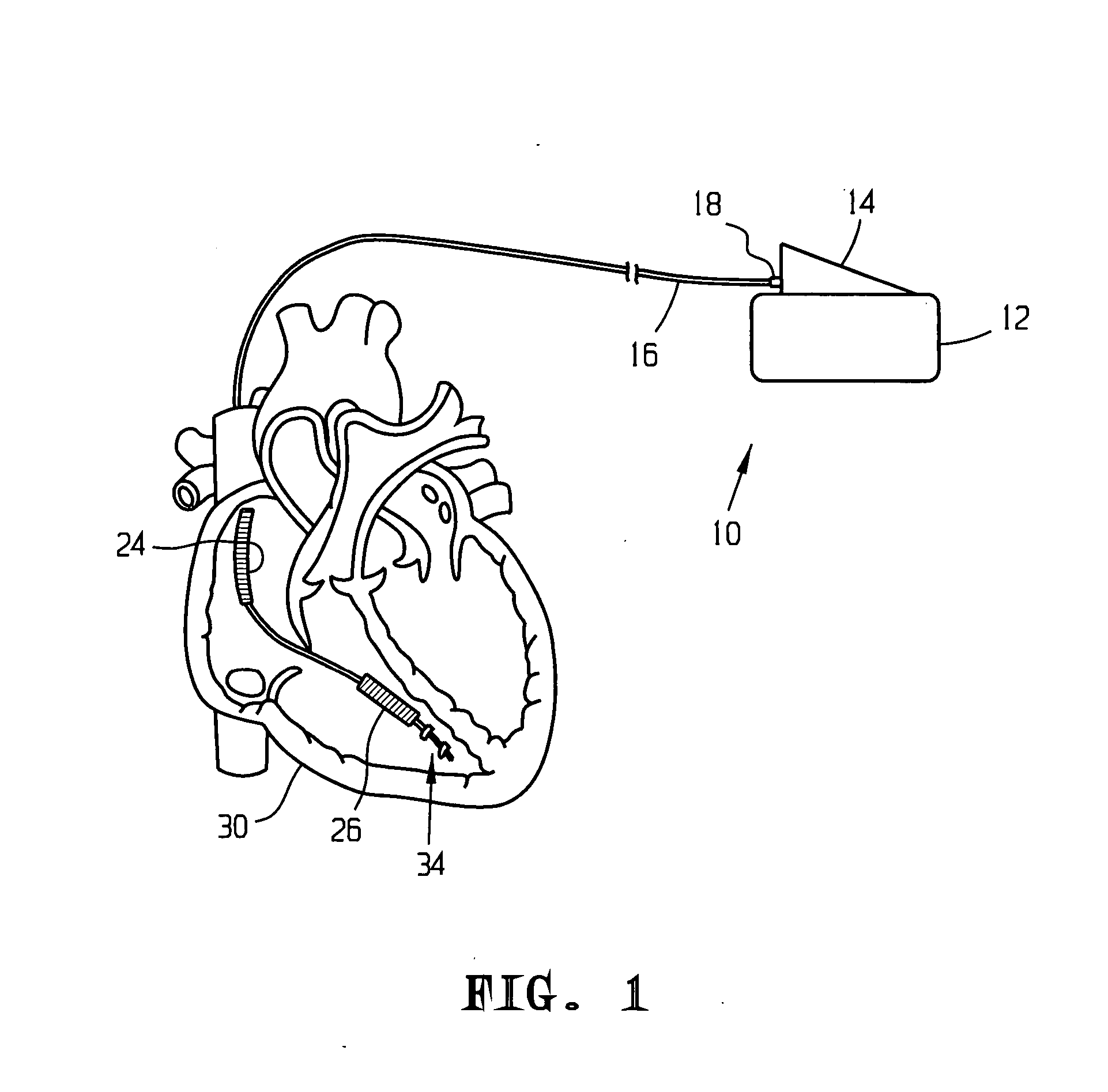
Apparatus and method for chronically monitoring heart sounds for deriving estimated blood pressure
ActiveUS6869404B2Simplified and minimized in sizeElectrocardiographyAuscultation instrumentsRegression analysisT wave
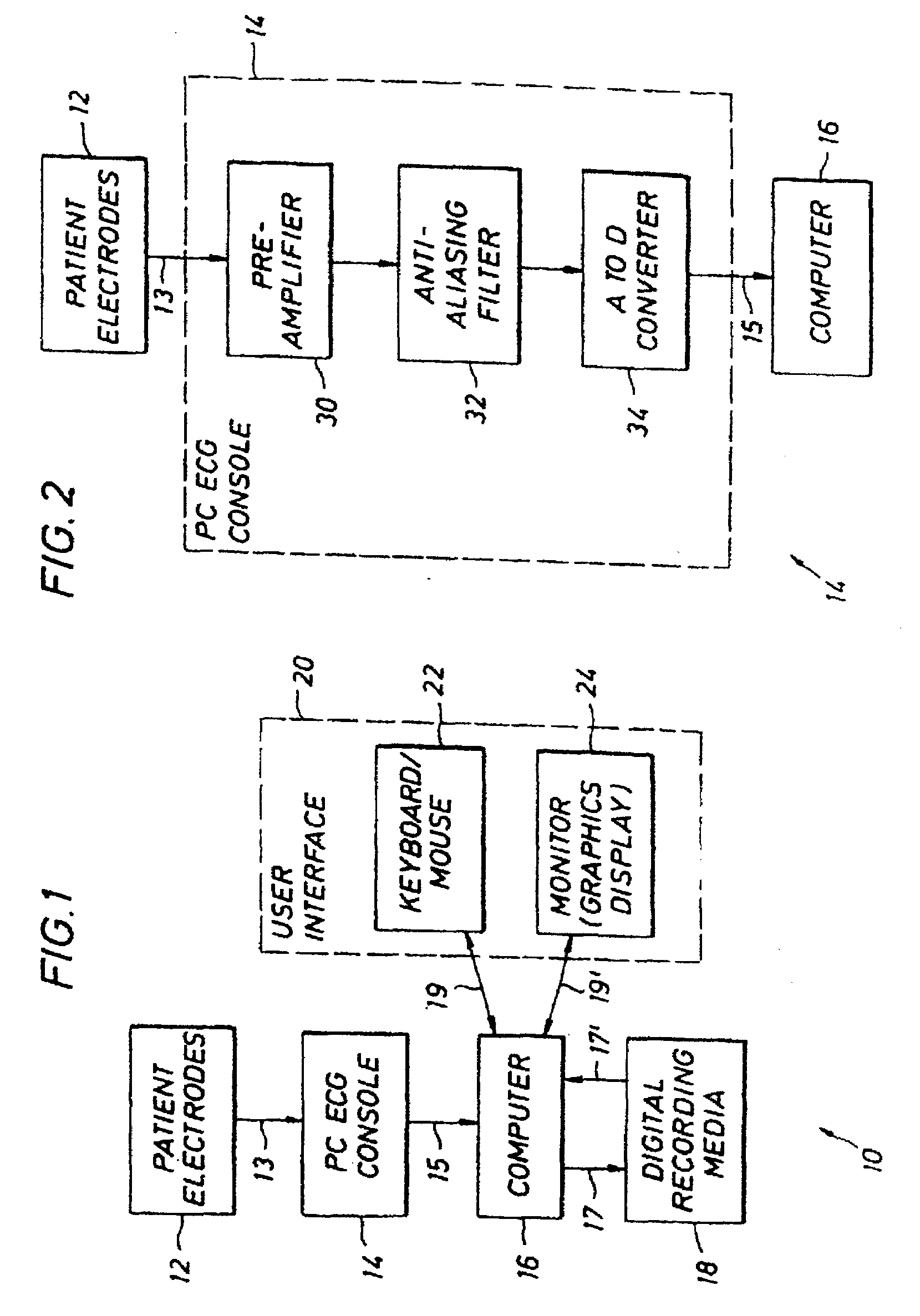
A minimally invasive, implantable heart sound and ECG monitor and associated method for deriving blood pressure from heart sound data. The device is equipped with an acoustical sensor for detecting first and second heart sounds which are sampled and stored during sensing windows following R-wave and T-wave detections, respectively. ECG and heart sound data are stored in a continuous, looping memory, and segments of data are stored in long-term memory upon an automatic or manual data storage triggering event. Estimated blood pressure is calculated based on custom spectral analysis and processing of the first and second heart sounds. A calibration method includes measuring a patient's blood pressure using a standard clinical method and performing regression analysis on multiple spectral variables to identify a set of best fit weighted equations for predicting blood pressure. Concurrent ECG and estimated blood pressure may be displayed for review by a physician.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
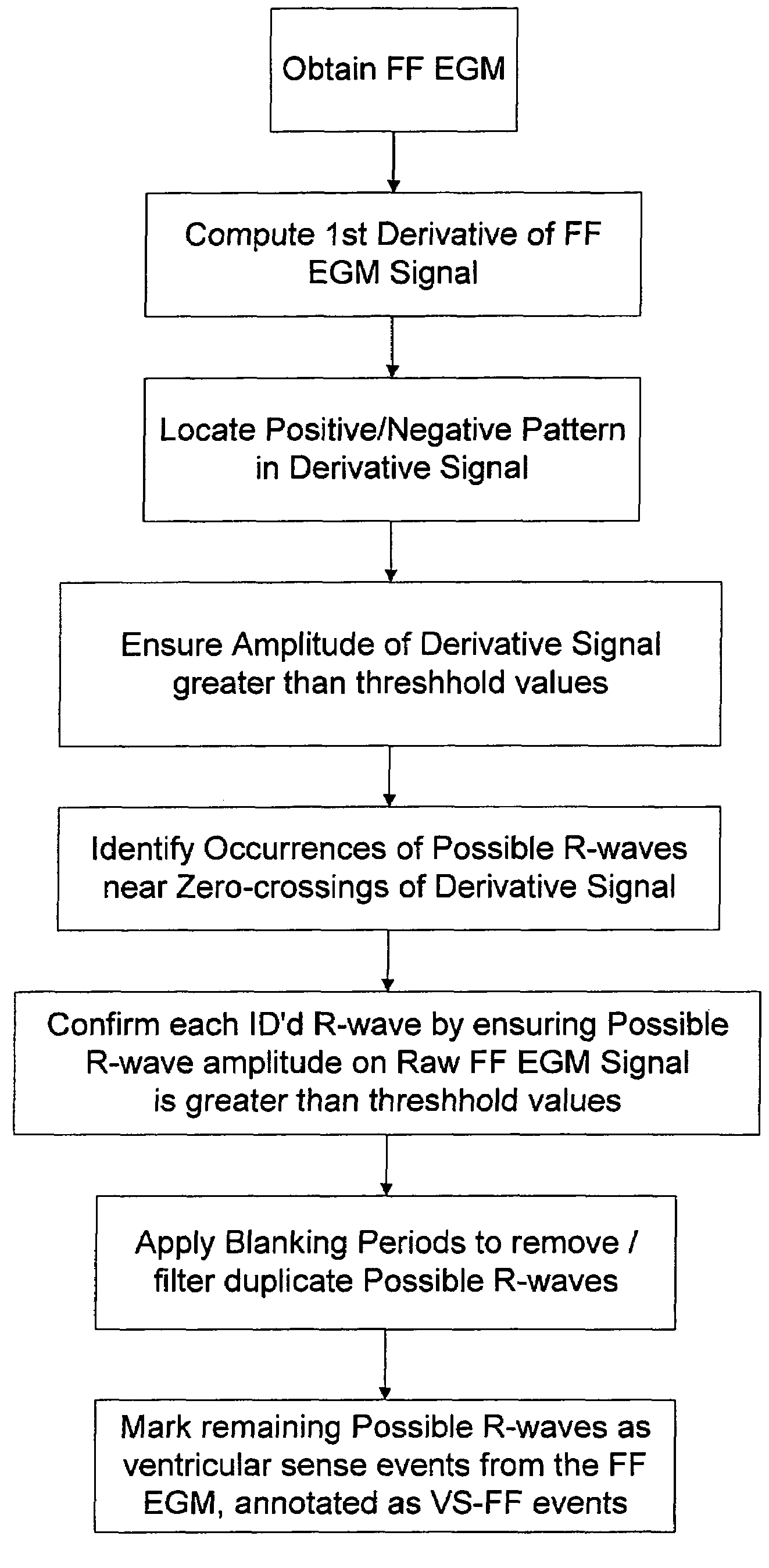
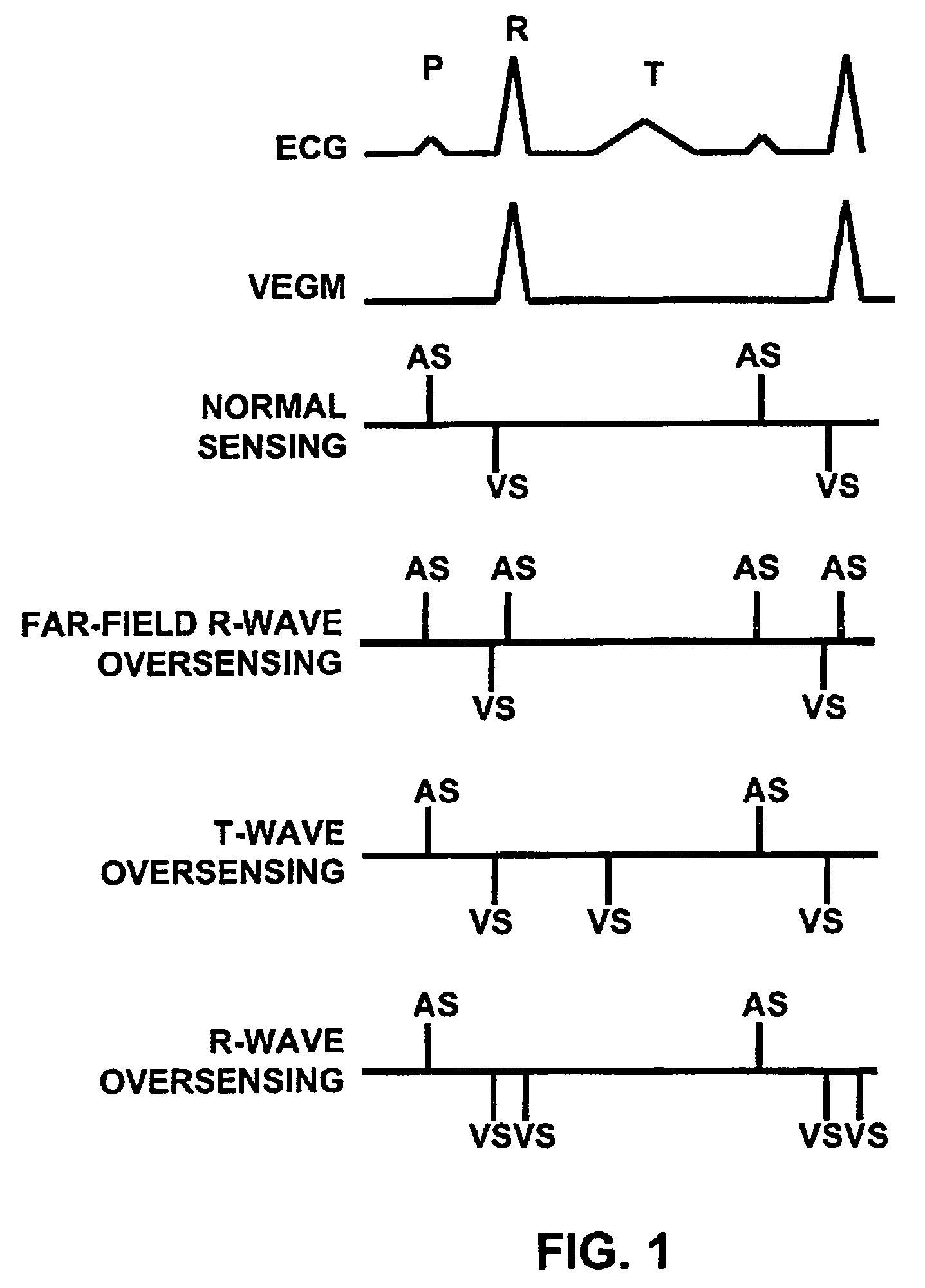
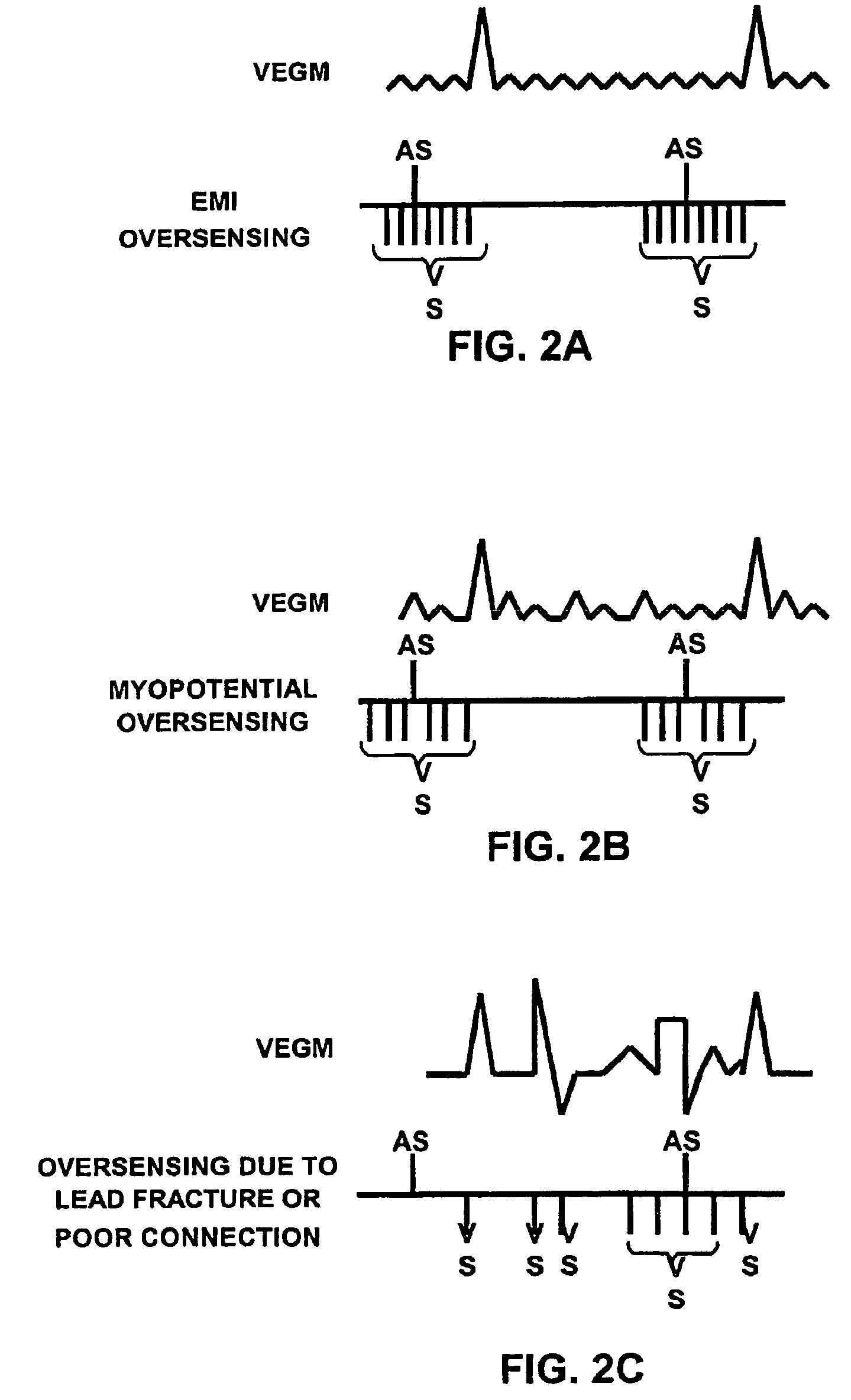
Method and apparatus for identifying oversensing using far-field intracardiac electrograms and marker channels
A method for identifying and classifying various types of oversensing in implantable medical devices (IMDs), such as implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), to assist a physician in choosing corrective action to reduce the likelihood of oversensing and inappropriate therapy delivery. Far-field electrogram (EGM) signals are analyzed to detect the occurrence of R-waves, and the result is compared to the number and pattern of R-waves sensed by the IMD and indicated on the marker channel. A marker channel with more sensed R-waves than indicated by analysis of the far-field EGM indicates the presence of oversensing, including double-counting of R-waves, T-wave oversensing, lead malfunction or failure, poor lead connections, noise associated with electromagnetic interference, non-cardiac myopotentials, etc. Identification of the type of oversensing may be determined by analysis of the number and pattern of marker channel sensed R-waves with respect to the timing of the R-waves detected from the far-field EGM.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and methods for detecting ischemia with a limited extracardiac lead set
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions from a reduced number of extracardiac leads. A right side lead measures the electrical signal between the middle superior chest region over the heart and inferior right torso position. A left side lead measures the electrical signal between the left precordial chest region and an inferior left lateral or posterior torso position. The lead montage is preferably chosen so that, regardless of patient position (e.g. supine, upright), negative ST segments and / or T waves are used to detect right coronary or left circumflex ischemia. Also, in these positions, reduced slope of the final deflection in the QRS can be used to detect these types of ischemia. To detect transmural ischemia, the system examines changes in QRS slopes, ST segment, T wave and the difference between the J point and the PQ potentials. In addition, for transmural ischemia associated with the left anterior descending artery, a proxy for the propagation time across the front of the heart is examined by comparing QRS features of the right side lead with QRS features of the left side lead. Histogram profiles, trends, and statistical summaries, especially running averages, of all of the above mentioned features, corrected for heart rate, are maintained.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
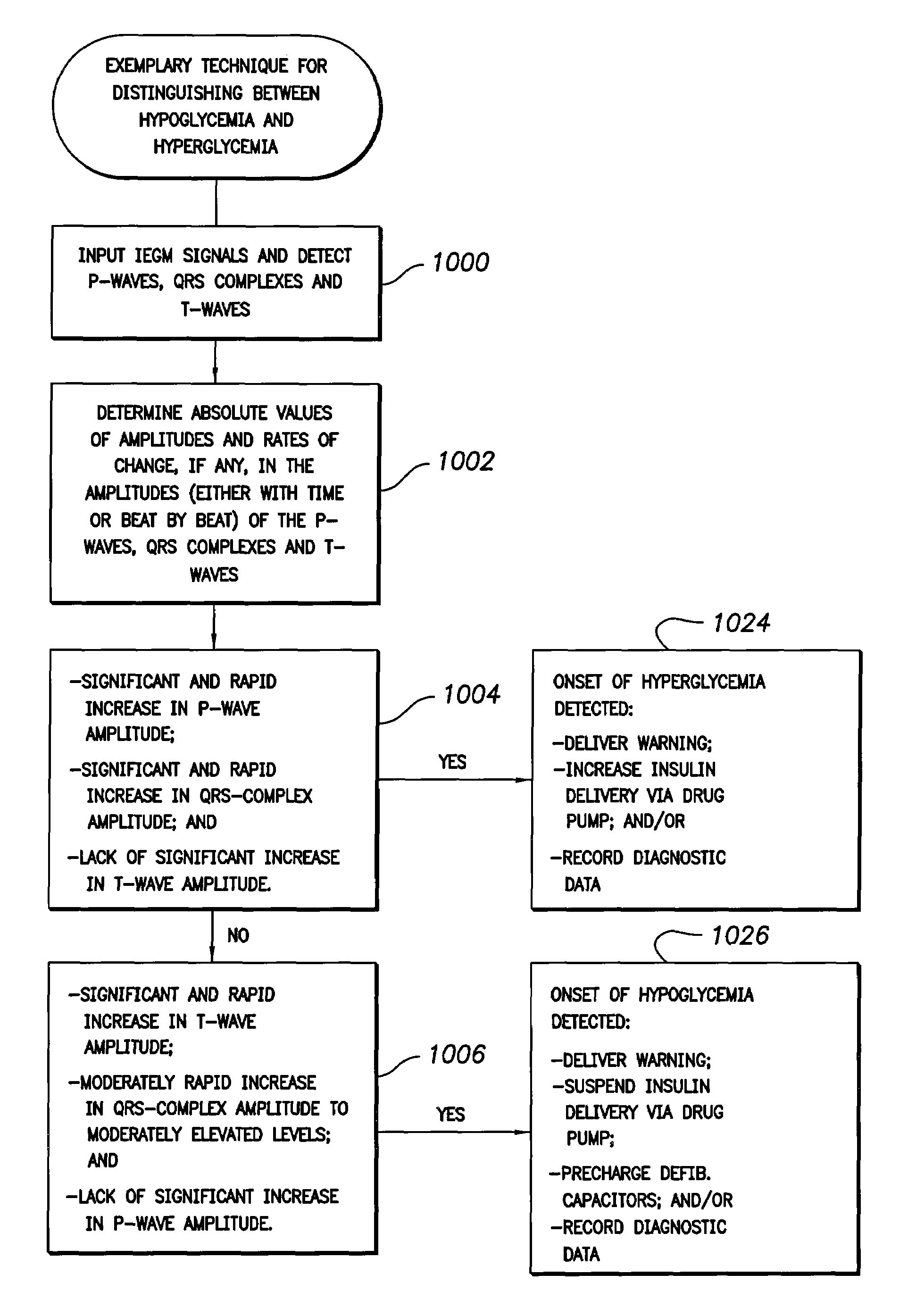
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7524287B2Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
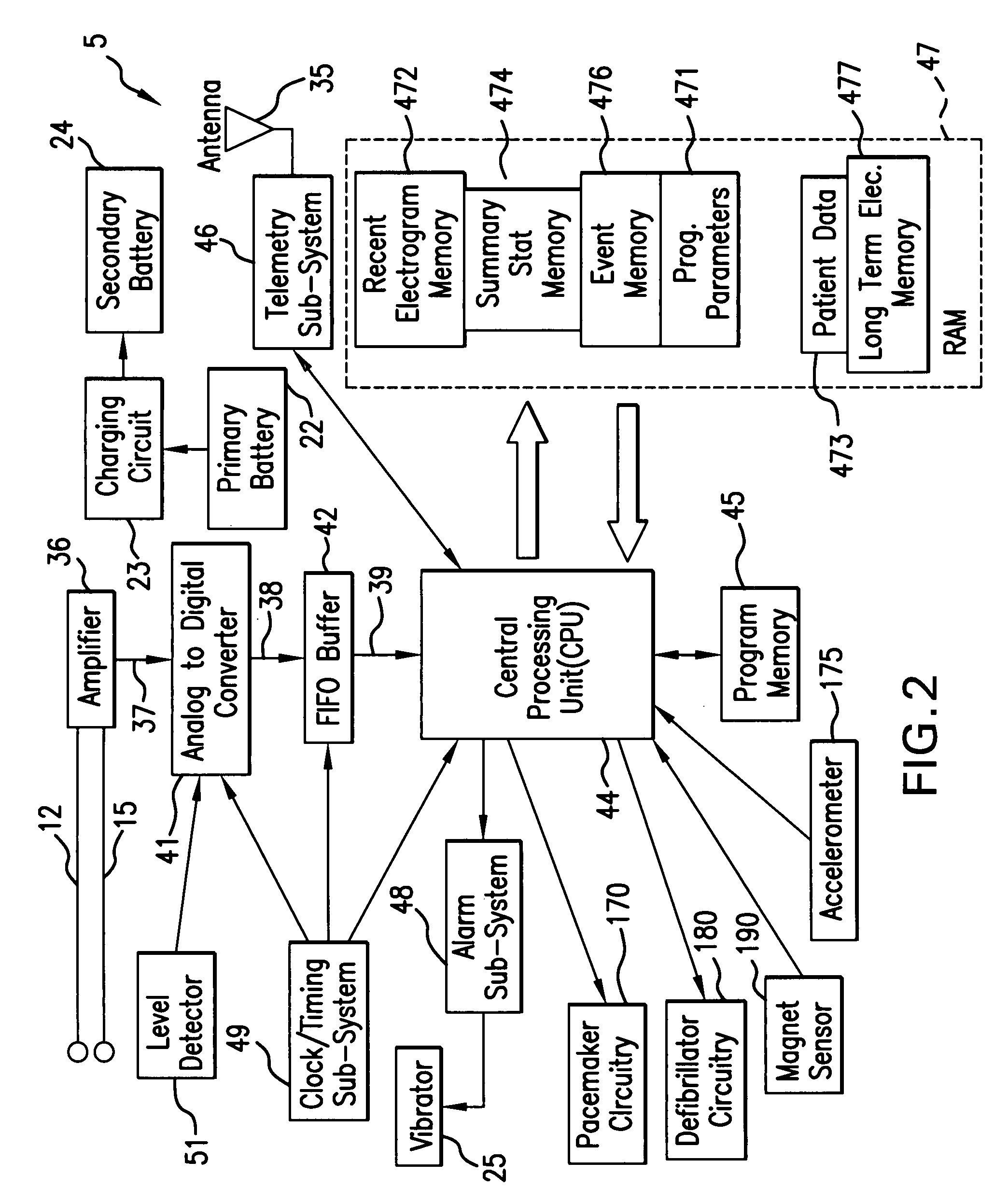
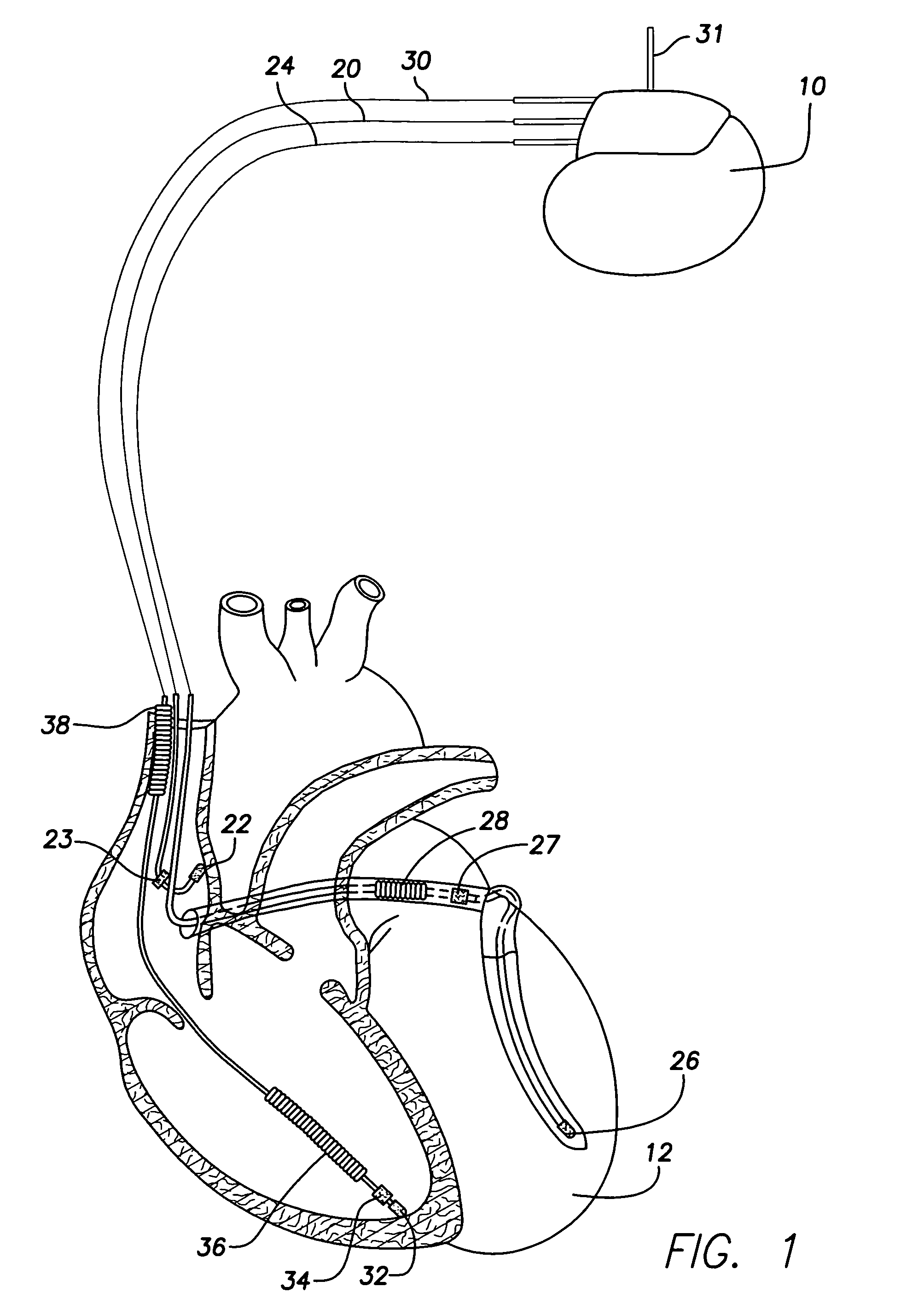
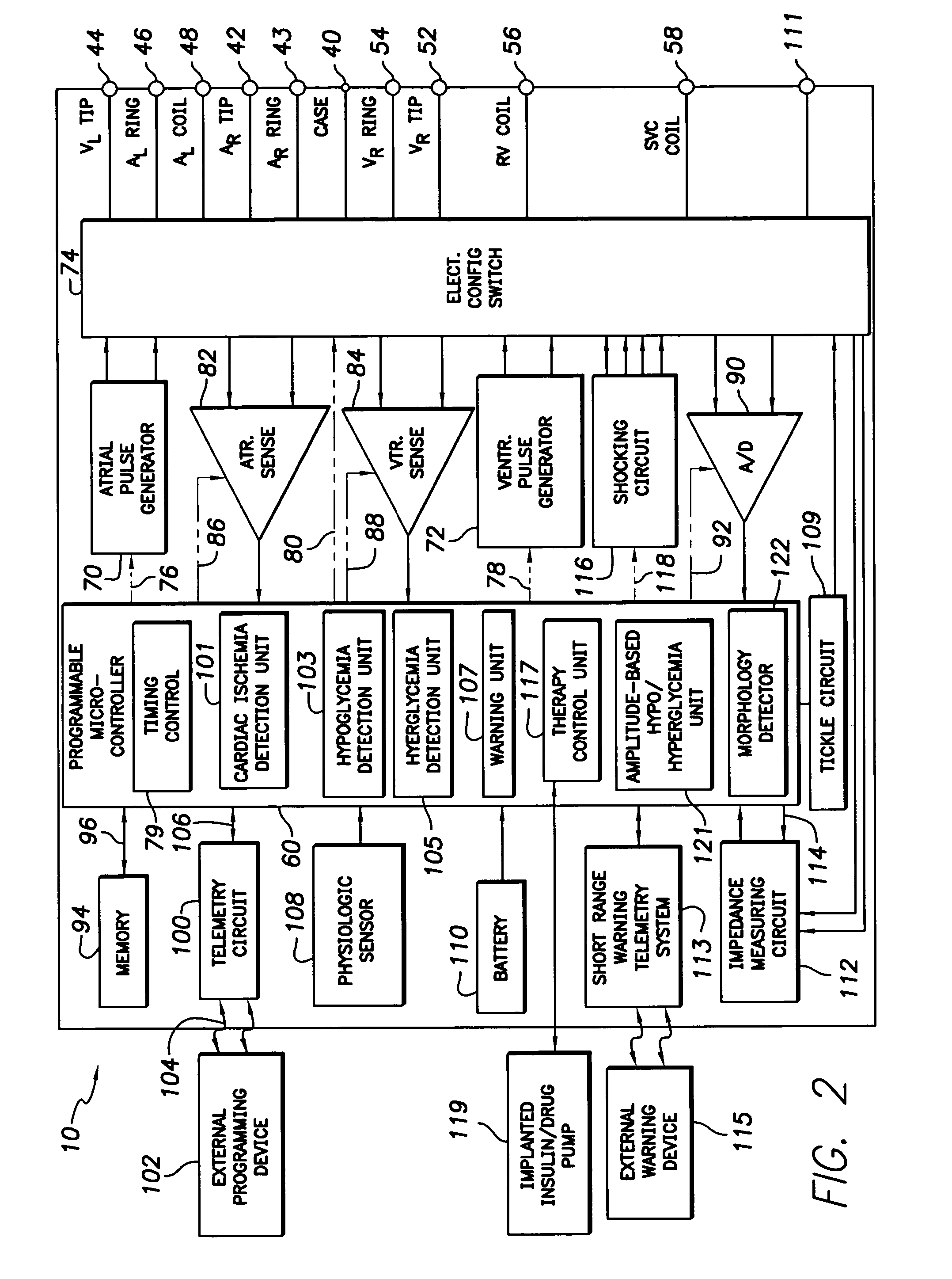
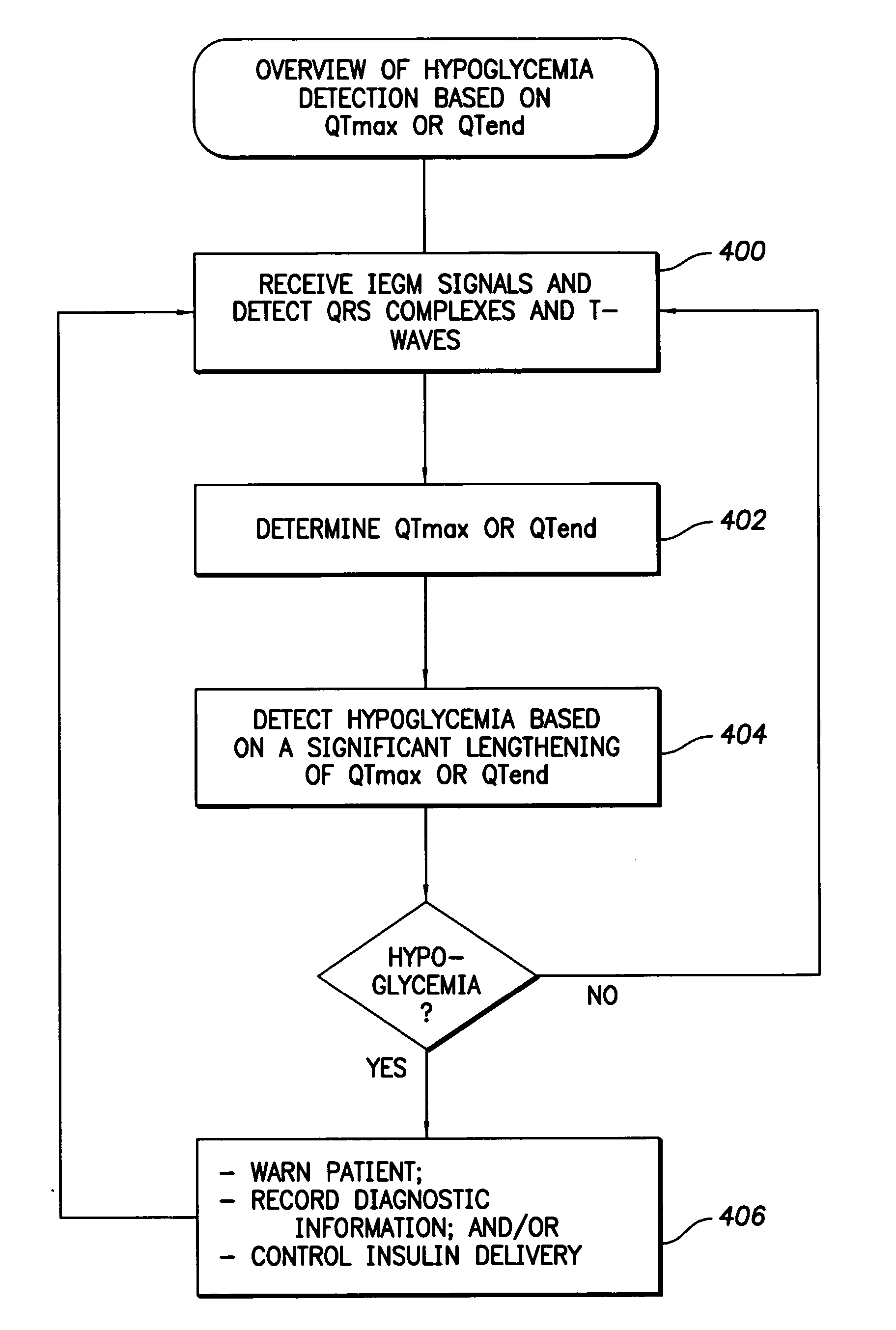
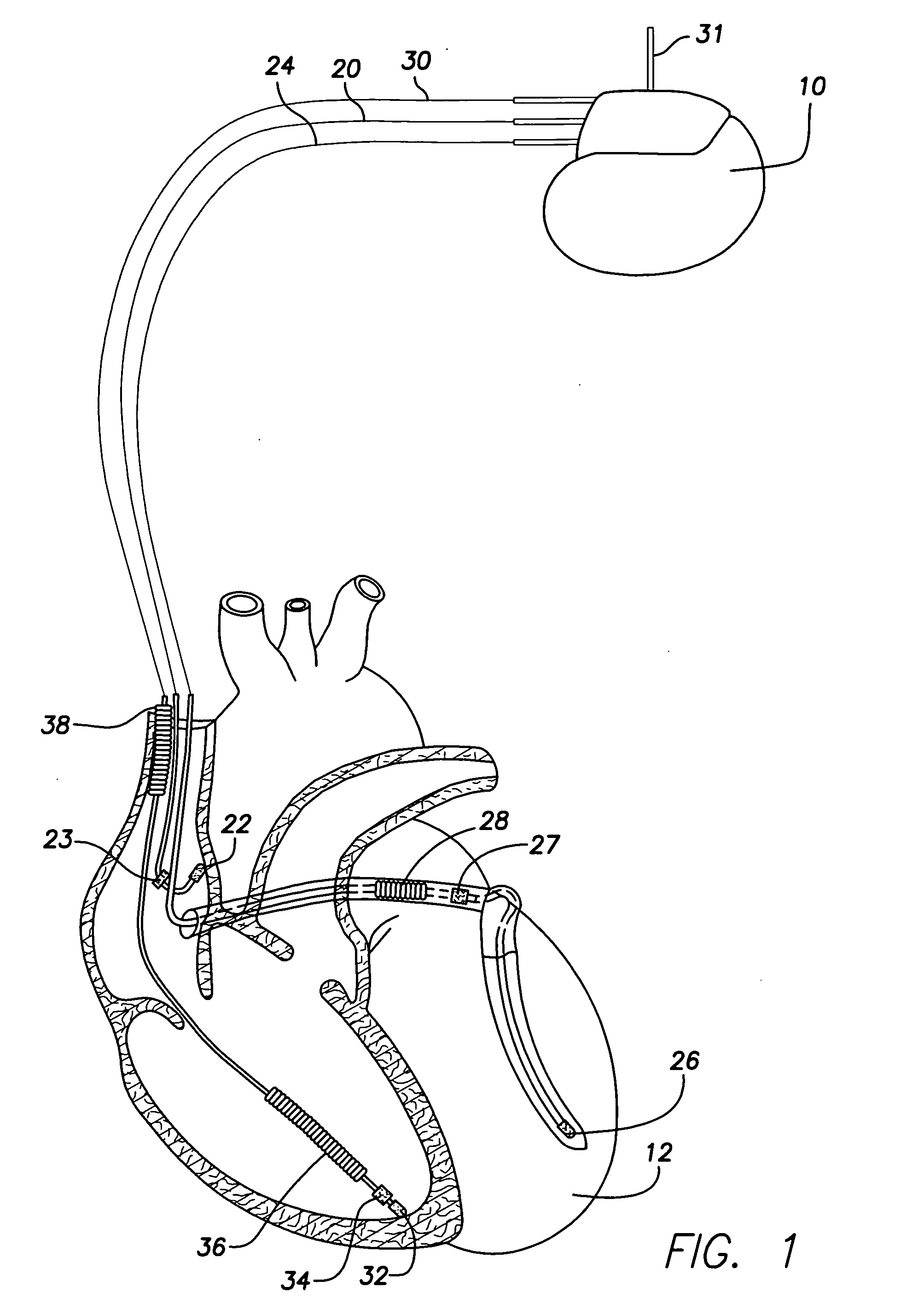
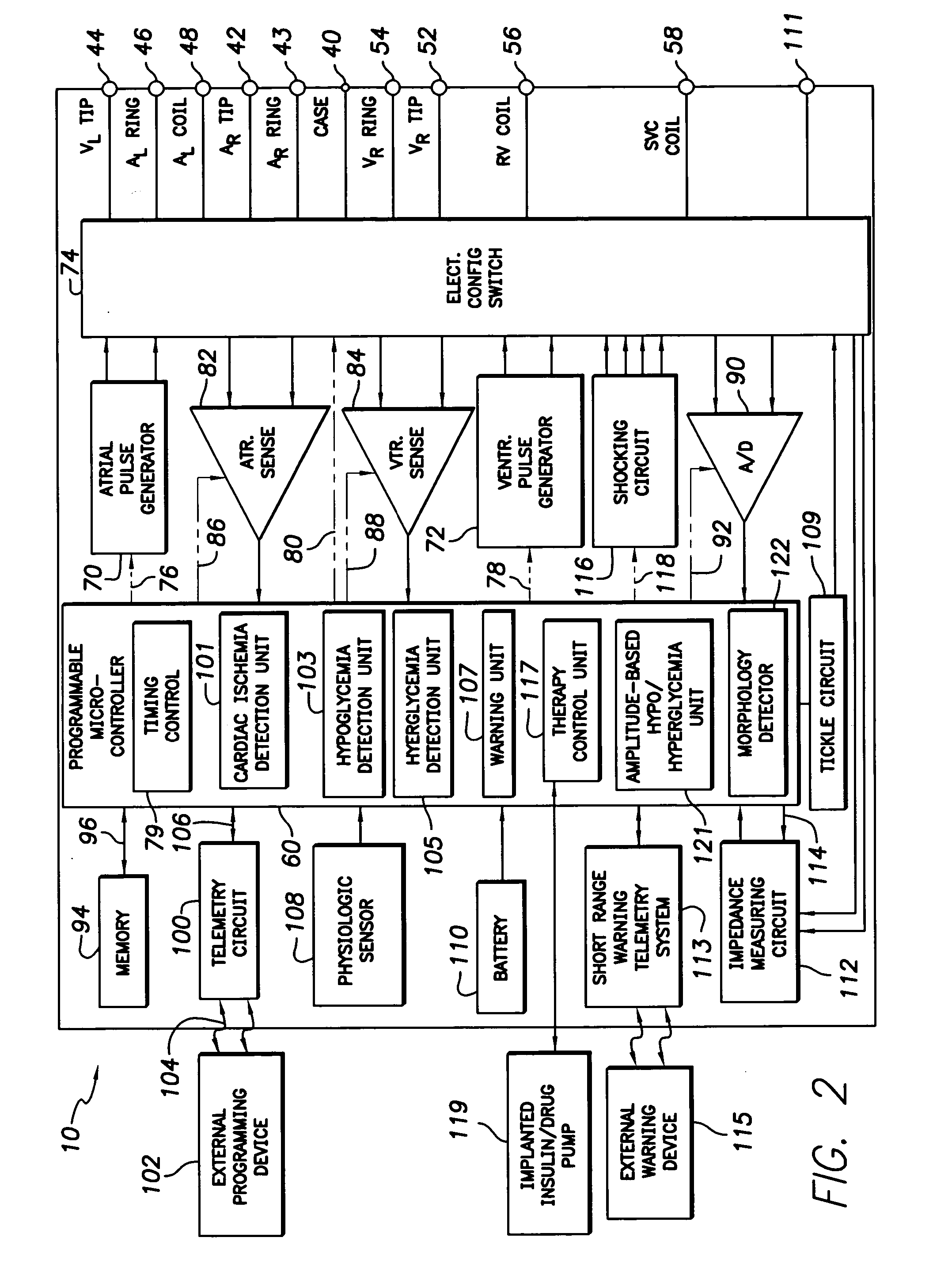
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20060167365A1Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System for Cardiac Medical Condition Detection and Characterization
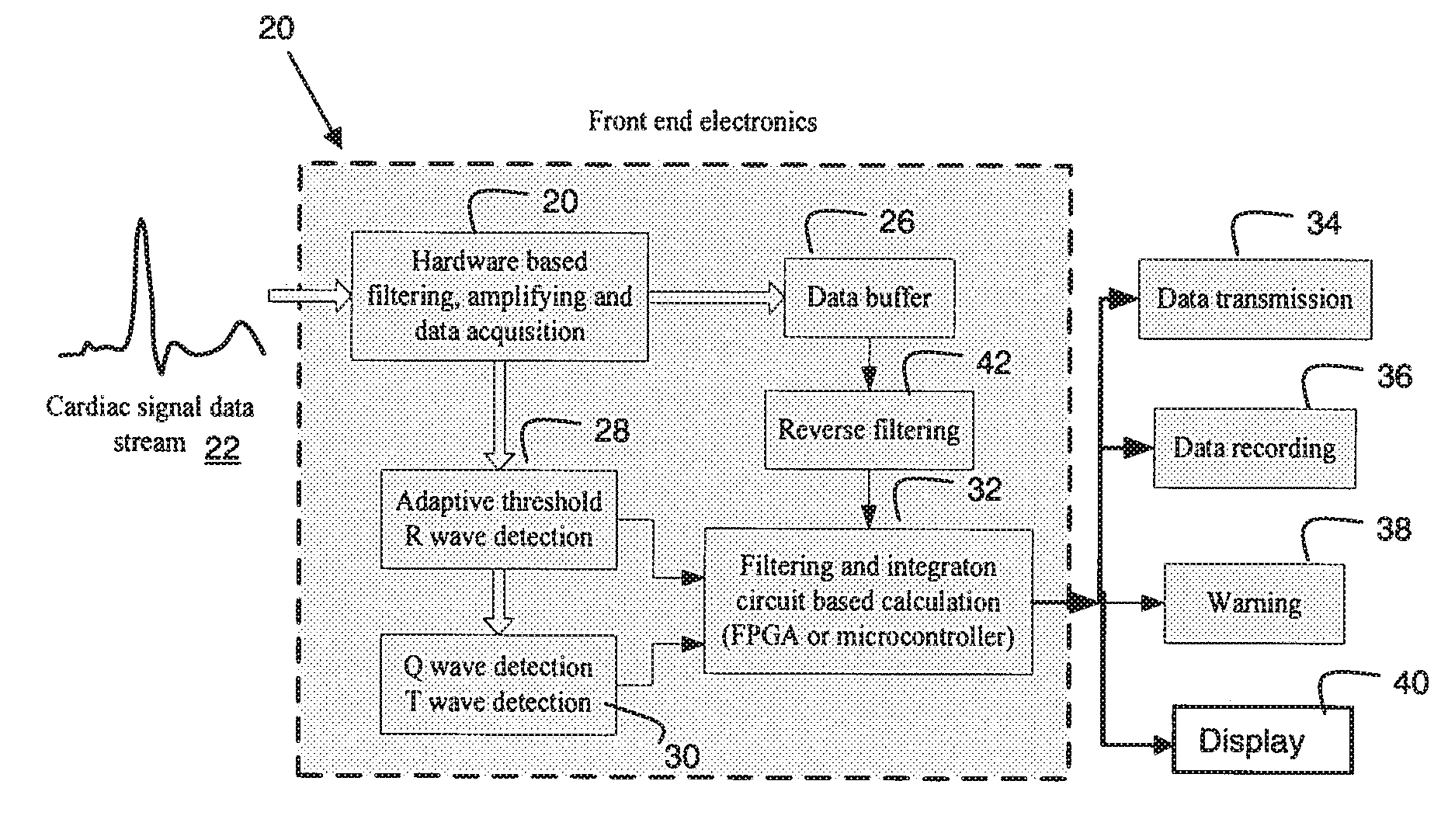
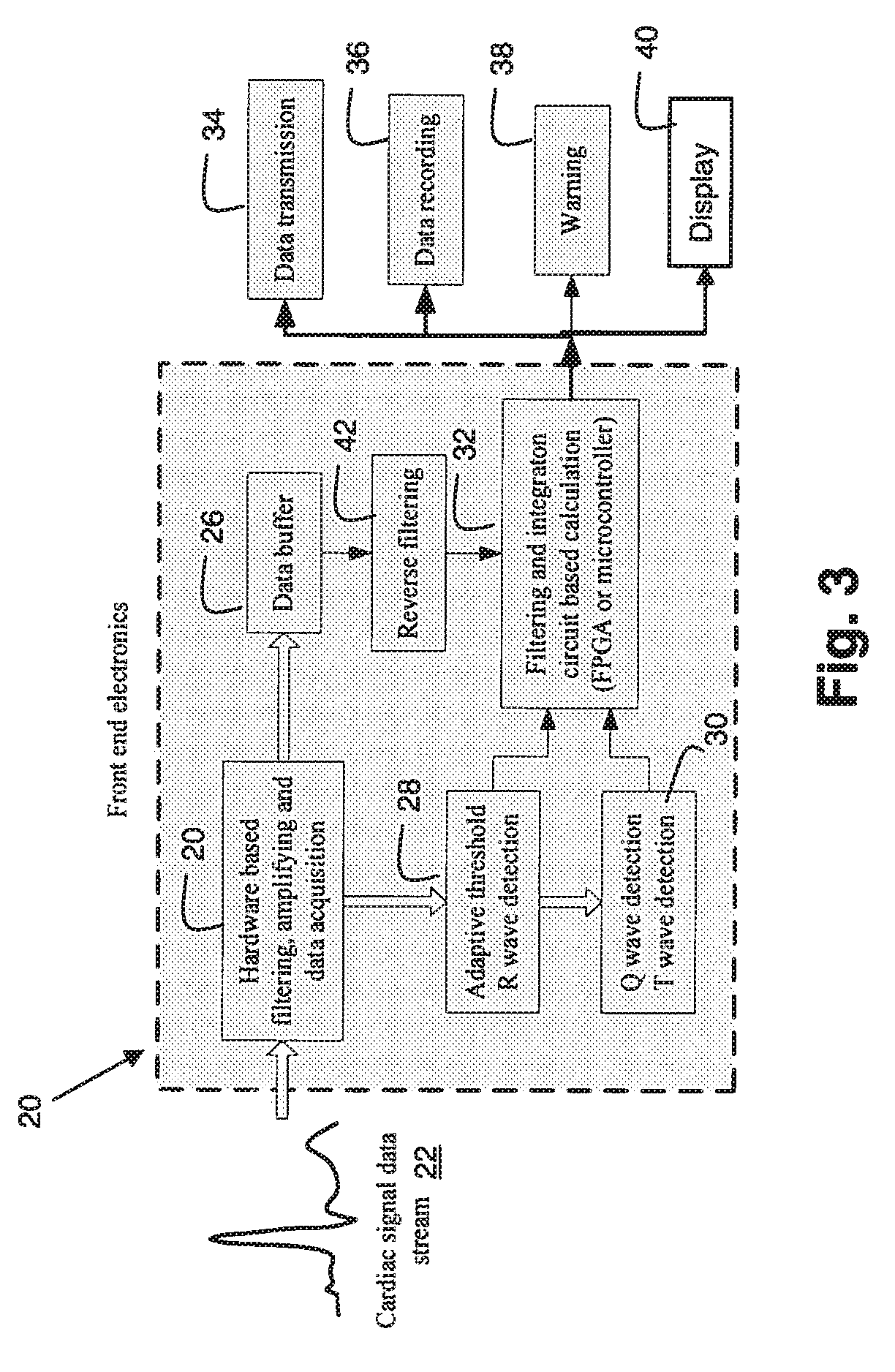
A system and method provides monitoring for atrial fibrillation. A data acquisition processor acquires a cardiac signal data stream from a patient and a wave detector detects an R-wave in a cardiac signal of the data stream. A T-wave in the cardiac signal occurring after the detected R-wave and a Q-wave in a subsequent cardiac signal of the data stream is also detected by the wave detector. A filter provides signal gating and extraction of data representing a Region of Interest (ROI) time window from the detected T-wave to the Q-wave. An integration processor detects characteristics of a P wave signal occurring within the ROI time window. At least one of the detected P wave characteristics is compared to characteristics derived from data representing at least one P wave signal and generating an output signal in response to the comparison for use in determining if the patient is in atrial fibrillation.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Automatic electrocardiogram recognition system
InactiveCN103110417AImprove analysis efficiencyPrioritizeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsT waveComputer-aided
The invention discloses an automatic electrocardiogram recognition system. The system comprises an electrocardiogram acquisition device, a wireless / wired network transmission module, an electrocardiogram collection and time domain feature recognizer, an electrocardiogram dominant wave interphase recognizer, an electrocardiogram QRS wave group similarity recognizer and an electrocardiogram queuing recognizer, the electrocardiogram acquisition device inputs acquired data to the electrocardiogram collection and time domain feature recognizer via the transmission module, the electrocardiogram collection and time domain feature recognizer recognizes to obtain positions of peak points of P waves, QRS waves and T waves on a 12-lead, the electrocardiogram dominant wave interphase recognizer recognizes heart rate to obtain normal and abnormal results of the heart rate, the electrocardiogram QRS wave group similarity recognizer recognizes whether an electrocardiogram probably has premature beat or not, and the electrocardiogram queuing recognizer sequences and outputs. The system performs real-time computer-aided analysis of clinically acquired 12-lead electrocardiograms to automatically recognize arrhythmia and premature beat electrocardiograms, and accordingly efficiency of electrocardiogram analysis is improved while a priority processing means is provided for emergency electrocardiograms.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
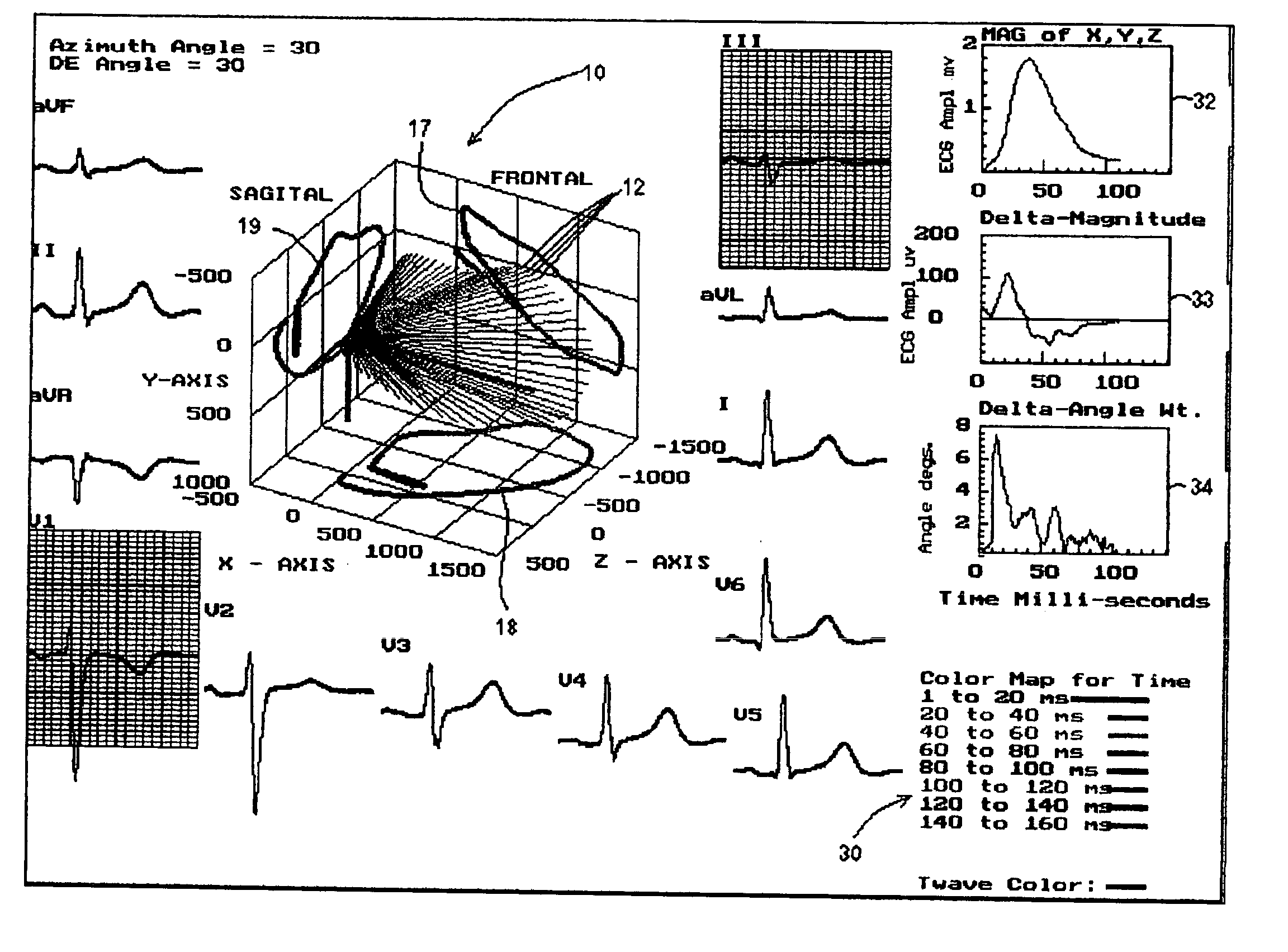
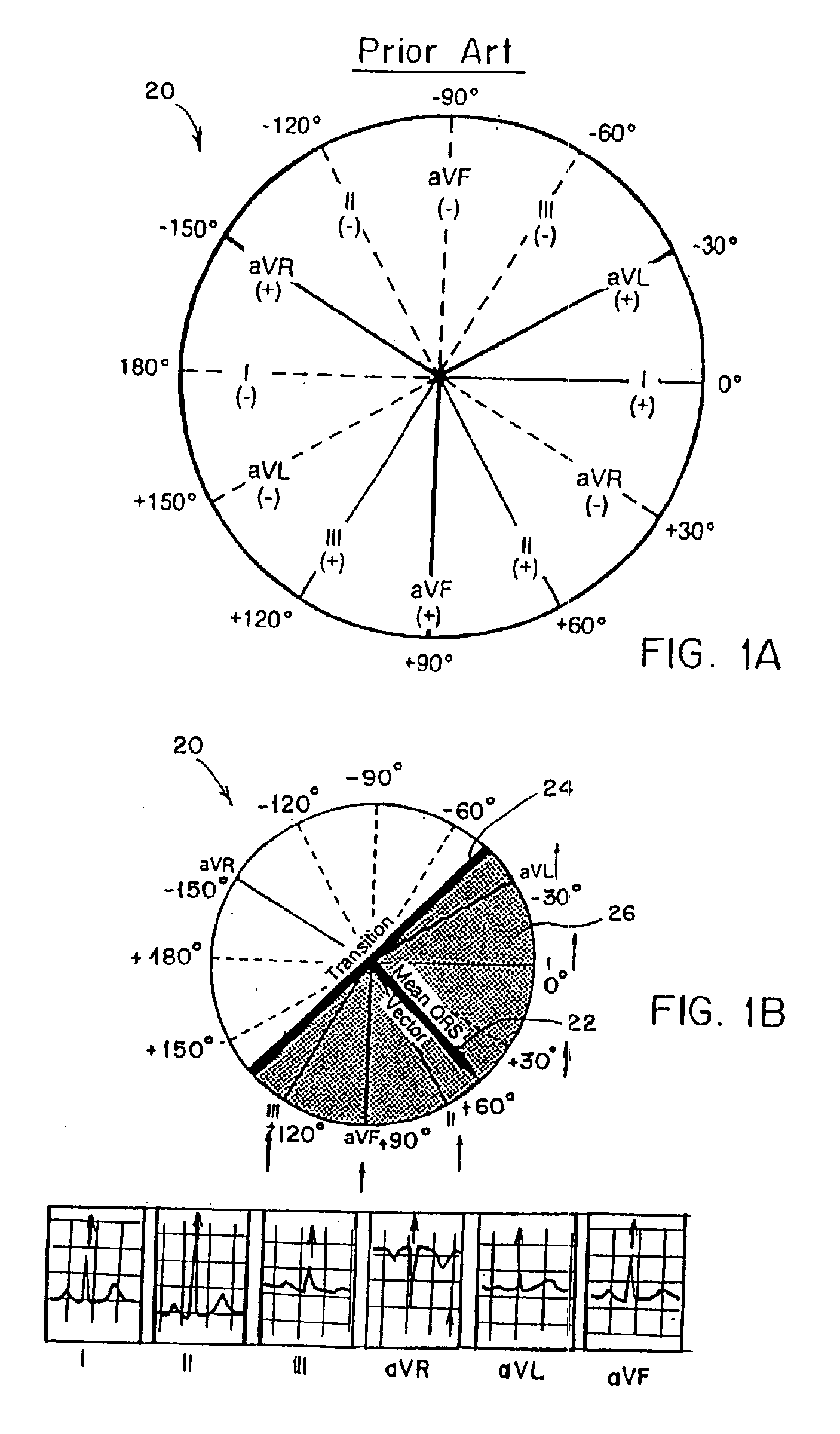
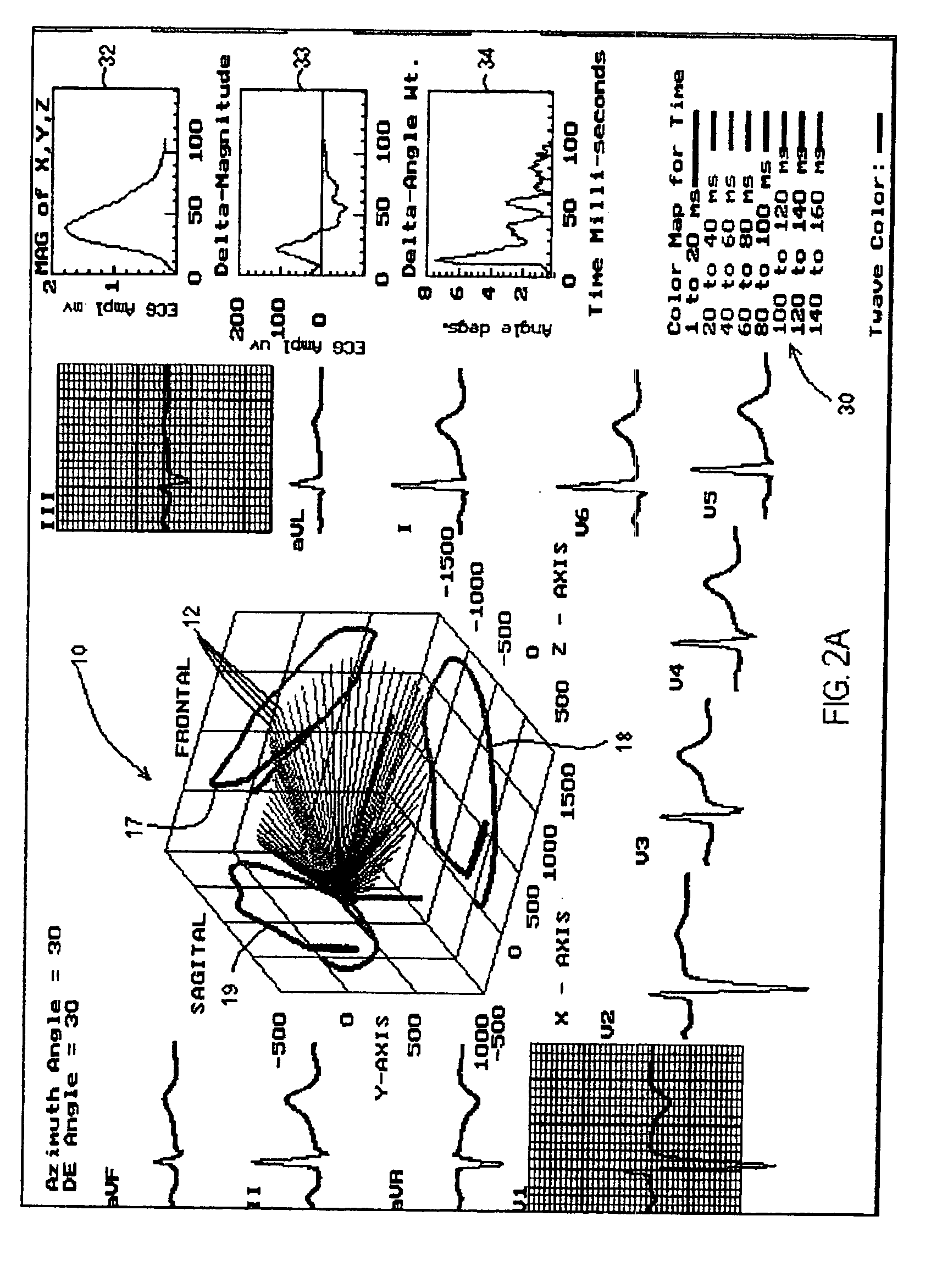
Three dimensional vector cardiograph and method for detecting and monitoring ischemic events
InactiveUS6884218B2Easy to analyzeGood techniqueElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesMaximum magnitudeT wave
A method of determining an ischemic event includes the steps of: monitoring and storing an initial electrocardiogram vector signal (x, y, z) of a known non-ischemic condition over the QRS, ST and T wave intervals; calculating and storing a J-point of the vector signal and a maximum magnitude of a signal level over the T wave interval; monitoring a subsequent electrocardiogram vector signal over the QRS, ST and T wave intervals; measuring and storing the magnitude (Mag.) of the vector difference between a subsequent vector signal and the initial vector signal; measuring and storing the angle (Ang.) difference between a subsequent vector and the initial vector at points; regressing a line from points about 25 milliseconds prior to the J point and about 60 milliseconds after the J-point and determining the slope of the regression line and the deviation of the angle difference of the regression line; regressing a line from points about 100 milliseconds prior to the maximum magnitude of the signal level over the T wave interval and determining the slope of the regressing line and the deviation of the angle difference of the regression line; and comparing the slope and deviation of the lines from the J point and the T wave interval to a set of known values to determine the presence of an ischemic event.
Owner:ECG TECH CORP
System and method for detecting abnormal respiration via respiratory parameters derived from intracardiac electrogram signals
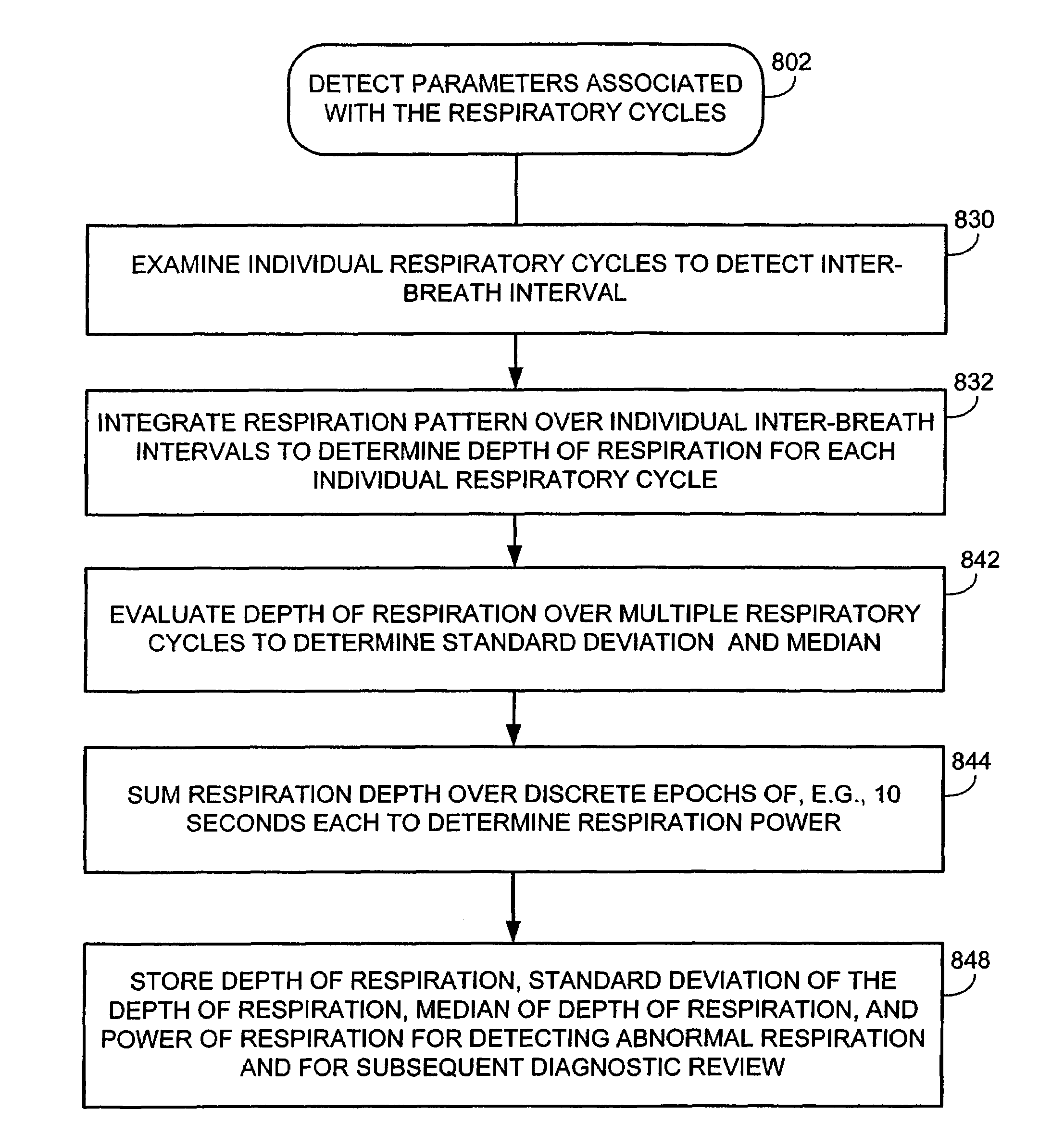
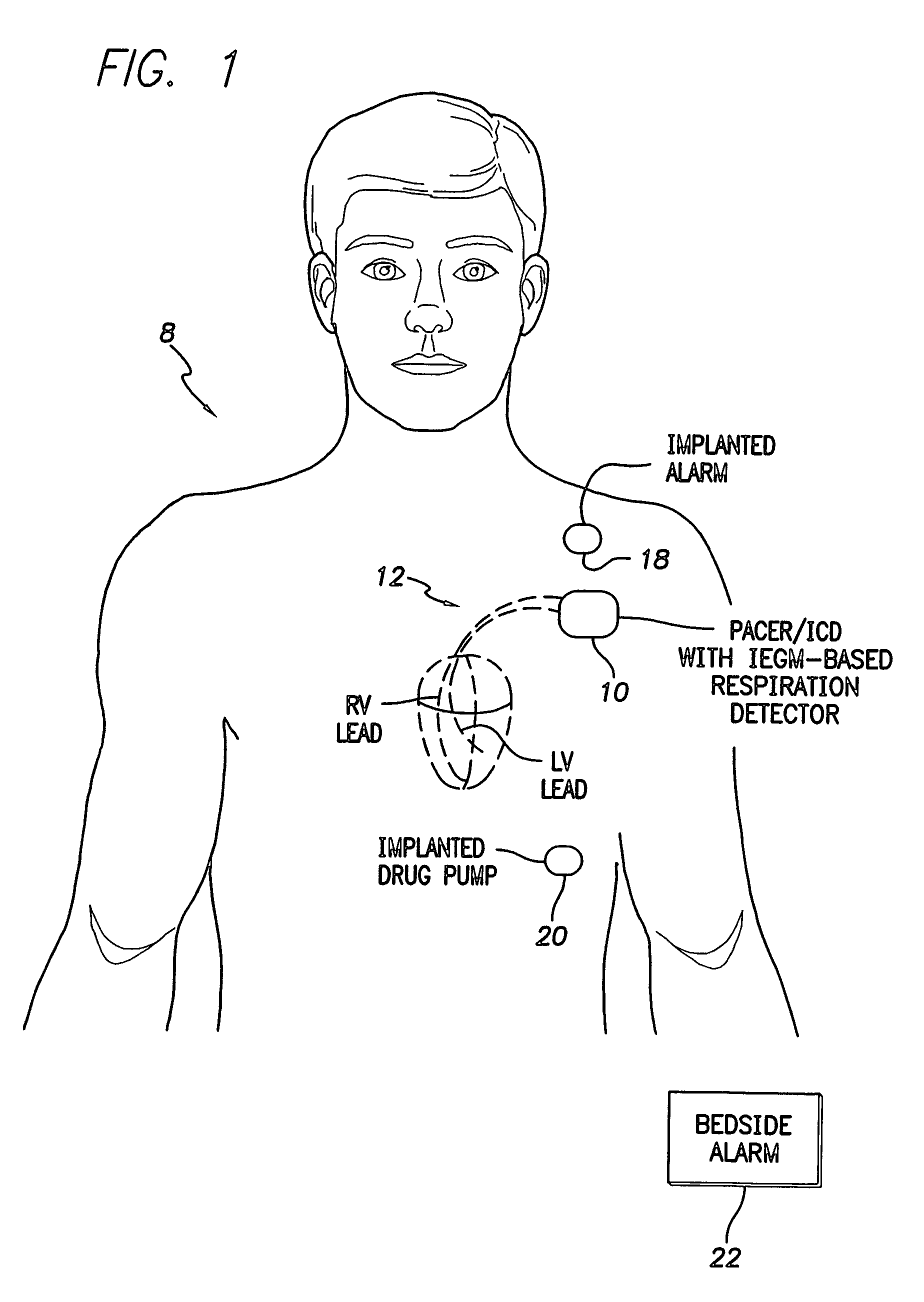
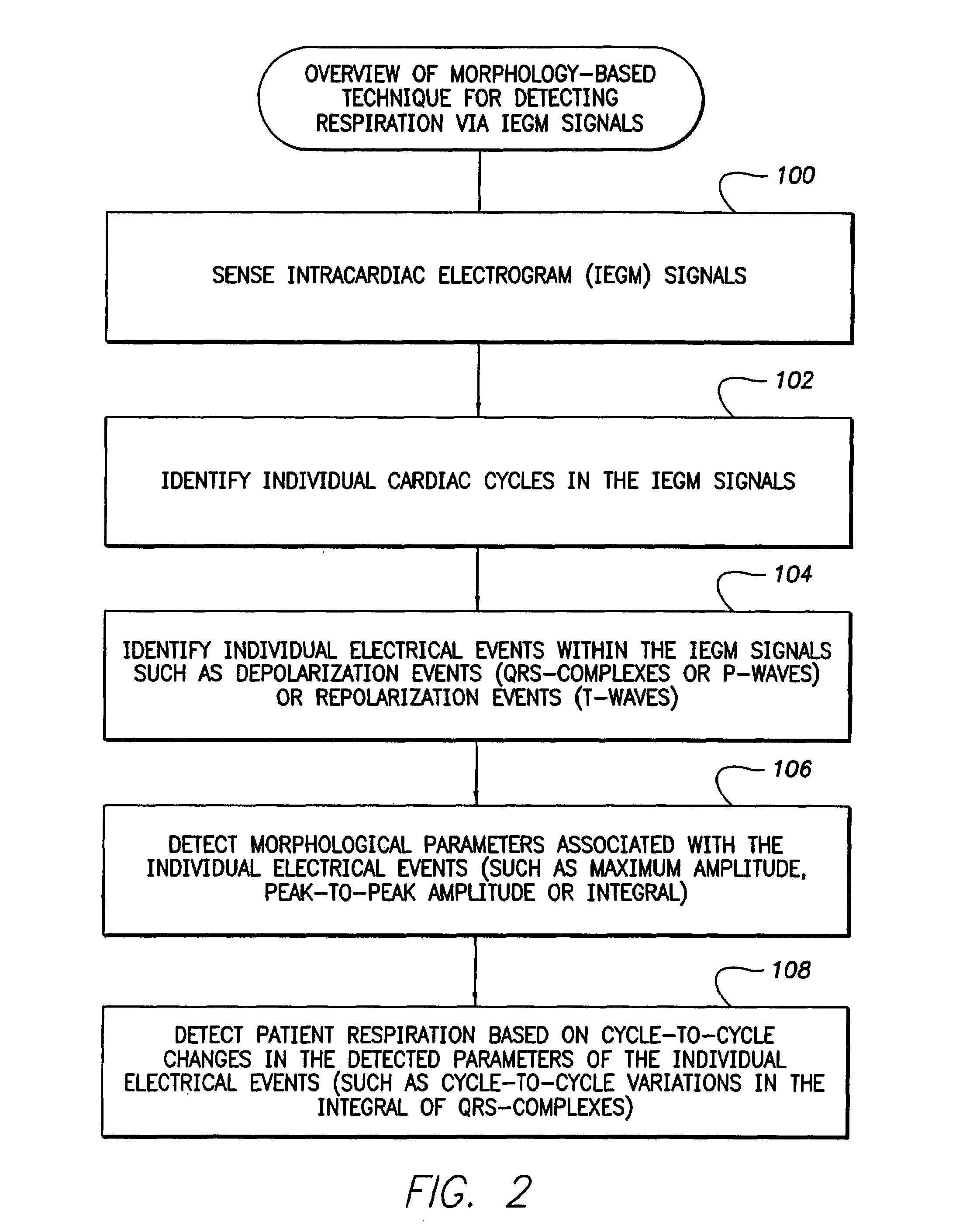
Techniques are provided for tracking patient respiration based upon intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals or other electrical cardiac signals. Briefly, respiration patterns are detected based upon cycle-to-cycle changes in morphological features associated with individual electrical events with the IEGM signals. For example, slight changes in the peak amplitudes of QRS-complexes, P-waves or T-waves are tracked to identify cyclical variations representative of patient respiration. Alternatively, the integrals of the morphological features of the individual events may be calculated for use in tracking respiration. In any case, once respiration patterns have been identified, episodes of abnormal respiration, such as apnea, hyperpnea, nocturnal asthma, or the like, may be detected and therapy automatically delivered. In particular, techniques for detecting abnormal respiration based on various respiratory parameters derived from the IEGM—such as respiration depth and respiration power—are described.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Shock timing technology
ActiveUS20080033494A1Improve accuracyImprove securityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineT wave
A method for accurately determining timing points for T-wave shocks is particularly useful in a system for determining a cardiac shock strength in an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD. The method involves acquiring at least one first signal, acquiring at least a second signal, comparing the signals, and selecting a timing point with the T-wave of the signal. The first and second signals may be two different aspects of a single electrogram, first and second electrograms, or a combination thereof. Comparison preferably involves signal alignment and qualitative analysis.
Owner:IMPERCEPTION
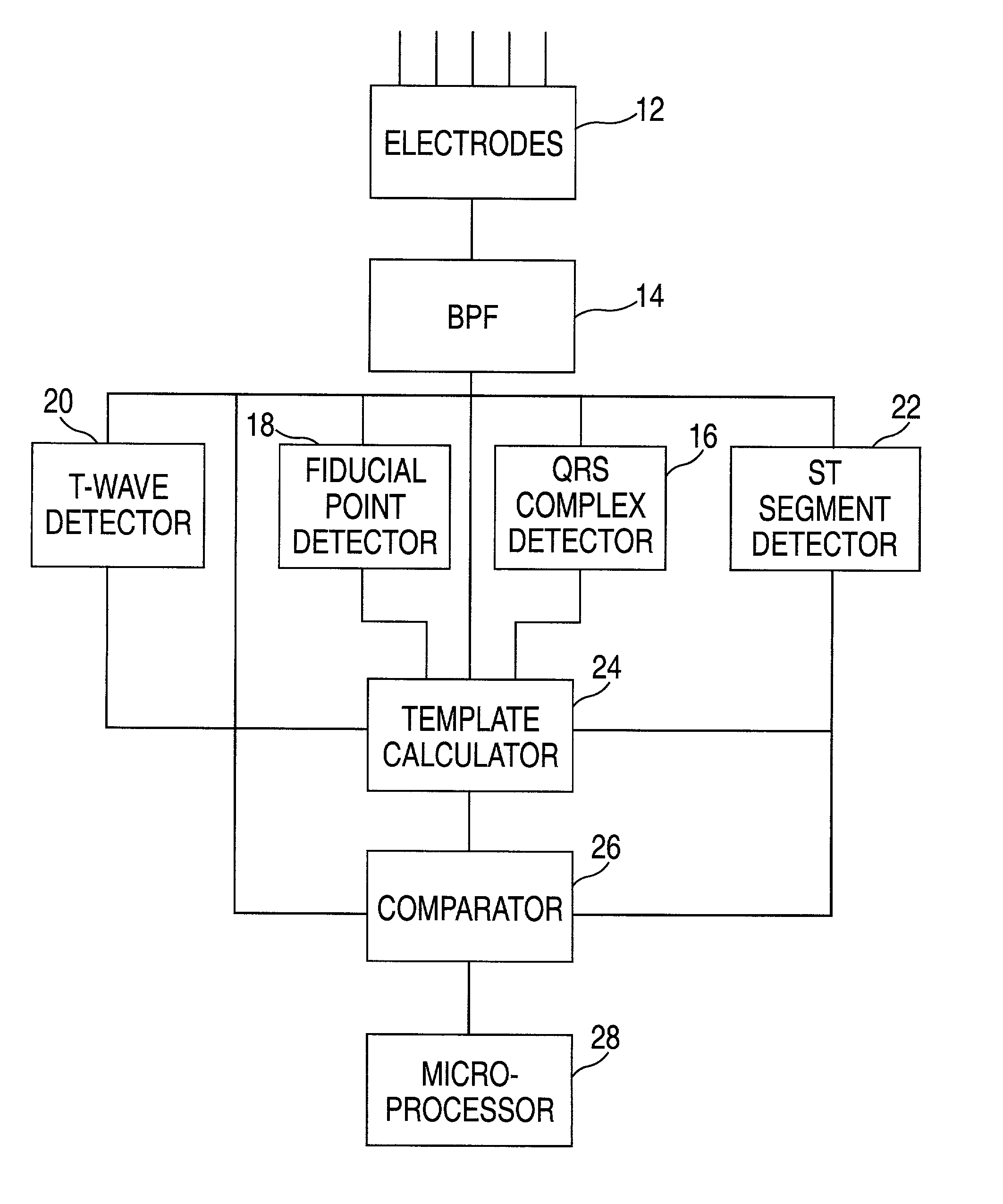
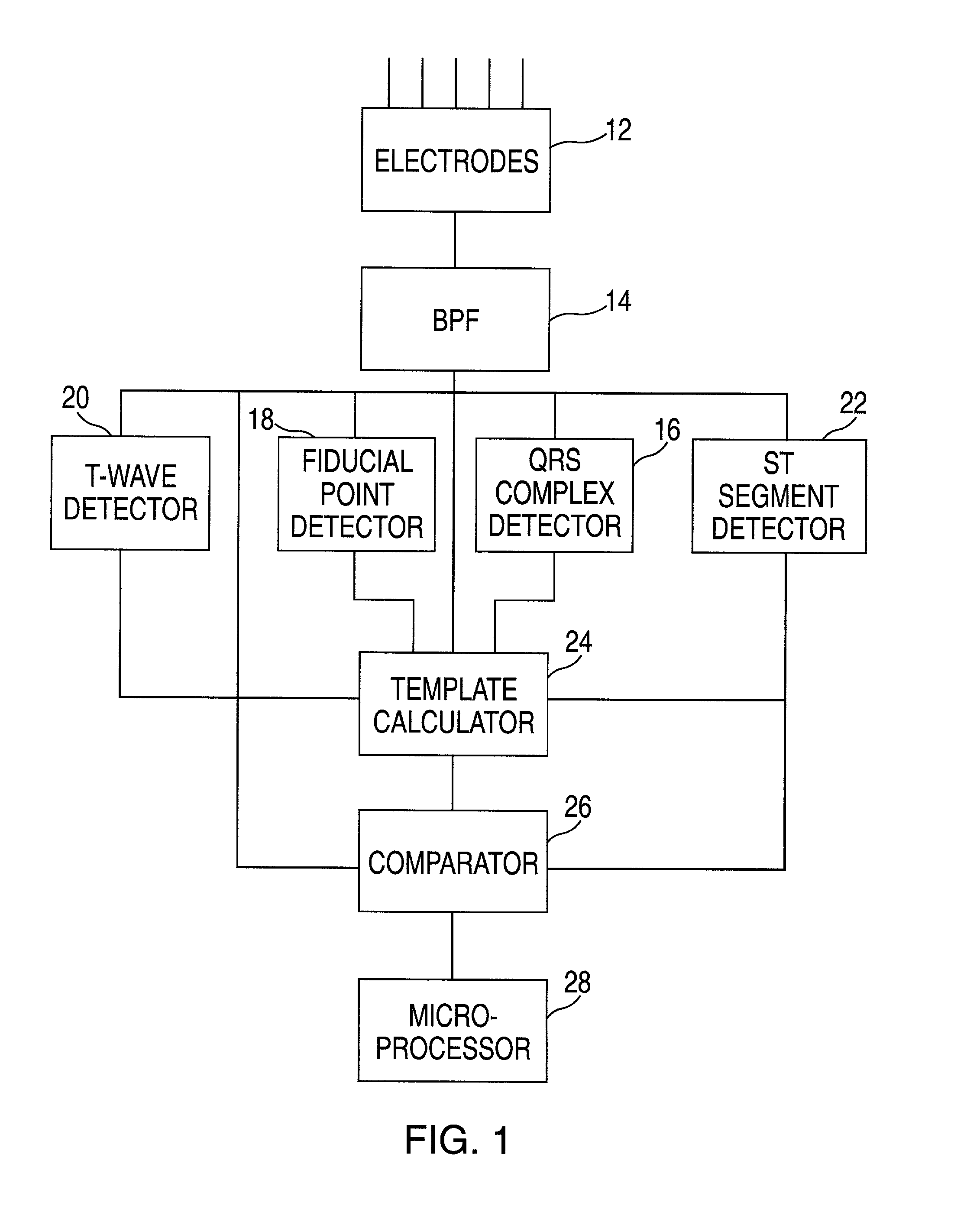
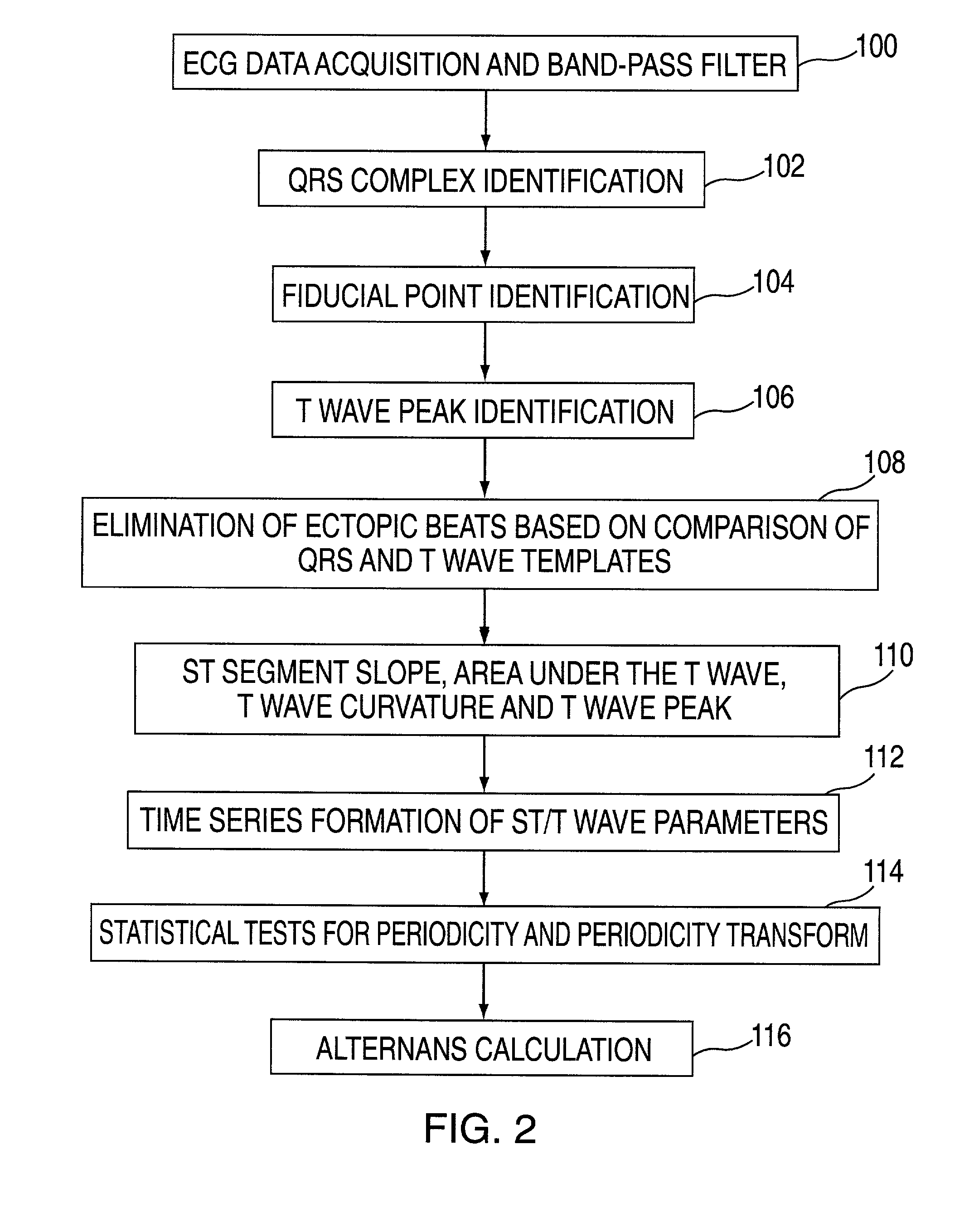
Method and apparatus for monitoring cardiac patients for T-wave alternans
InactiveUS6983183B2Eliminate the effects ofReliable measurementElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalArray data structure
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
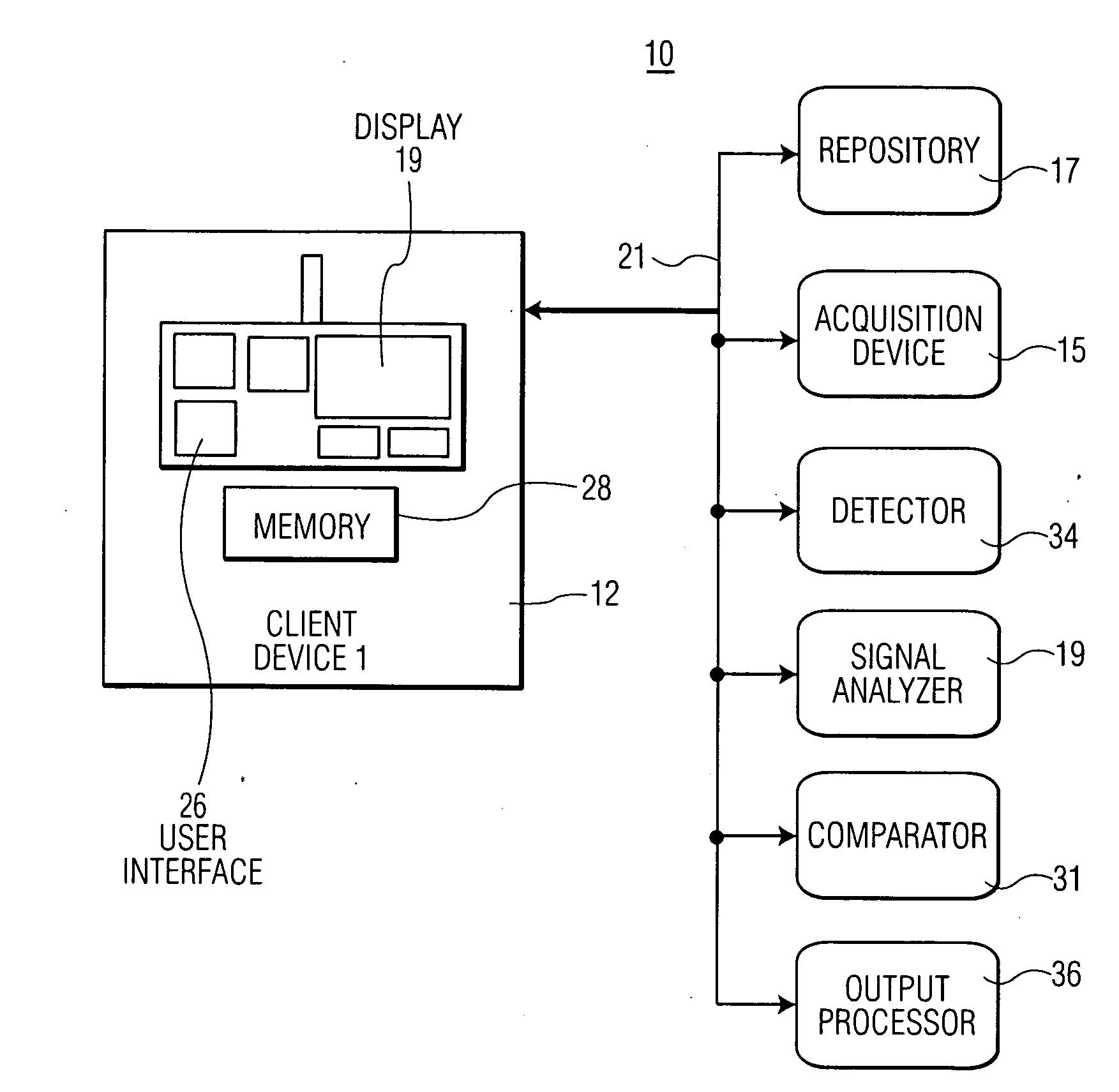
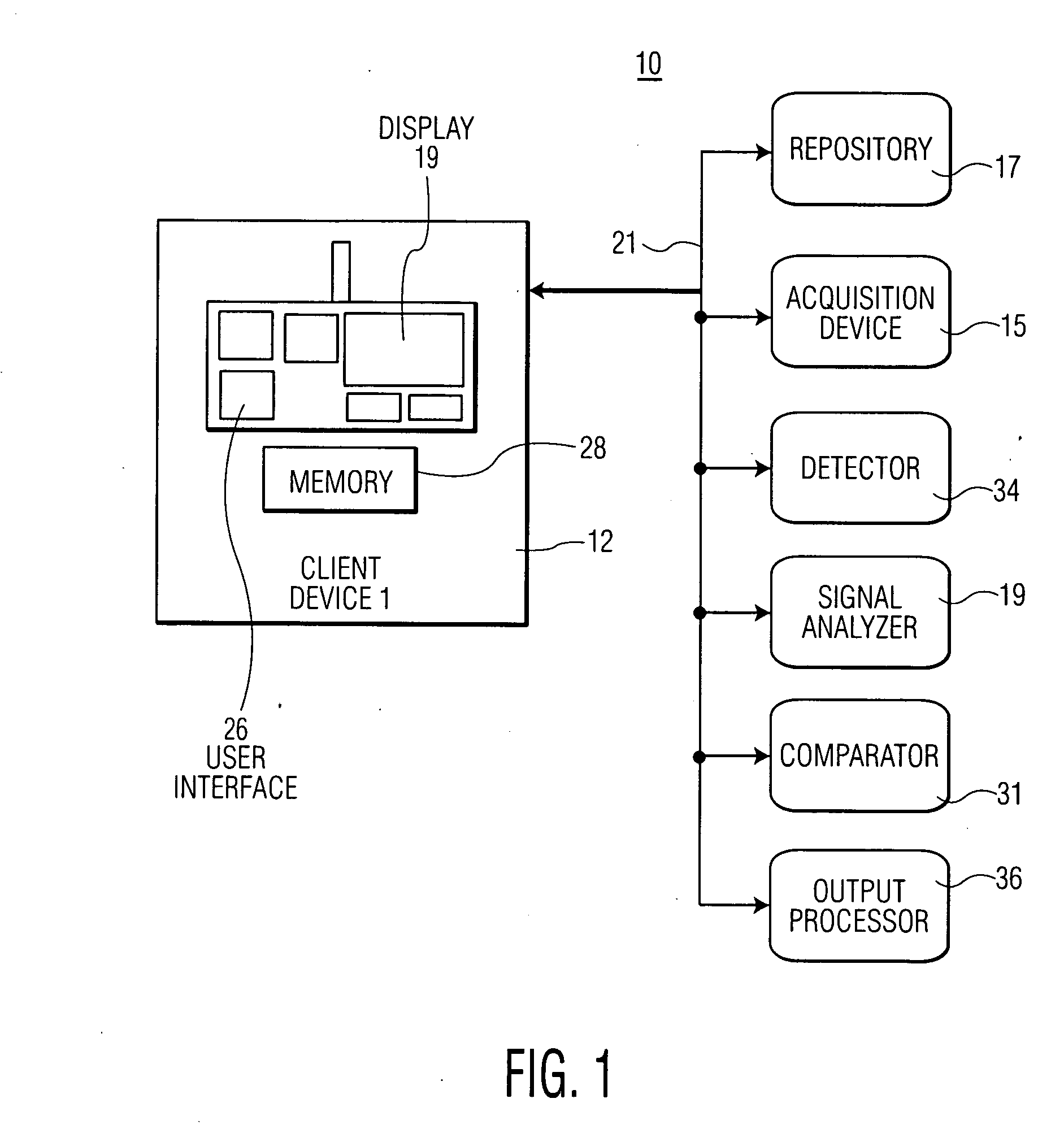
System for Heart Performance Characterization and Abnormality Detection
ActiveUS20090281441A1Improve precisionImprove reliabilityElectrocardiographyMedical devicesT wavePeak value
A system for heart performance characterization and abnormality detection includes an acquisition device for acquiring an electrophysiological signal representing heart beat cycles of a patient heart. A detector detects one or more parameters of the electrophysiological signal of parameter type comprising at least one of, (a) amplitude, (b) time duration, (c) peak frequency and (d) frequency bandwidth, of multiple different portions of a single heart beat cycle of the heart beat cycles selected in response to first predetermined data. The multiple different portions of the single heart beat cycle being selected from, a P wave portion, a QRS complex portion, an ST segment portion and a T wave portion in response to second predetermined data. A signal analyzer calculates a ratio of detected parameters of a single parameter type of the multiple different portions of the single heart beat cycle. An output processor generates data representing an alert message in response to a calculated ratio exceeding a predetermined threshold.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
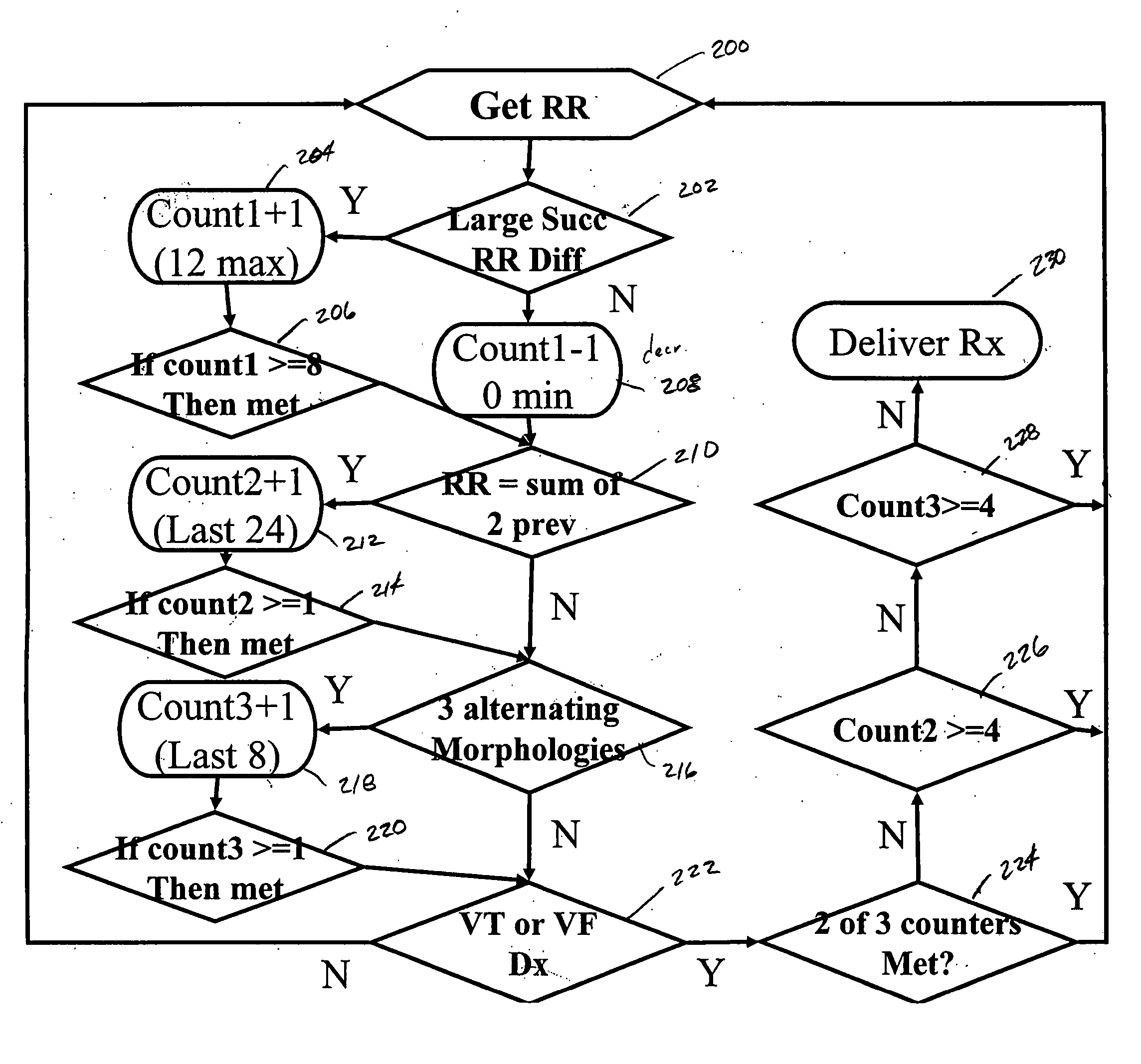
Implantable medical device with real time T-wave oversensing detection
ActiveUS20060224075A1ElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsSustained ventricular tachycardiaVentricular depolarization
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) senses ventricular depolarizations (R-waves) in an electrogram signal to detect a ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation episodes. The EGM signal is also monitored in real time for characteristics that uniquely identify instances of T-wave oversensing. The ICD determines whether detection of a tachycardia or fibrillation episode is appropriate based upon counts of each of the unique characteristics evidencing T-wave oversensing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
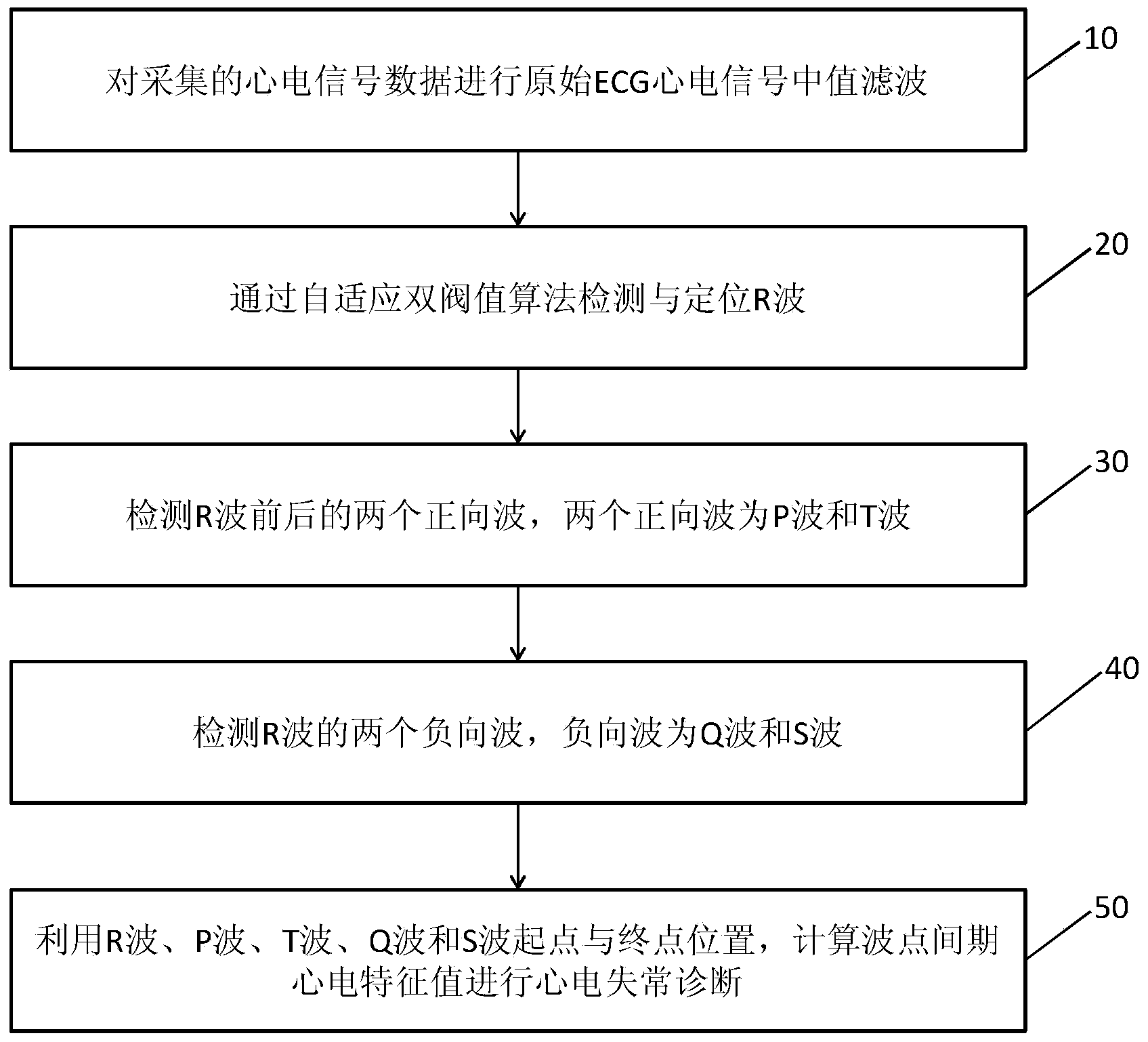
Electrocardiogram (ECG) data analysis method suitable for mobile platform
InactiveCN104173043ASimple structureImprove processing efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsS-waveT wave
The invention discloses an electrocardiosignal (ECG) data analysis method suitable for a mobile platform. The electrocardiosignal (ECG) data analysis method includes subjecting collected electrocardiosignal data to original ECG electrocardiosignal median filtering; detecting and positioning an R wave through a self-adaption dual-threshold algorithm; detecting two forward waves before and after the R wave, wherein the two forward waves are a P wave and a T wave; detecting two negative waves on two sides of the R wave, wherein the two negative waves are a Q wave and an S wave; using starting point and terminal point positions of the R wave, the P wave, the T wave, the Q wave, and the S wave to calculate ECG feature values of wave point intervals for arrhythmia diagnosis. According to the ECG data analysis method suitable for the mobile platform, the accuracy for detection of arrhythmia can reach over 92%; since an algorithm structure is concise, processing efficiency is high, only 12s is required for processing one-minute ECG data on a Cortex A8 / Android mobile platform, and the method is suitable for developing a mobile platform based portable admeasuring apparatus.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Multi-Channel System for Beat to Beat QT Interval Variability
InactiveUS20070203418A1Reduce the impact of noiseRapid and regular updatingElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographySingular value decompositionT wave
The measurement of beat-to-beat QT interval variability (QTV) shows clinical promise for identifying several types of cardiac pathology. However, until now, there has been no device capable of displaying, in real time on a beat-to-beat basis, changes in QTV in all 12 conventional leads in a continuously monitored patient. While several software programs have been designed to analyze QTV, heretofore, such programs have all involved only a few channels (at most) and / or have required laborious user interaction or off-line calculations and post-processing, limiting their clinical utility. This invention discloses a PC-based ECG software program that in real time, acquires, analyzes and displays QTV and PQ interval variability (PQV) in each of the independent channels that constitute the 12-lead conventional and / or Frank X, Y, Z lead ECG. The system also analyzes and displays the QTV and PQV from QT and PQ interval signals that are derived from multiple channels and from singular value decomposition such that the effect of noise and other artifacts on the QTV and PQV results are substantially reduced compared to existing single-channel methods. Moreover, this invention also discloses certain new parameters of T-wave (and QRS and P-wave) morphology, that in initial studies have improved clinical diagnostic utility and / or reproducibility and reliability compared to known existing parameters of T-wave morphology. Finally, it also discloses a method for determining the beat-to-beat variability these T, QRS and P-wave morphologic parameters.
Owner:CARDIOSOFT
System and method for detecting cardiac ischemia using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7274959B1Low costSave power consumptionElectrocardiographySensorsT waveSubcutaneous tissue
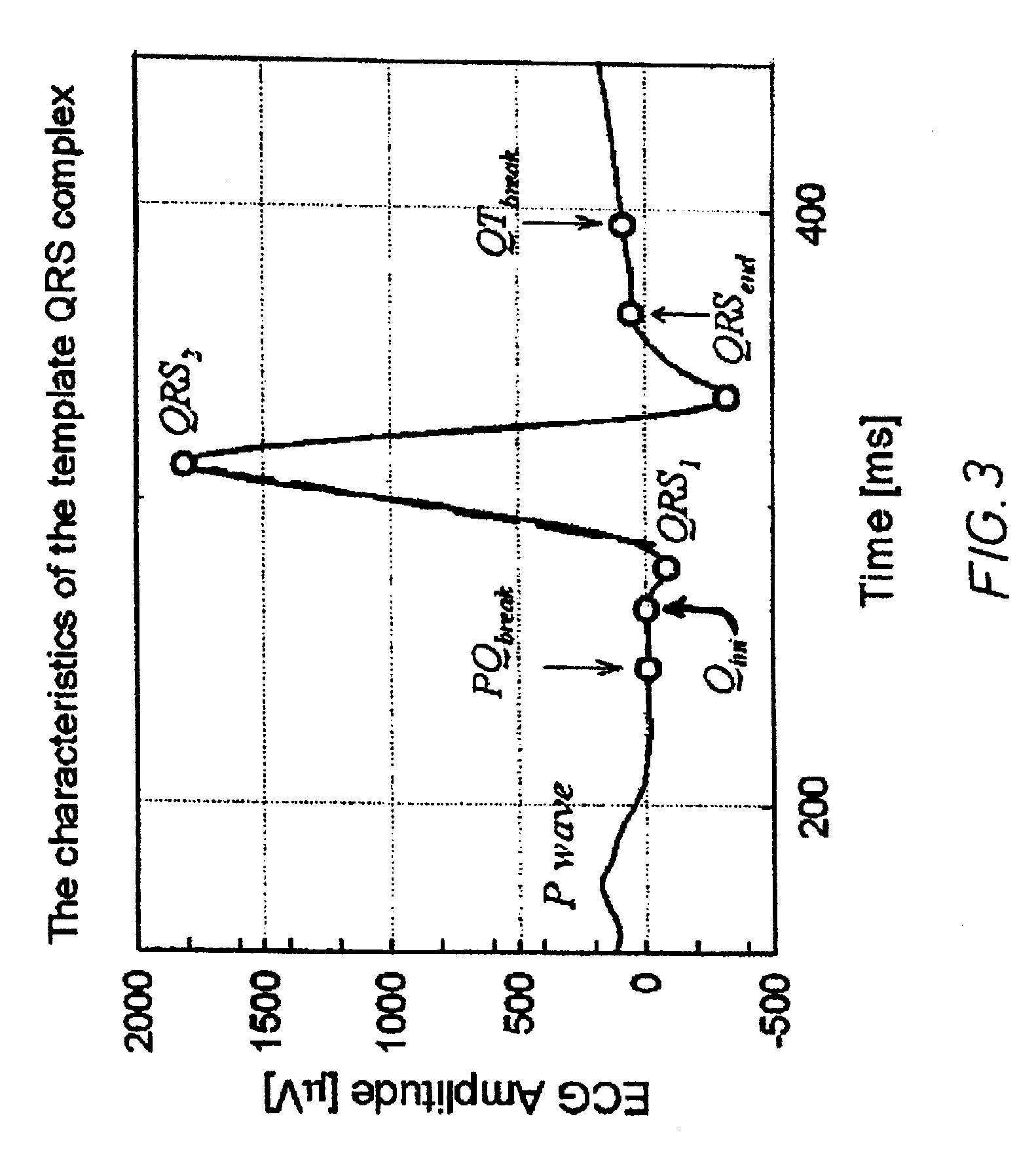
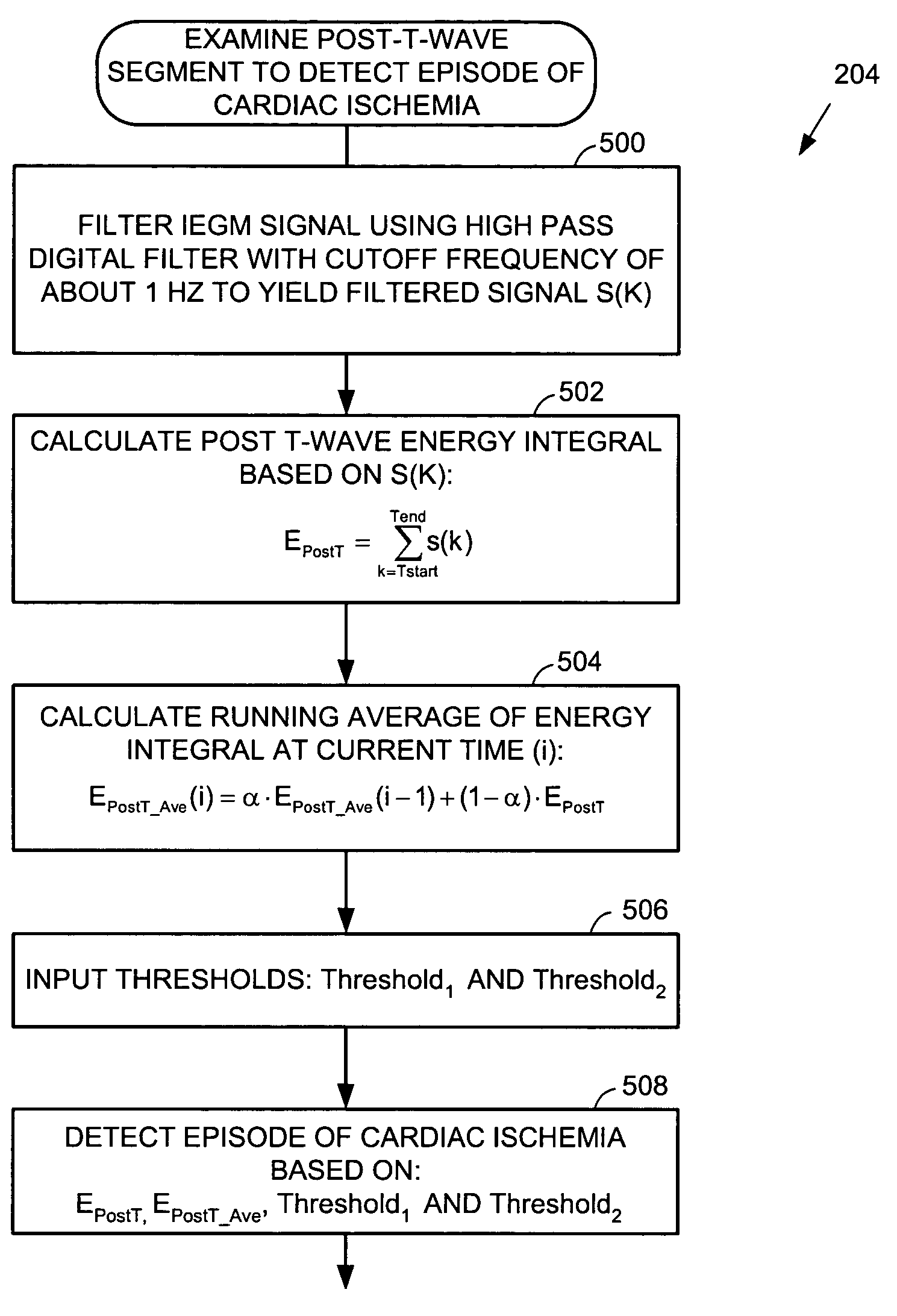
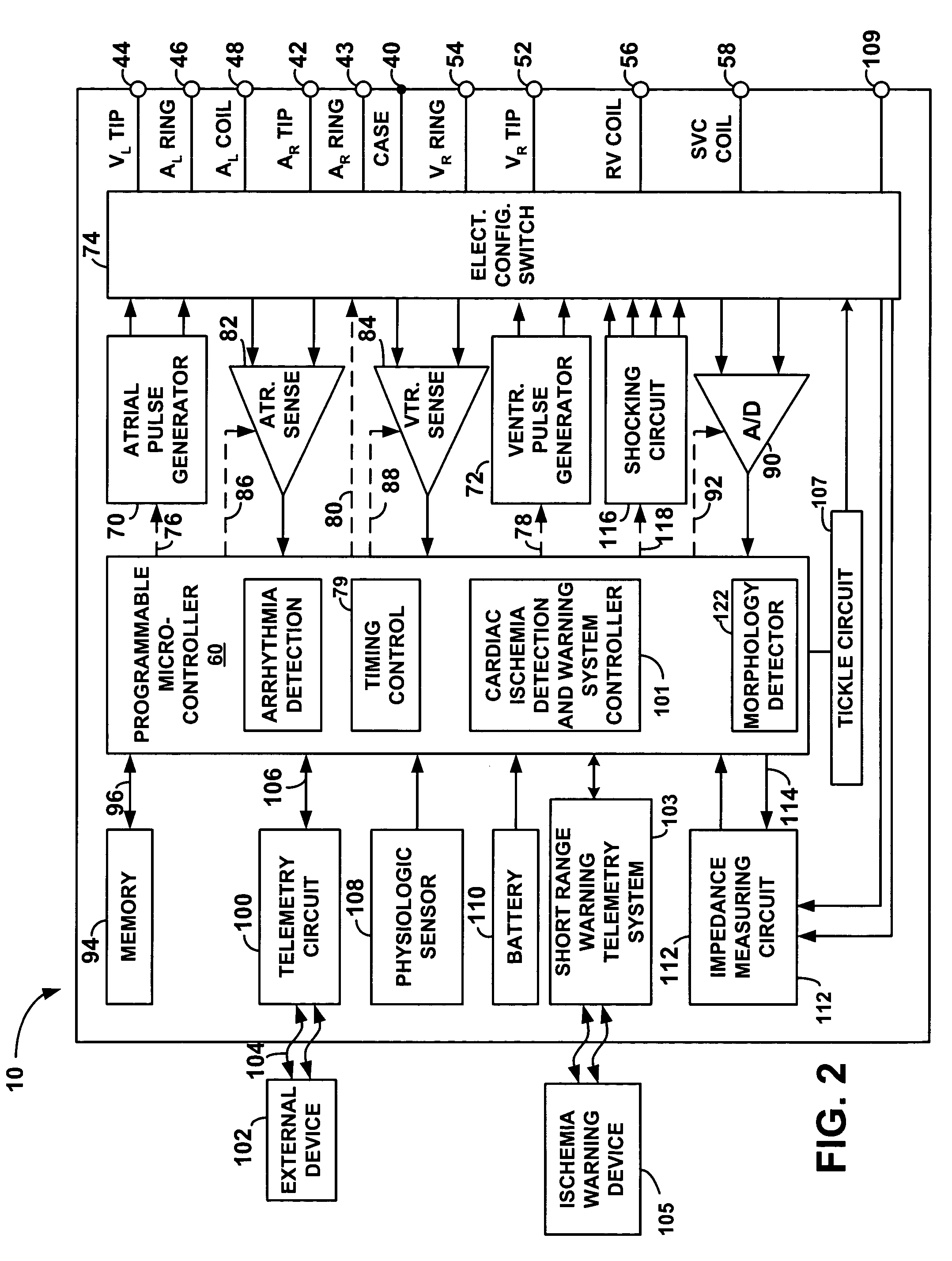
A technique is provided for detecting episodes of cardiac ischemia based on an examination of post-T-wave signal segments. Since cardiac ischemia is often a precursor to acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or ventricular fibrillation (VF), the technique thereby provides a method for predicting the possible onset of AMI or VF so that a warning may be delivered to the patient. The warning preferably includes both a perceptible electrical notification signal applied directly to subcutaneous tissue and a warning signal delivered via short range telemetry to a handheld warning device external to the patient. In one example, the onset of cardiac ischemia is identified by detecting a sharp falling edge within post-T-wave signals by filtering the signals using a high-pass filter having a cutoff frequency of at least 1 Hz. The total amount of energy in the filtered signal is calculated and compared against various thresholds.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
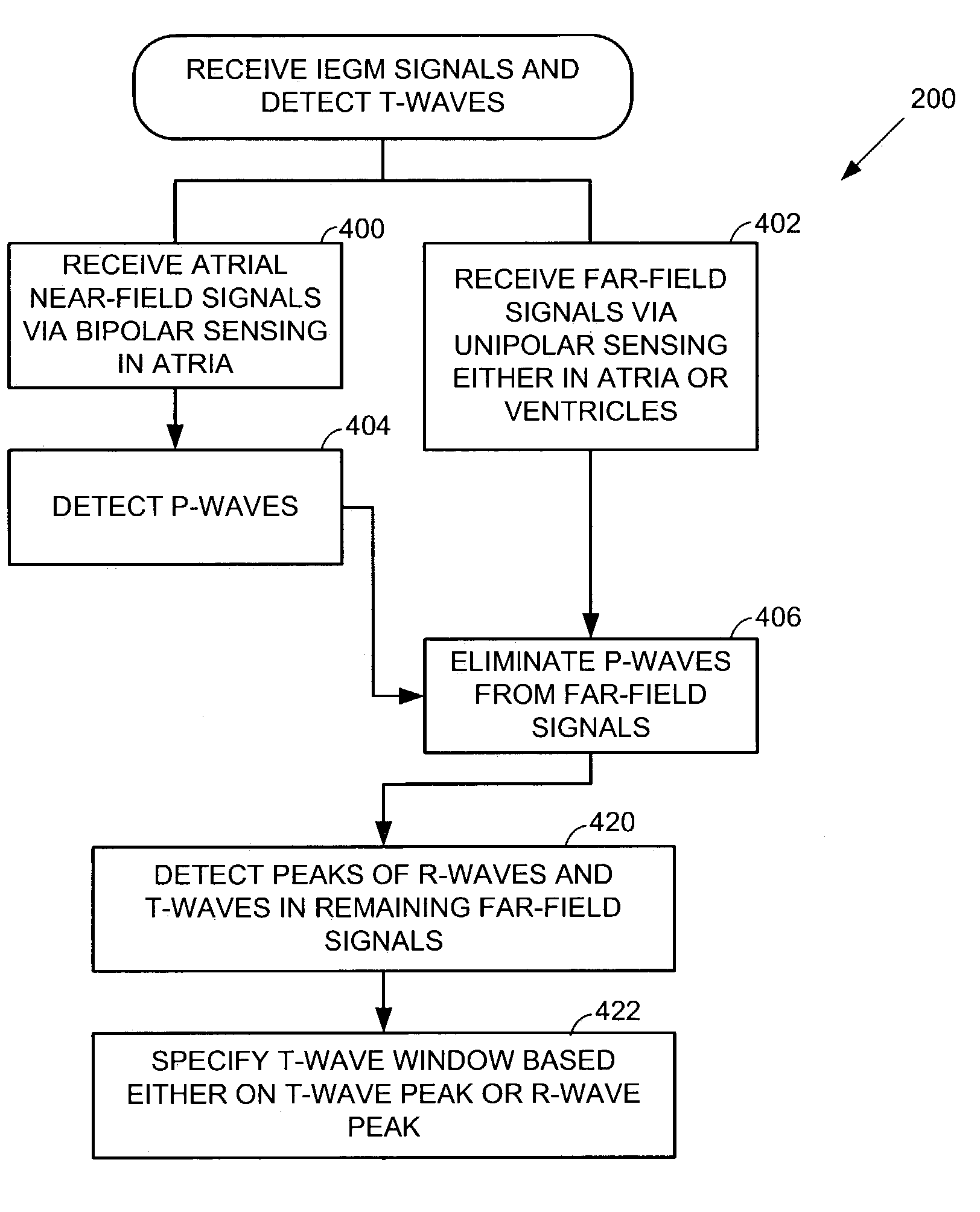
System and method for detecting cardiac ischemia based on T-waves using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7218960B1Reliable detectionSimple technologyElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsEcg signalT wave
A technique is provided for detecting episodes of cardiac ischemia based on an examination of the total energy of T-waves. Since cardiac ischemia is often a precursor to acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or ventricular fibrillation (VF), the technique thereby provides a method for predicting the possible onset of AMI or VF. Briefly, the technique integrates internal electrical cardiac signals occurring during T-waves and then compares the result against a running average. If the result exceeds the average by some predetermined amount, ischemia is thereby detected and a warning signal is provided to the patient. The maximum slope of the T-wave is also exploited. Techniques are also set forth herein for reliably detecting T-waves, which help prevent P-waves from being misinterpreted as T-waves on unipolar sensing channels. The T-wave detection technique may be used in conjunction with ischemia detection or for other purposes.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
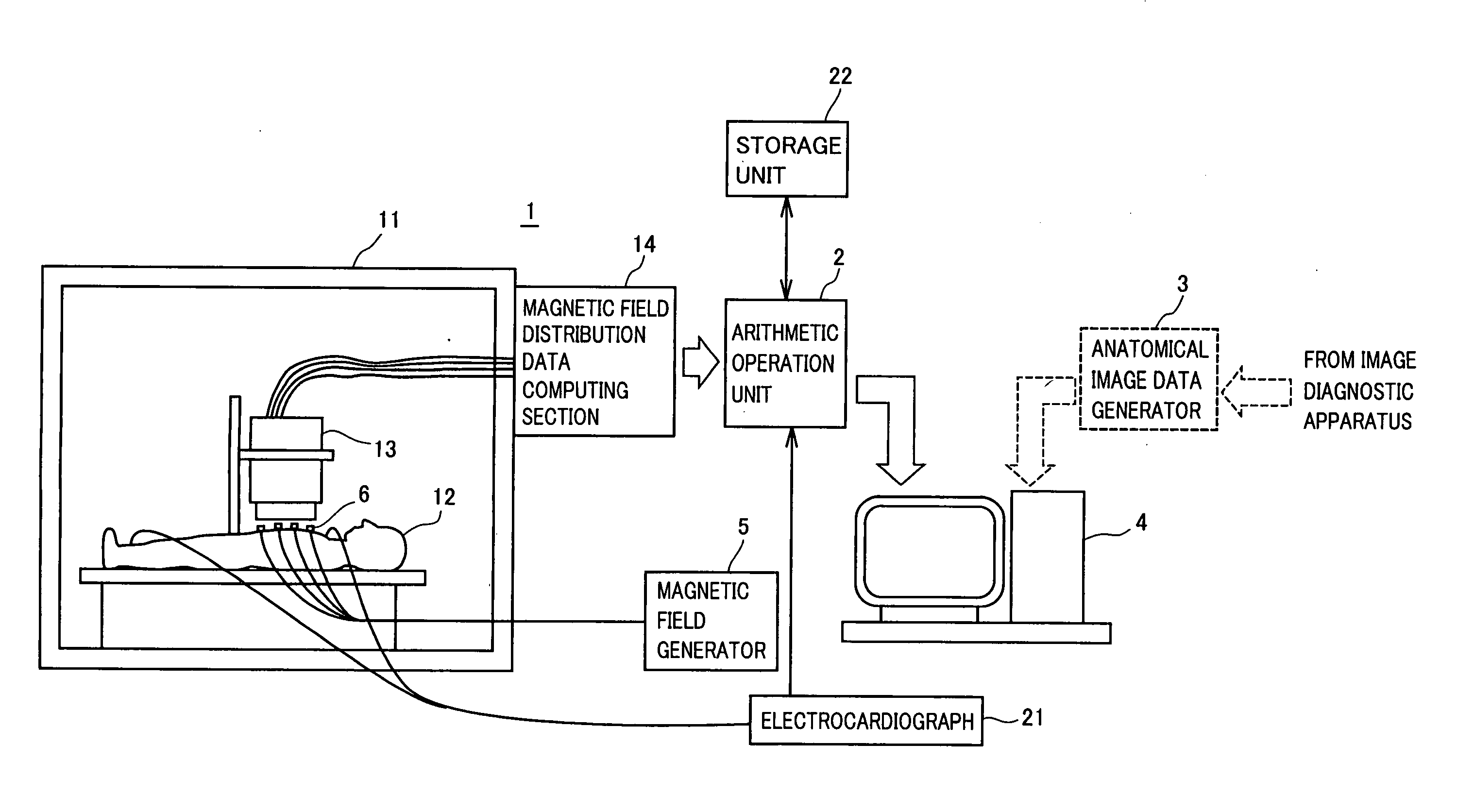
Cardiac Magnetic Field Diagnostic Apparatus and Evaluating Method of Three-Dimensional Localization of Myocardial Injury
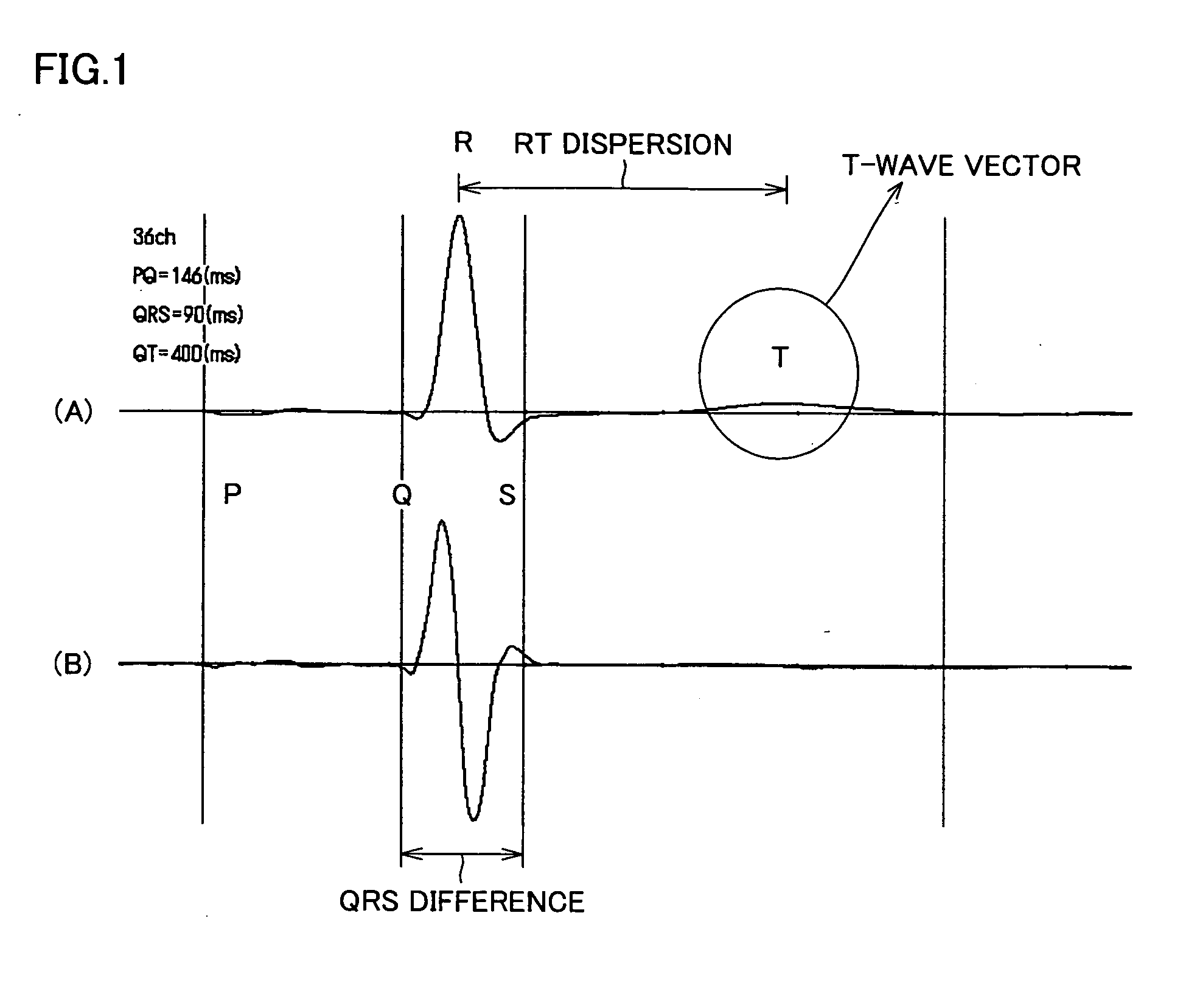
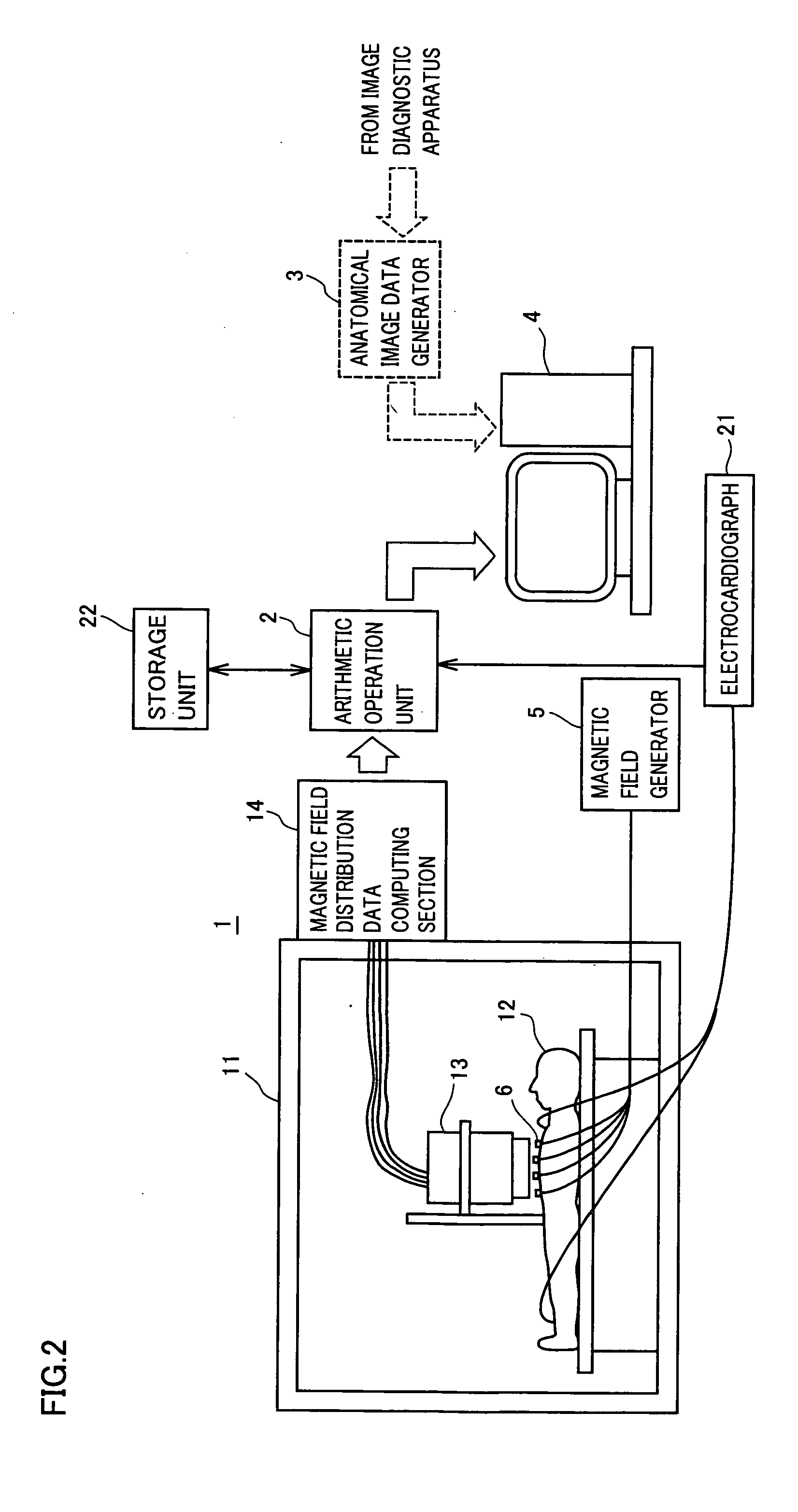
A cardiac magnetic field diagnostic apparatus for evaluating intracardiac three-dimensional localization of a myocardial injury by means of cardiac magnetic field measurement and a three-dimensional localization evaluating method of myocardial injury are disclosed. A magnetic field distribution measuring instrument (1) creates magnetic field distribution data by contactless magnetic field measurement on coordinates on the breast of a subject. An arithmetic operation unit (2) computers intracardiac three-dimensional current density distribution data from the magnetic field distribution data, draws a magnetic field integral cubic diagram as a cardiac contour cubic diagram according to the three-dimensional current density distribution data, creates data to draw the three-dimensional distribution of the QRS difference, the T-wave vector, or the RT dispersion of the same subject according to the three-dimensional current density distribution data, and reconstructs it on the cardiac contour. With this, evaluation of three-dimensional localization of a myocardial injury is possible.
Owner:IWATE UNIVERSITY
Method and system for performing superposition analysis on exercise load electrocardio waveforms
ActiveCN102397067AAccurate judgmentAccurate Waveform DataDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsT waveQT interval
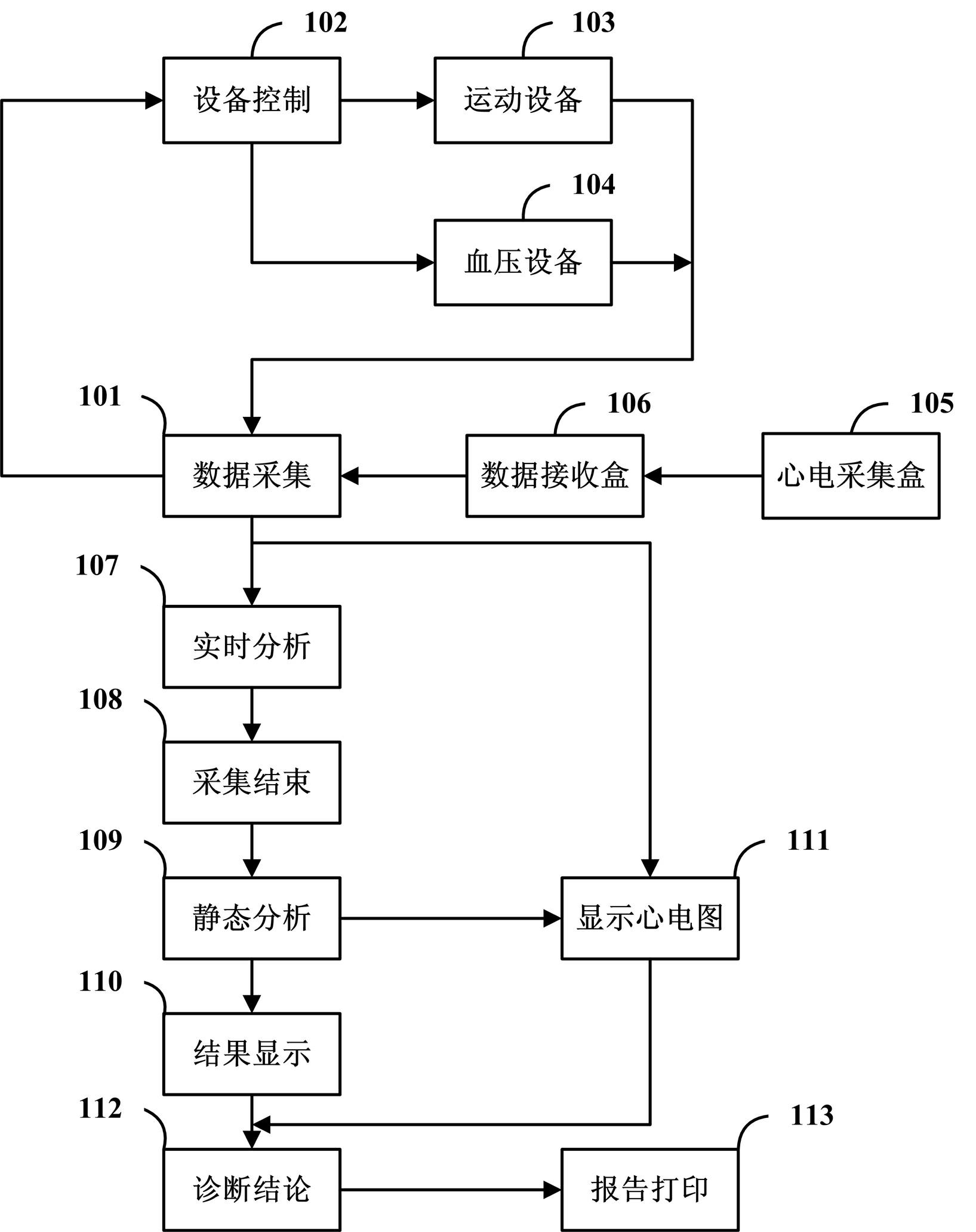
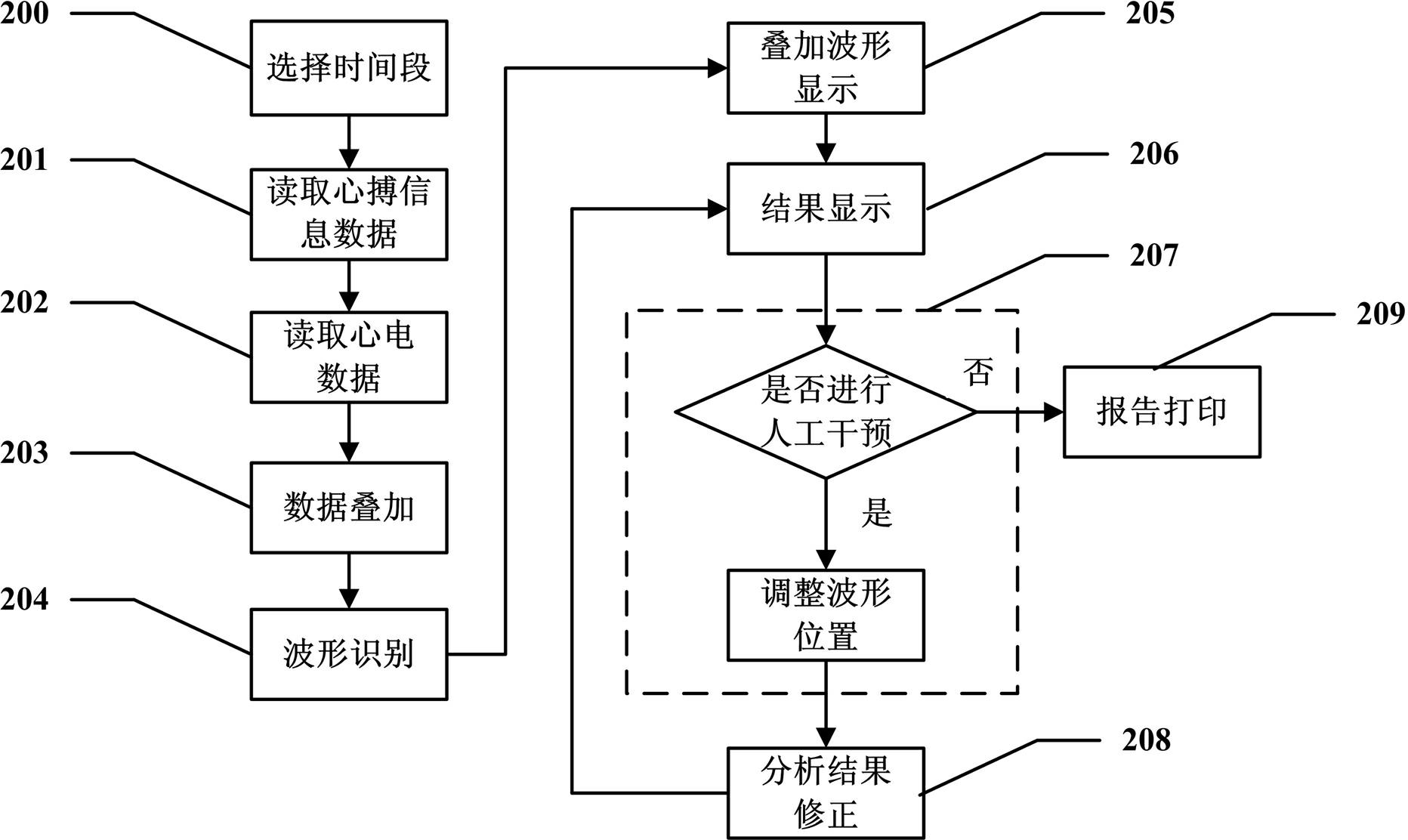
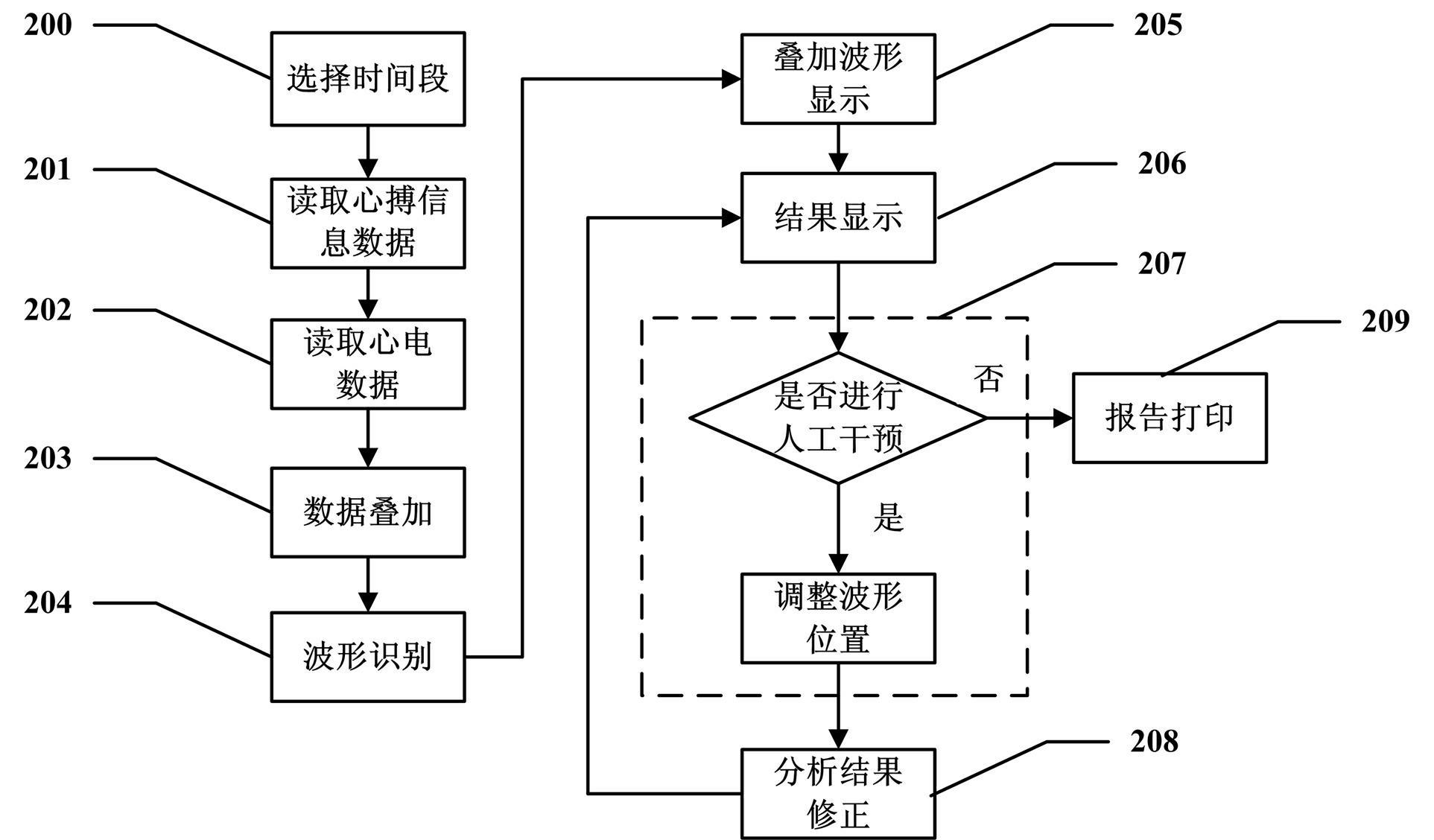
The invention discloses a method for performing superposition analysis on electrocardio data of any time segment. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting any segment of representative waveforms from an electrocardiogram; reading electrocardio data and waveform information in the time period; superposing the waveform of each heart beat in the time period and analyzing the waveform type of the superposed waveforms, the forward voltage and the negative voltage of a P wave, the voltage of a Q wave, an R wave and an S wave, the average voltage of an ST segment, the forward voltage and the negative voltage of a T wave, the time limit of the P wave, the Q wave, the R wave, the S wave and the T wave, a QT interval and other data; and providing a human-computer interaction interface, displaying an analysis result obtained after waveforms are superposed, and allowing a user to perform manual intervention on the analysis result. The application scope of an exercise load test is broadened, the accuracy of the test result is improved, and the diagnostic report has higher reference value.
Owner:CONTEC MEDICAL SYST
Method and system for detecting start-end points of P-waves and T-waves in multi-lead ECG signals
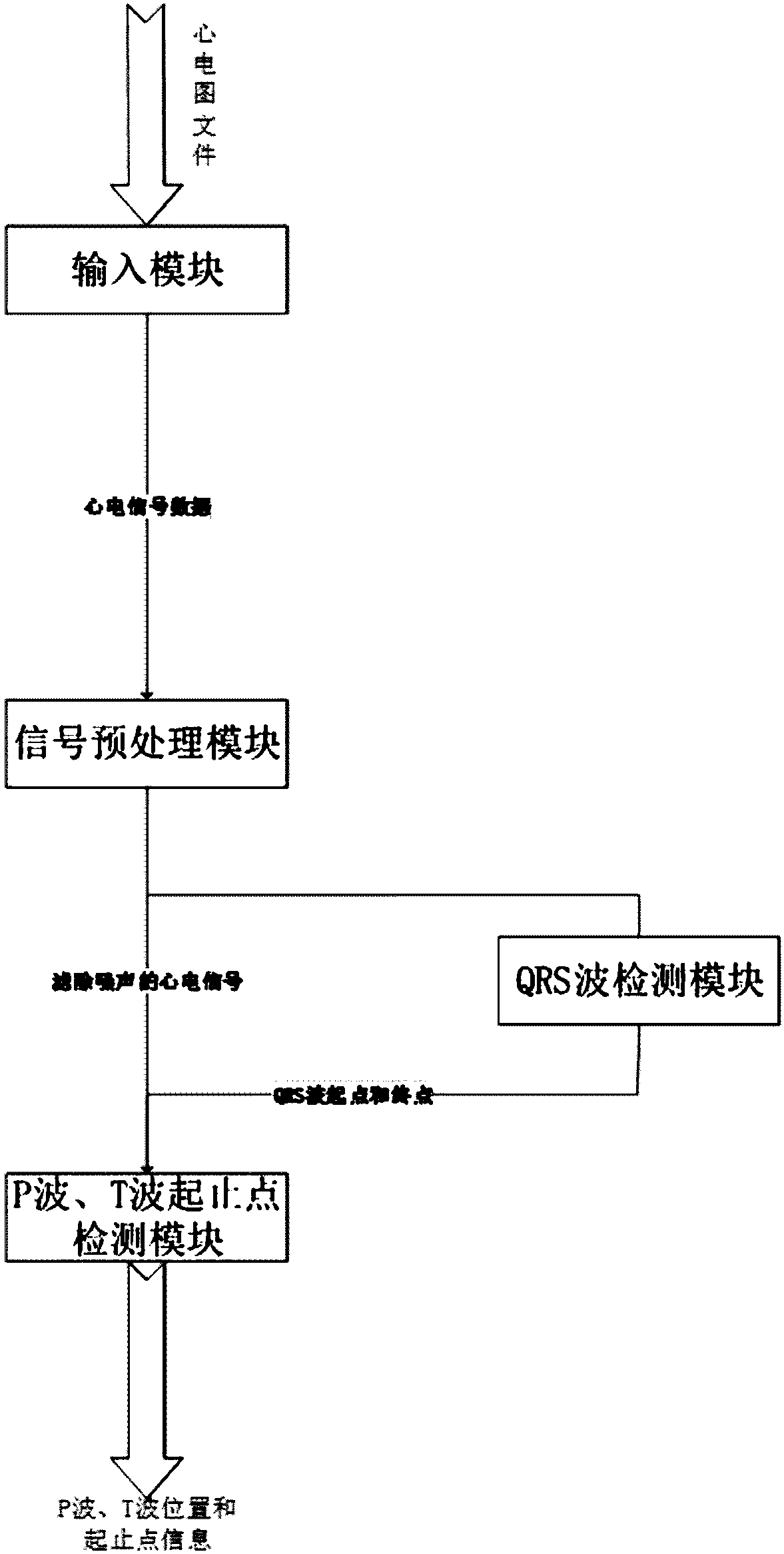
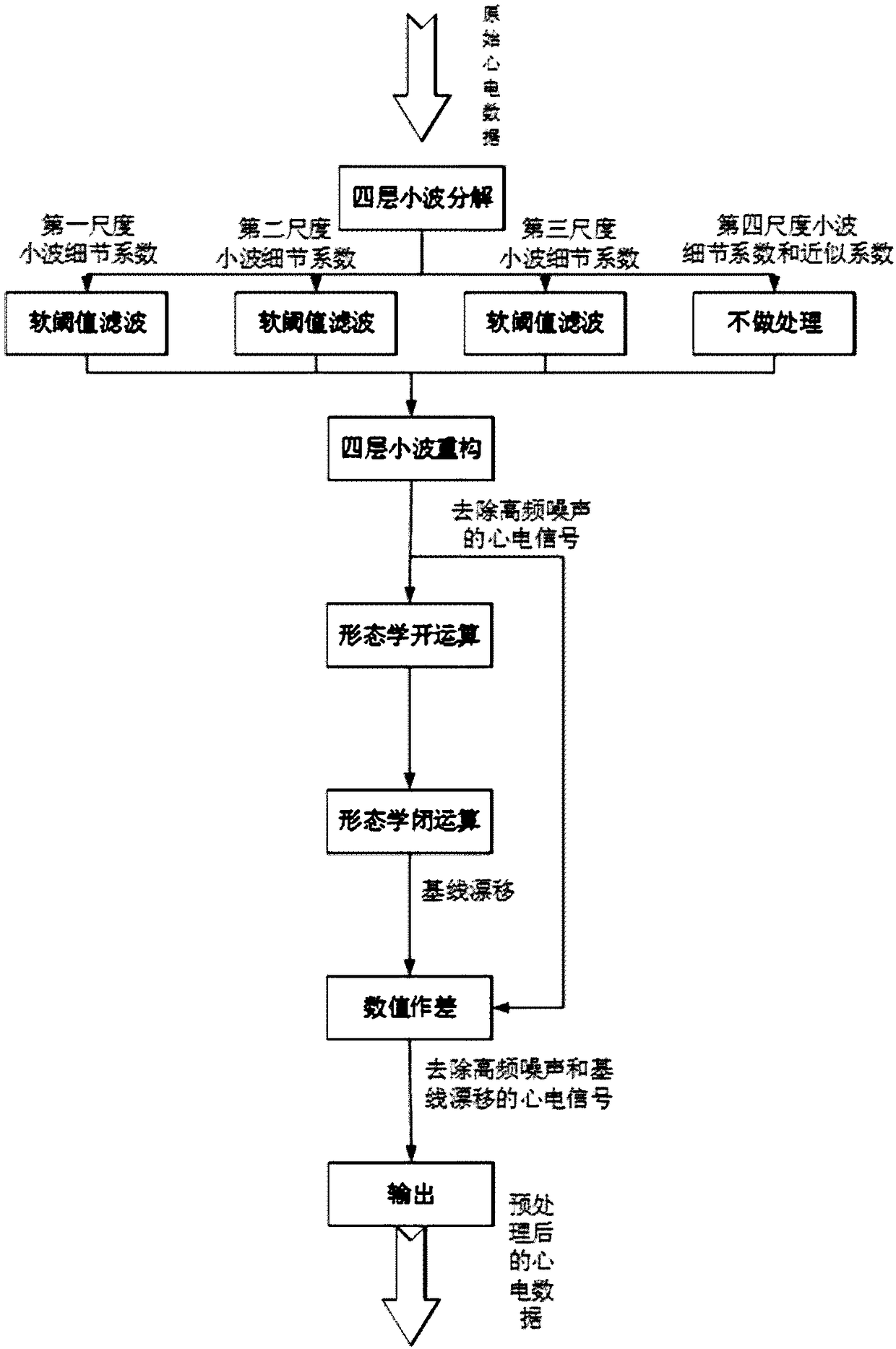
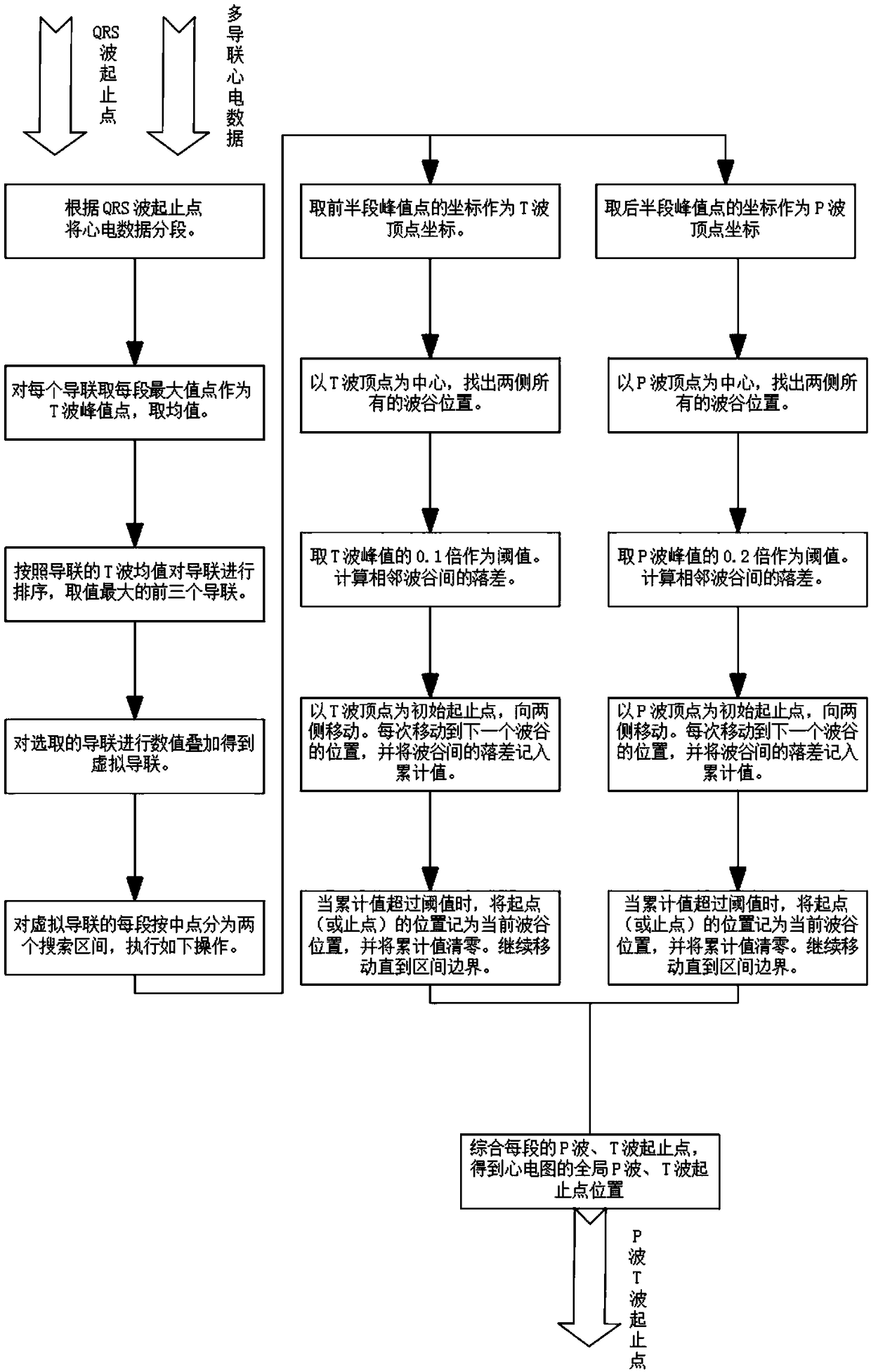
ActiveCN108294745AReduce distractionsImprove robustnessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method and system for detecting the start-end points of P-waves and T-waves in multi-lead ECG signals. The method includes the steps that firstly, according to the waveform and quality of each lead signal, three leads most suitable for P-wave and T-wave location and start-end detection are adaptively selected to be superimposed into a virtual lead; then, through the end point of the former one in two adjacent QRS waves and the start point of the latter one, the virtual lead is divided into a series of regions of search, it is determined that the first half of each region of search is a T-wave search range and the second half of each region of search is a P-wave search range, and the maximum peak values in the ranges are selected as the crests of corresponding characteristic waves; finally, the start-end points of P-waves and T-waves are detected respectively through an accumulative descent method based on dynamic thresholds. According to the method and system,by adopting the multi-lead adaptive selection technology, the robustness of the system is enhanced; by adopting the superposition-to-virtual-lead technology, the accuracy of detecting the start-end points of P-waves and T-waves is improved, and the number of algorithm detection times is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
System and method for detecting cardiac ischemia based on t-waves using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20070156056A1Reliable detectionSimple technologyElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsEcg signalT wave
A technique is provided for detecting episodes of cardiac ischemia based on an examination of the total energy of T-waves. Since cardiac ischemia is often a precursor to acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or ventricular fibrillation (VF), the technique thereby provides a method for predicting the possible onset of AMI or VF. Briefly, the technique integrates internal electrical cardiac signals occurring during T-waves and then compares the result against a running average. If the result exceeds the average by some predetermined amount, ischemia is thereby detected and a warning signal is provided to the patient. The maximum slope of the T-wave is also exploited. Techniques are also set forth herein for reliably detecting T-waves, which help prevent P-waves from being misinterpreted as T-waves on unipolar sensing channels. The T-wave detection technique may be used in conjunction with ischemia detection or for other purposes.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Methods and systems for analyzing t-wave alternants
InactiveUS20090318822A1Optimizing antiarrhythmia therapyReduce in quantityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyT waveInstability
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Detection method and system for detecting peak point of T waves as well as electrocardio monitoring system
ActiveCN102485172AConsistency measurePredict the likelihood of sudden cardiac deathDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalT wave
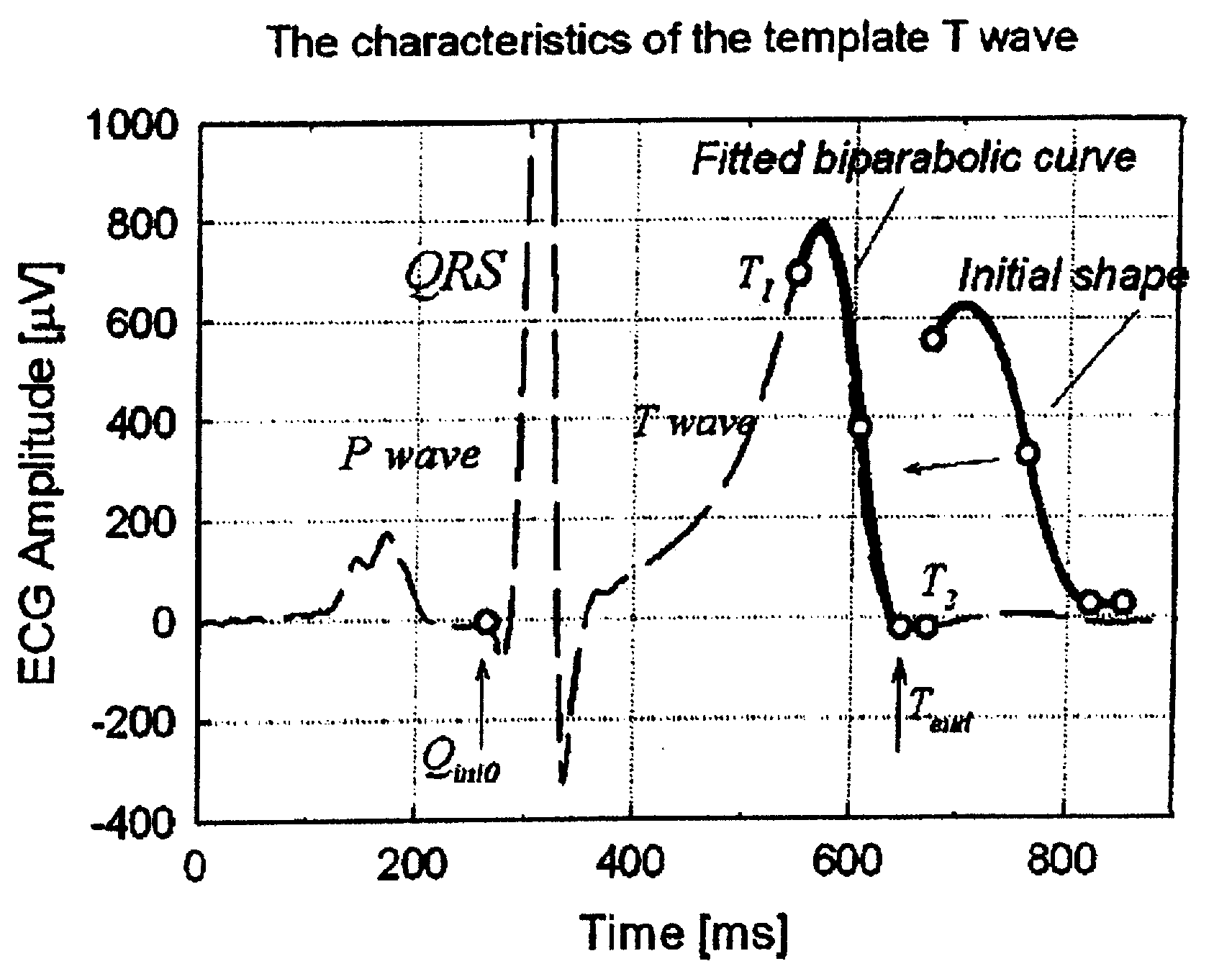
The invention discloses a detection method and a detection system for detecting a peak point of T waves from electrocardio signals, and also provides an electrocardio monitoring system based on the detection method. The detection method at least comprises the following steps of: obtaining electrocardio signals from a data collection device; selecting the electrocardio signals corresponding to the T waves in the electrocardio signals from the obtained electrocardio signals; fitting the T waves by a preset function, wherein the preset function comprises characteristic parameters requiring to be solved; solving the characteristic parameters by the selected electrocardio signals to obtain the fitted function; and obtaining the peak point of the T waves from the fitted function. A technical measure of using the preset function for fitting the T waves to obtain the dummy peak point of the T waves is used, so the technical problem of poor consistency when the traditional method is used for detecting the peak point of the T waves can be solved, and the technical effect of higher measurement consistency of the peak pint of the T waves is obtained.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
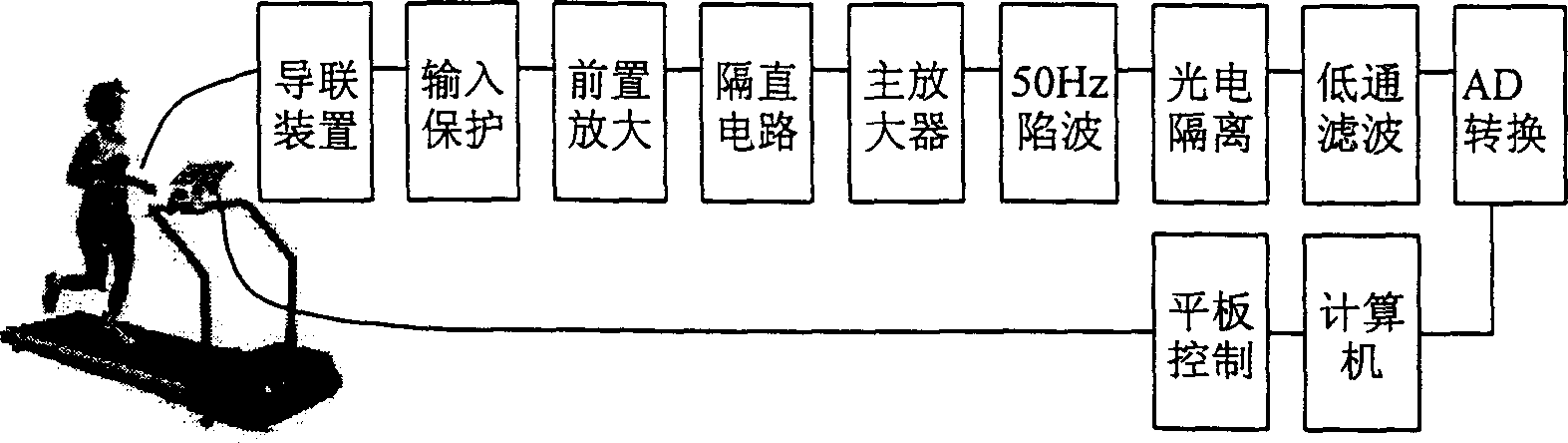
Alternating T-wave measuring method and device for sports electrocardiogram
The present invention belongs to the field of medical detection technology, and is the T-wave alternation detecting method and device for sports electrocardiogram. The method includes dividing into four stages of regulating one, first heart rate one, second heart rate one and restoring one; setting the sustaining period of each stage and controlling the moving speed and slope of the plate to makethe heart rate enter into the four stages successively and recording the electrocardiogram signal of both first heart rate stage and the second heart rate. The device includes connecting unit, input protector circuit, amplifier system, A / D converter, microcomputer and plate and plate control interface circuit. The present invention is used to detect T-wave alternation in microvolt level in T-wavealternation research and relevant clinical research.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Differentiating ischemic from non-ischemic T-wave inversion
A method of differentiating between ischemic and cardiac memory inverted T-waves includes performing an electrocardiogram of a patient; identifying inverted T-waves in at least some of precordial leads; identifying T-waves in leads I and aVL; diagnosing ischemia if leads I and aVL show inverted T-waves; and diagnosing cardiac memory if the leads I and aVL show non-inverted T-waves. The method may also include identifying T-waves in lead III; confirming ischemic diagnosis if the lead III shows deeper inverted T-waves than in the precordial leads; and confirming cardiac memory diagnosis otherwise.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
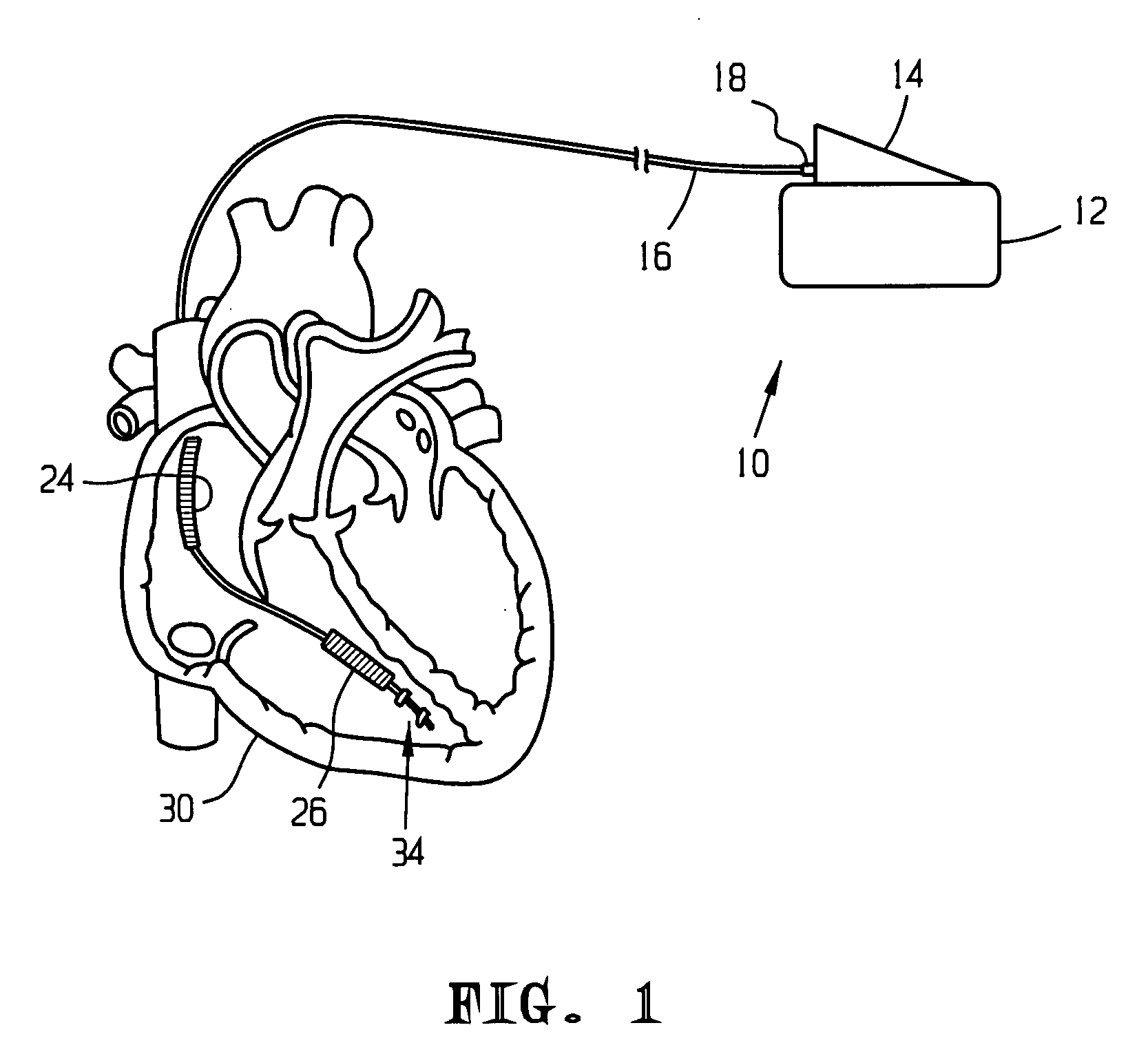
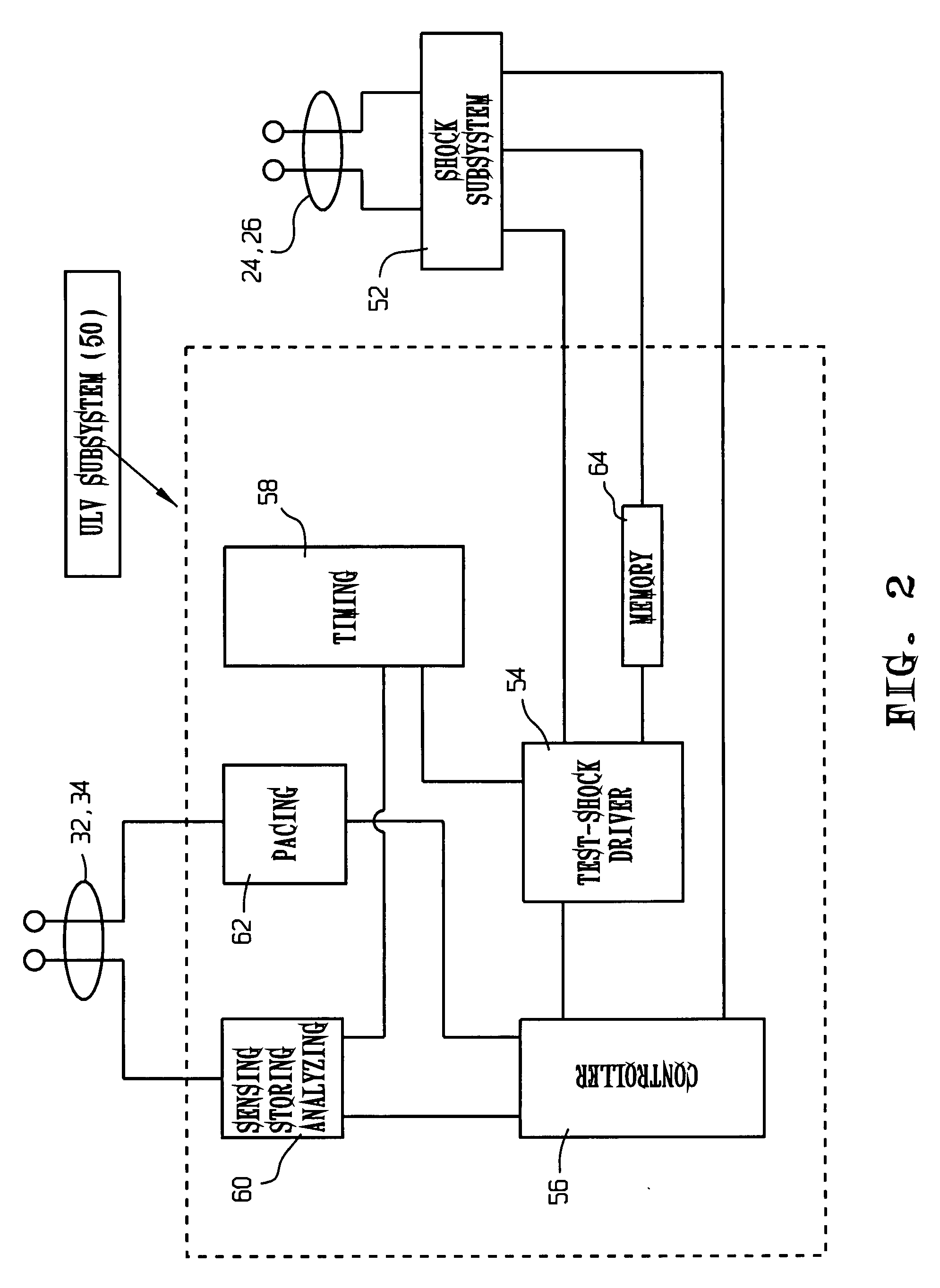
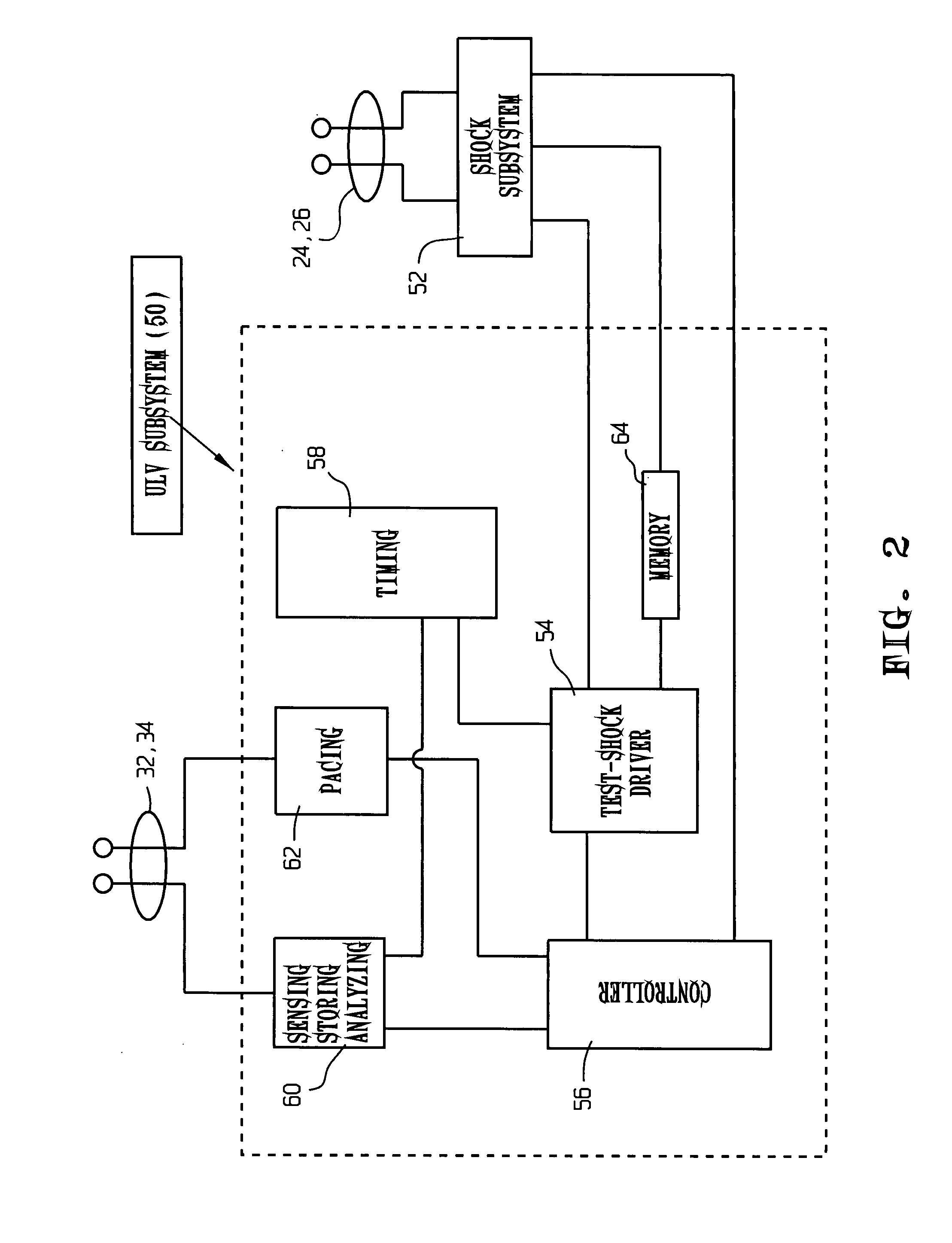
Defibrillation shock strength determination technology
InactiveUS20080051841A1Quickly and accurately determinesPractical and reliable and accurateElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsSpecific testT wave
A method for determining a cardiac shock strength, for example the programmed first-therapeutic shock strength of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), including the steps of sensing a change in a T-wave of an electrogram with respect to time such as the maximum of the first derivative of a T-wave of an electrogram; delivering a test shock by (i) delivering a test shock at a test-shock strength and at a test-shock time relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave with respect to time; and (ii) sensing for cardiac fibrillation. If fibrillation is not sensed, test-shock delivery is repeated at the same test-shock strength and at specific, different test-shock times relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave. If fibrillation is still not sensed, the shock strength is decreased and test shocks are repeated at the same specific test shock times relative to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave. And if fibrillation is sensed, the programmed therapeutic shock strength of the ICD is set as a function of the incrementally greater test-shock strength. Also disclosed is an apparatus for selecting a programmed first-shock strength of an ICD, including a shock subsystem for delivering therapeutic shocks and test shocks to the heart, and a ULV subsystem connected to the shock subsystem, to provide test shocks of test-shock strengths and at test-shock times relating to the maximum of the first derivative of the T-wave with respect to time, and to determine the therapeutic shock strength of the ICD as a function of the test-shock strengths.
Owner:IMPERCEPTION
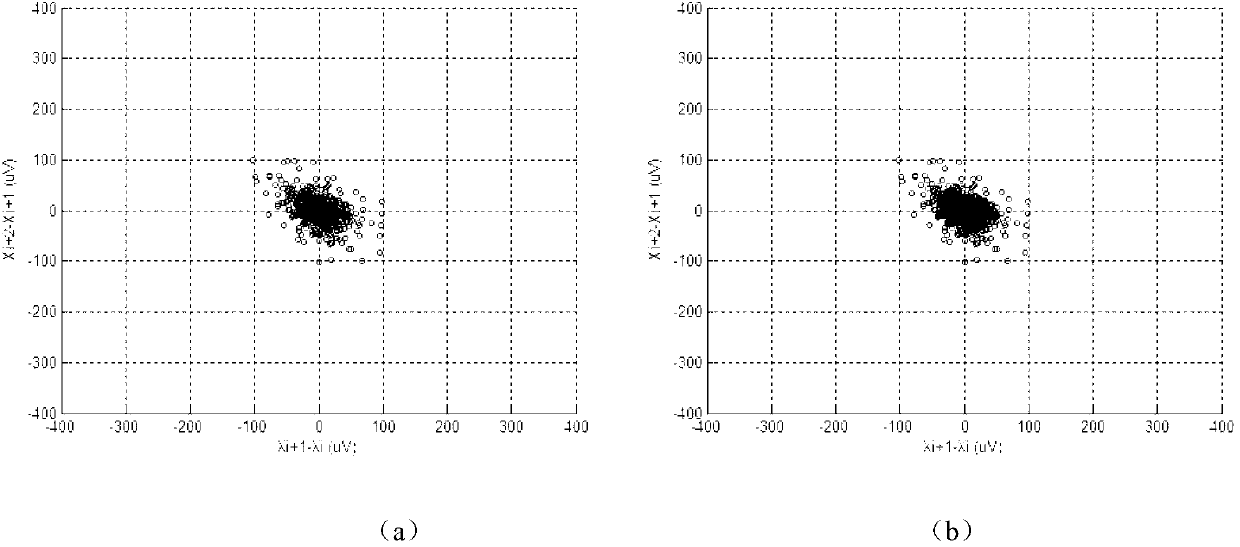
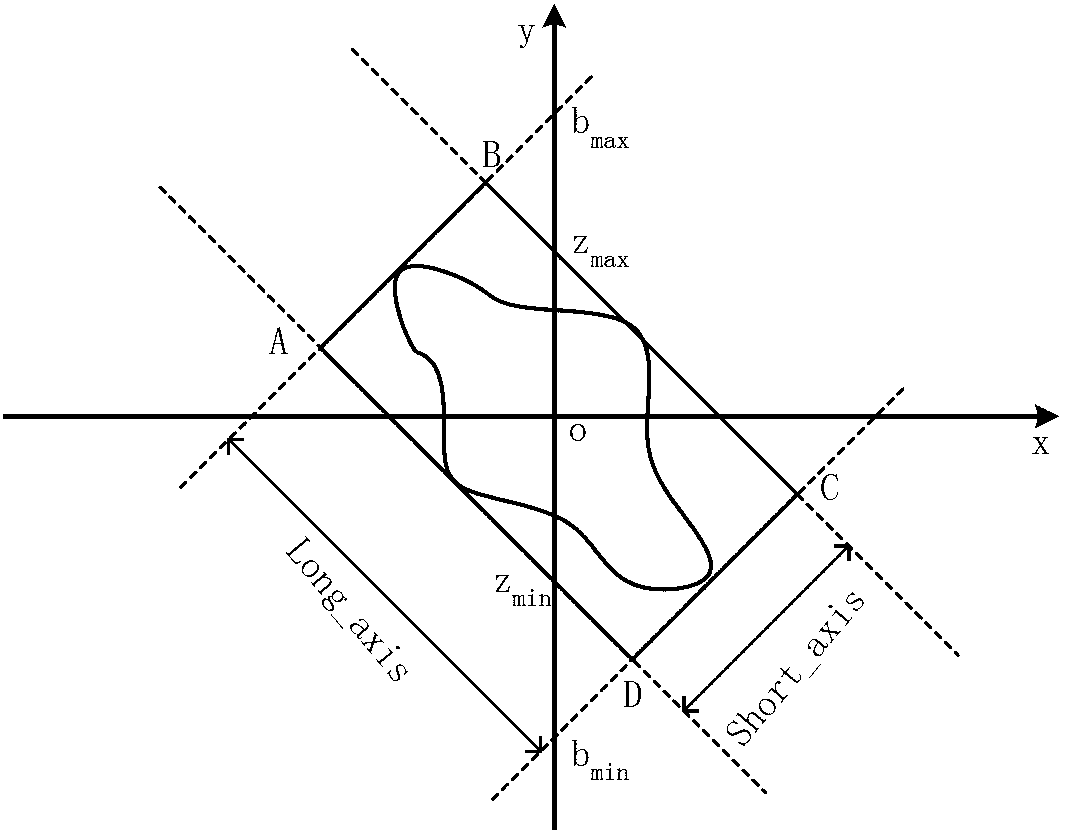
Method for quantitatively detecting microvolt T-wave alternans
InactiveCN103006206ANo high quality requirementsSimple calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPoint sequenceT wave
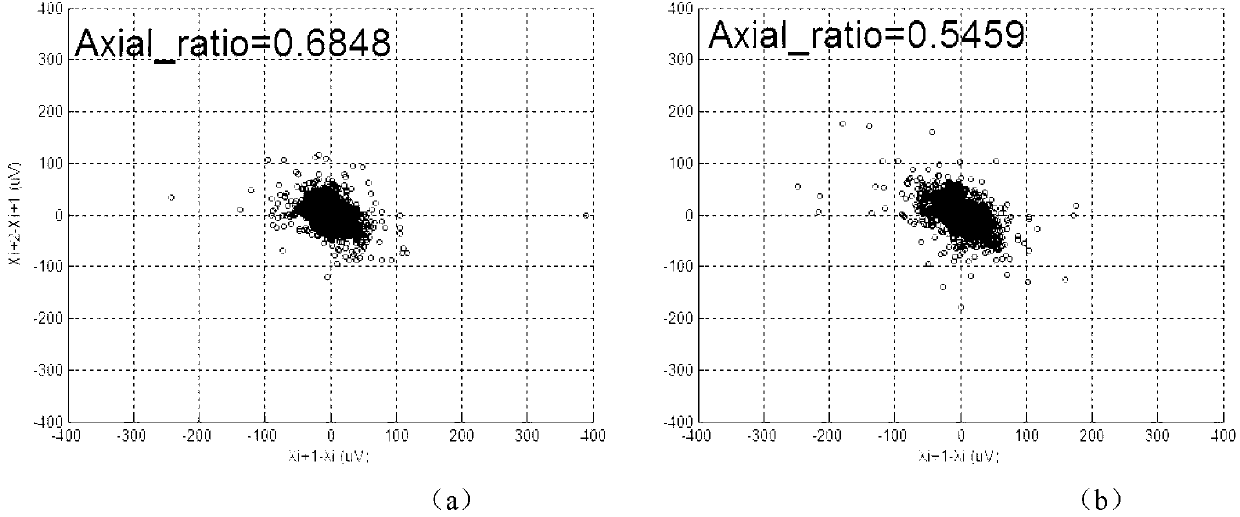
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting microvolt T-wave alternans. A new effective quantitative TWA (T-wave alternans) detection index is provided by analyzing external shape of a T-wave alternans scatter diagram according to the relation of the external shape and the T-wave alternans. By means of improved T-wave window analysis method, the method includes: subjecting 128 continuous heartbeat T-wave sampling point sequences to first difference and drawing a scatter diagram, analyzing the relation of the external shape of the scatter diagram and the T-wave alternans, researching an effective 'cross searching method' to subject the scatter diagram to edge extraction, then defining three quantitative parameters of short axis, long axis and the ratio of the short axis to the long axis at the 'edge' of the scatter diagram, utilizing the ratio of the short axis to the long axis as quantitative detection index Axial_ratio, and finding a proper threshold to judge whether the T-wave alternans exist or not.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
R wave detection algorithm based on extremum field mean mode decomposition and improved Hilbert enveloping
InactiveCN103190901AImprove detection accuracyFast operationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalElectricity
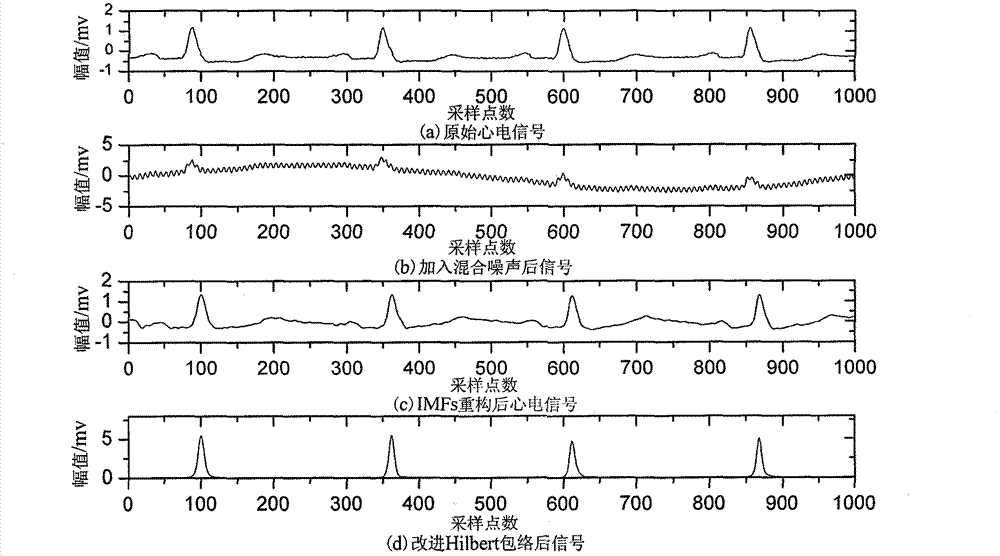
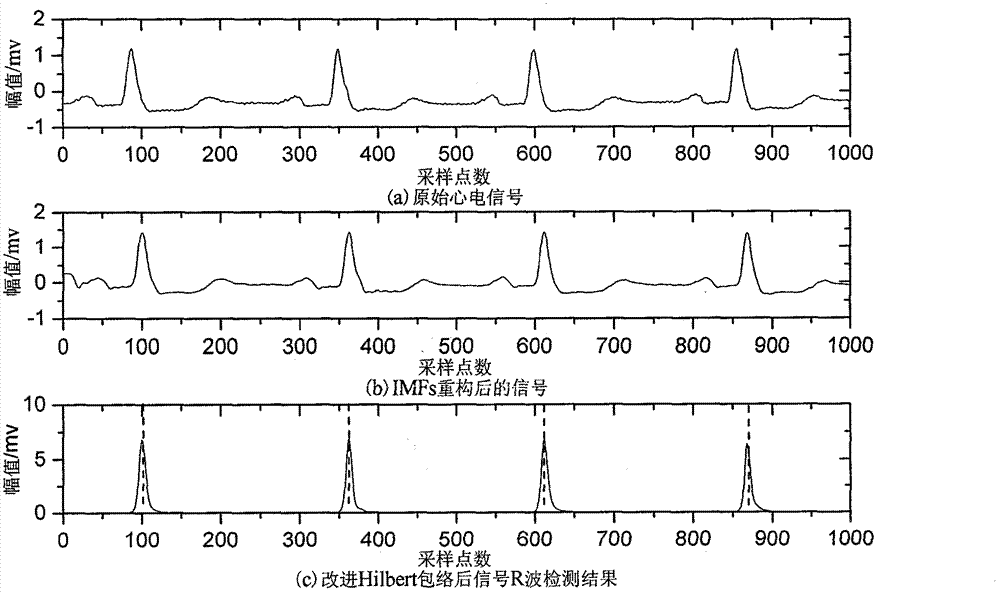
The invention discloses an R wave detection algorithm based on extremum field mean mode decomposition and improved Hilbert enveloping and belongs to the technical field of weak biological signal processing. An electrocardio signal pre-processing algorithm based on the extremum field mean mode decomposition and the improved Hilbert enveloping and an R wave detection algorithm based on slope threshold are provided. Detection criteria are set according to wave form characteristics and time domain distribution characters of electrocardio signals, and positions of R waves with most obvious characters and highest information amount in the electrocardio signals are detected. An extremum field mean mode decomposition algorithm improves empirical mode decomposition speed and can effectively restrain mode superimposition and boundary effect. The improved Hilbert enveloping can effectively restrain interference of noise and other characteristic waves an can also enhance energy of the R waves. The R wave detection algorithm based on the extremum field mean mode decomposition and the improved Hilbert enveloping can also detect positions of R points accurately even if interference of strong noise and large P / T waves exists. A Massachusetts institute of technology-Beth Israel hospital (MIT-BIH) data base is used for detecting the R wave detection algorithm. Sensitivity of the R wave detection algorithm is 99.94%, and positive predictive rate is 99.87%.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
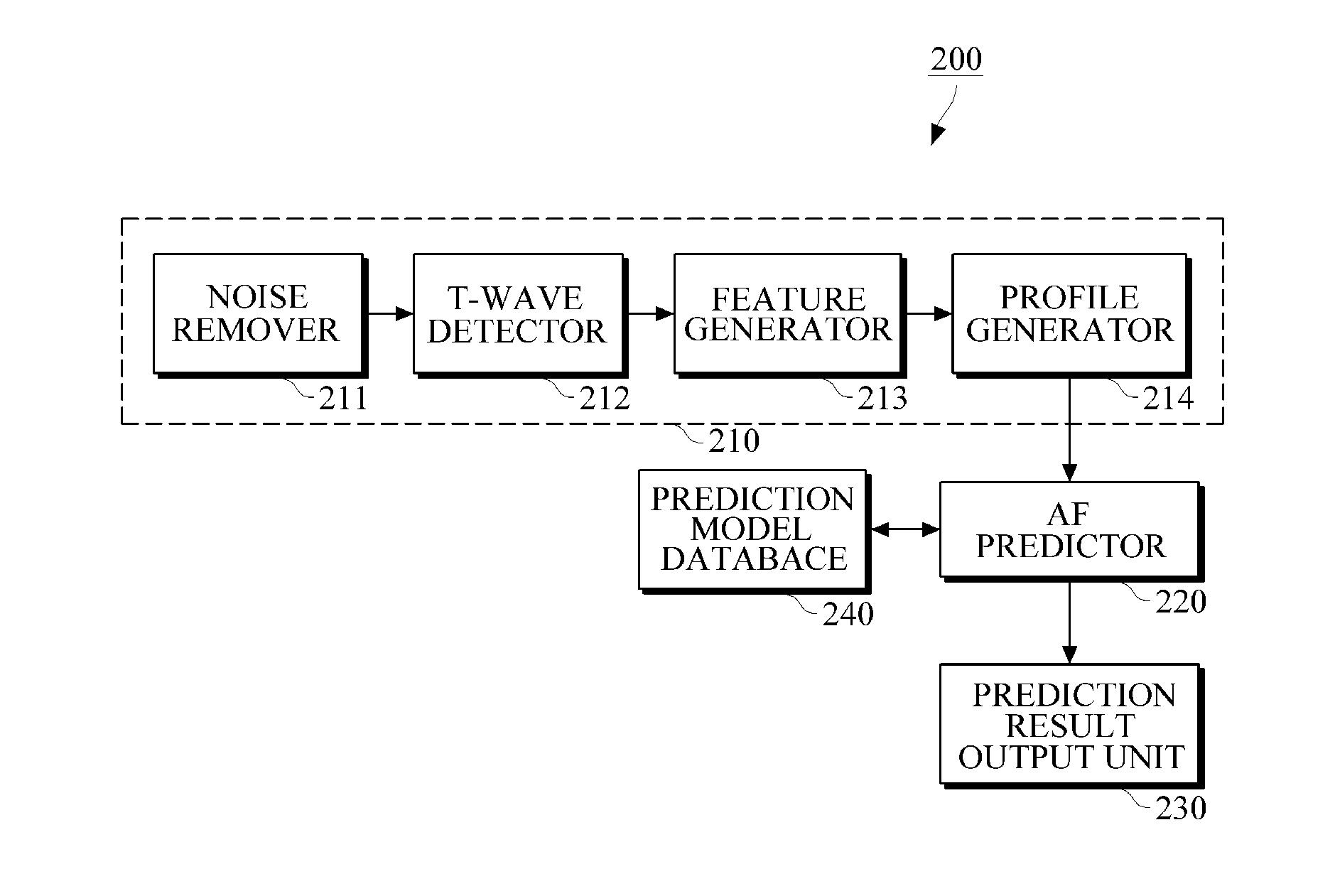
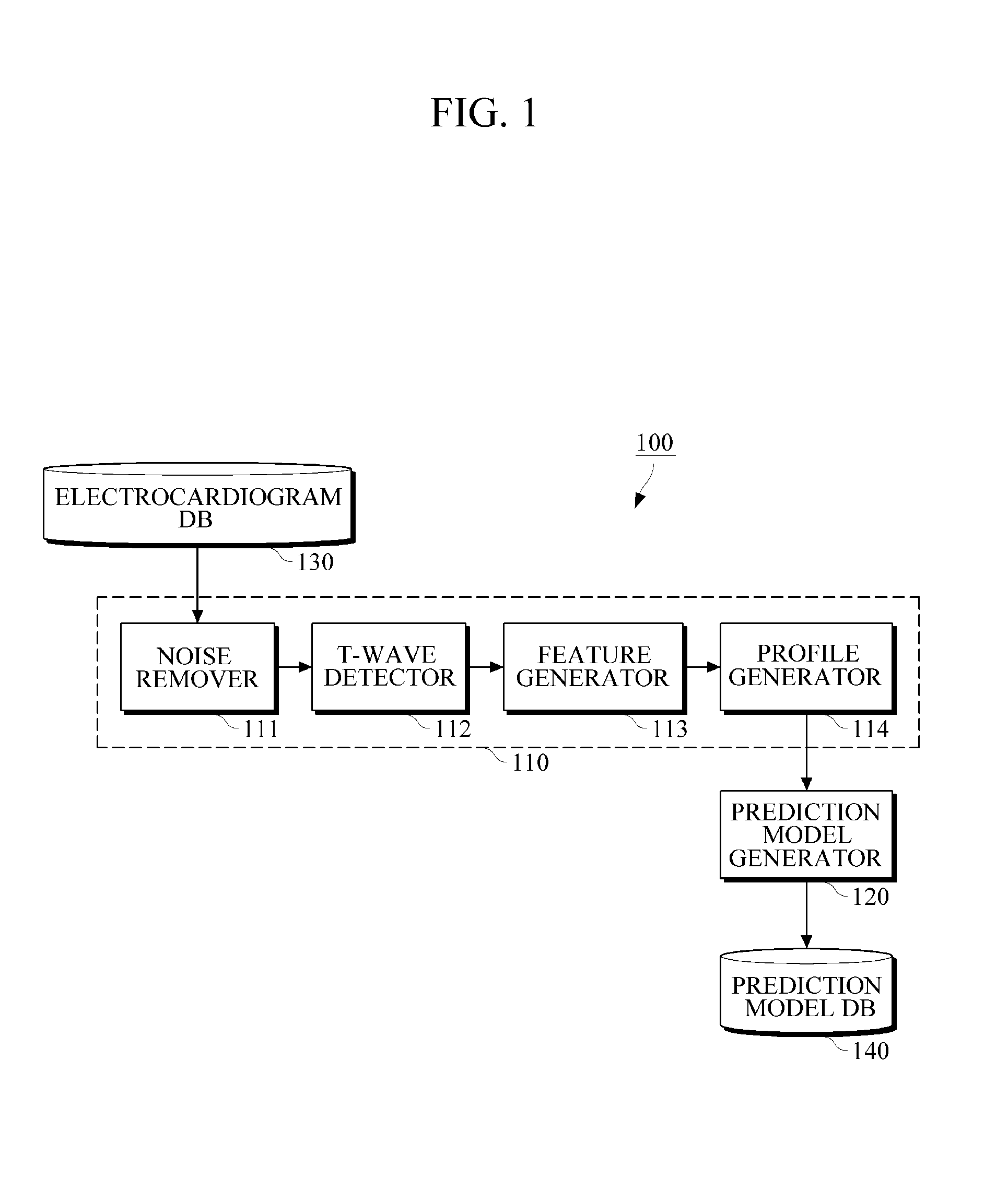
Apparatus and method for generating atrial fibrillation prediction model, and apparatus and method for predicting atrial fibrillation
An apparatus and a method to generate an atrial fibrillation prediction model, and an apparatus and a method to predict atrial fibrillation are provided. An atrial fibrillation (AF) prediction model generating apparatus includes a feature extractor configured to extract T-wave features in a predetermined time period from electrocardiogram data and generate a T-wave feature profile based on the extracted features, and a prediction model generator configured to classify the generated T-wave feature profile and generate an AF prediction model using the classified feature profile.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Alternating T-wave measuring method for sports electrocardiogram
The present invention belongs to the field of medical test technology, and the T-wave alternation measuring method for sports electrocardiogram beings from the No.113 beat of electrocardiogram signaland analyzes in 16 beats as one analysis window unit. Maximum heart rate is first judged to estimate the noise level. The power spectrum is then analyzed and judged based on noise, whether to exist obvious RR interphase alternation is judged, and if no, the ratio of component at 0.25 and the alternative component before deducing noise level is calculated. When the ratio is smaller than some value, obvious T-wave alternation is considered found out. The method of the present invention solves the problem of detecting weak T-wave alternation signal for predicting malignant arrhythmia.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com