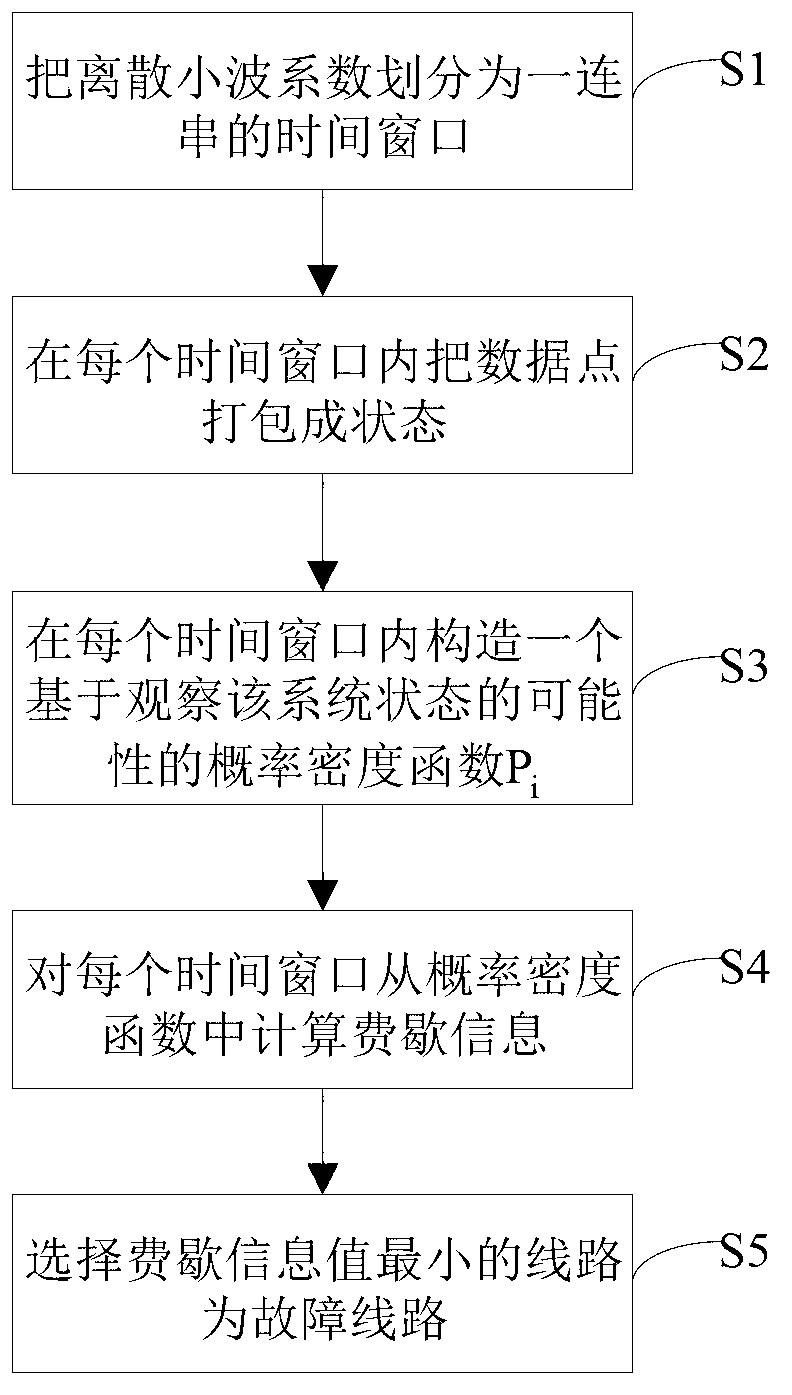
Small current grounding system single-phase ground fault line selection method based on fisher information
A single-phase grounding fault, small current grounding technology, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve the problems of inconspicuous fault characteristics, weak fault signals, and difficulty in obtaining satisfactory results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0067] Example 1: An example of line selection for a single-phase ground fault in a neutral point ungrounded system.
[0068] Assume that the three outgoing lines of the 35kv / 10kv neutral point ungrounded system are L1, L2 and L3, and the positive sequence parameter of the line is R 1 =0.484Ω / km, L 1 =0.3454mH / km, C 1 =0.0345μF / km, zero sequence parameter R 0 =1.16Ω / km, L 0 =1.10362mH / km, C 0 =0.0219μF / km, other parameters are the same as above.
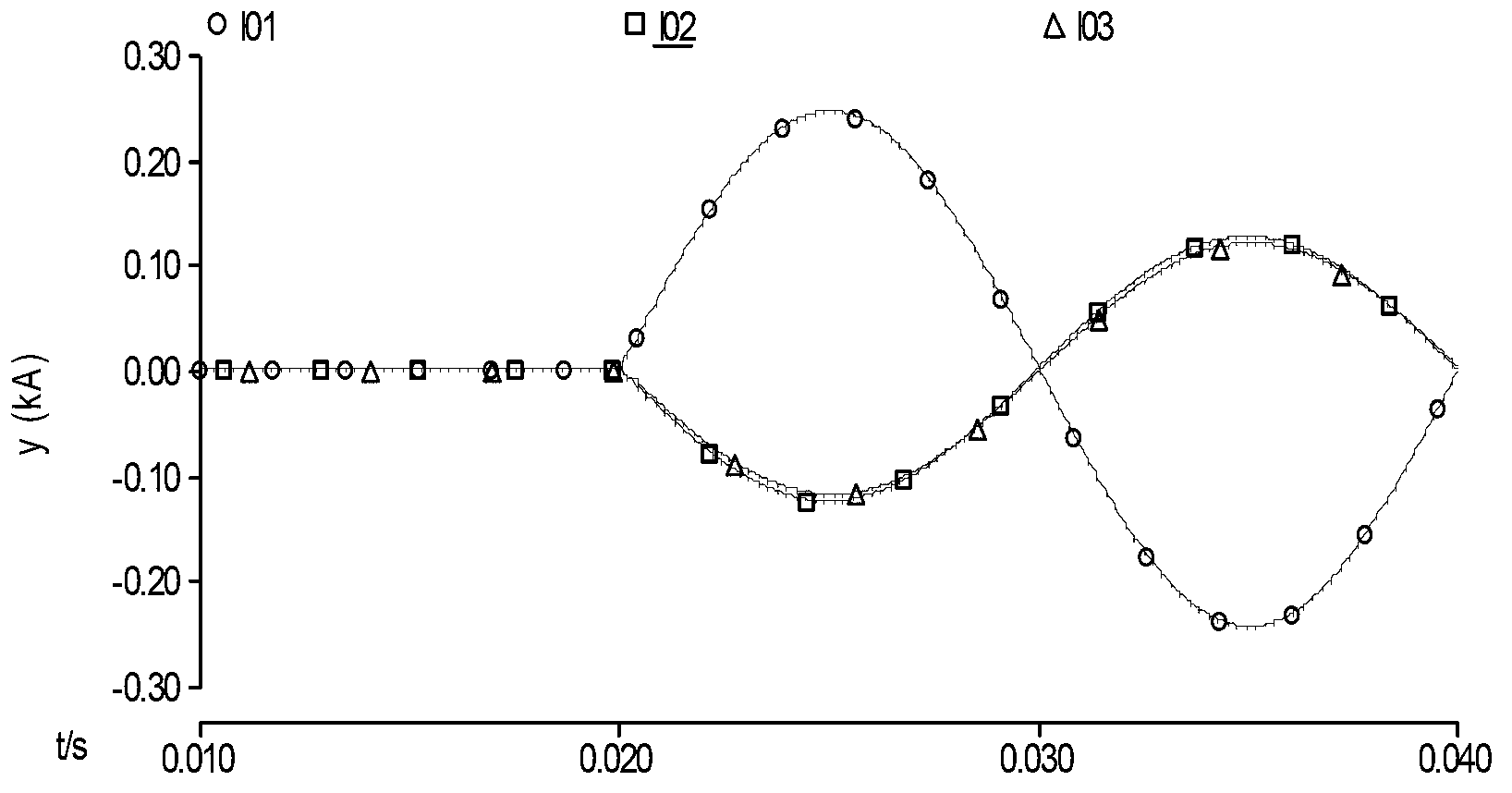
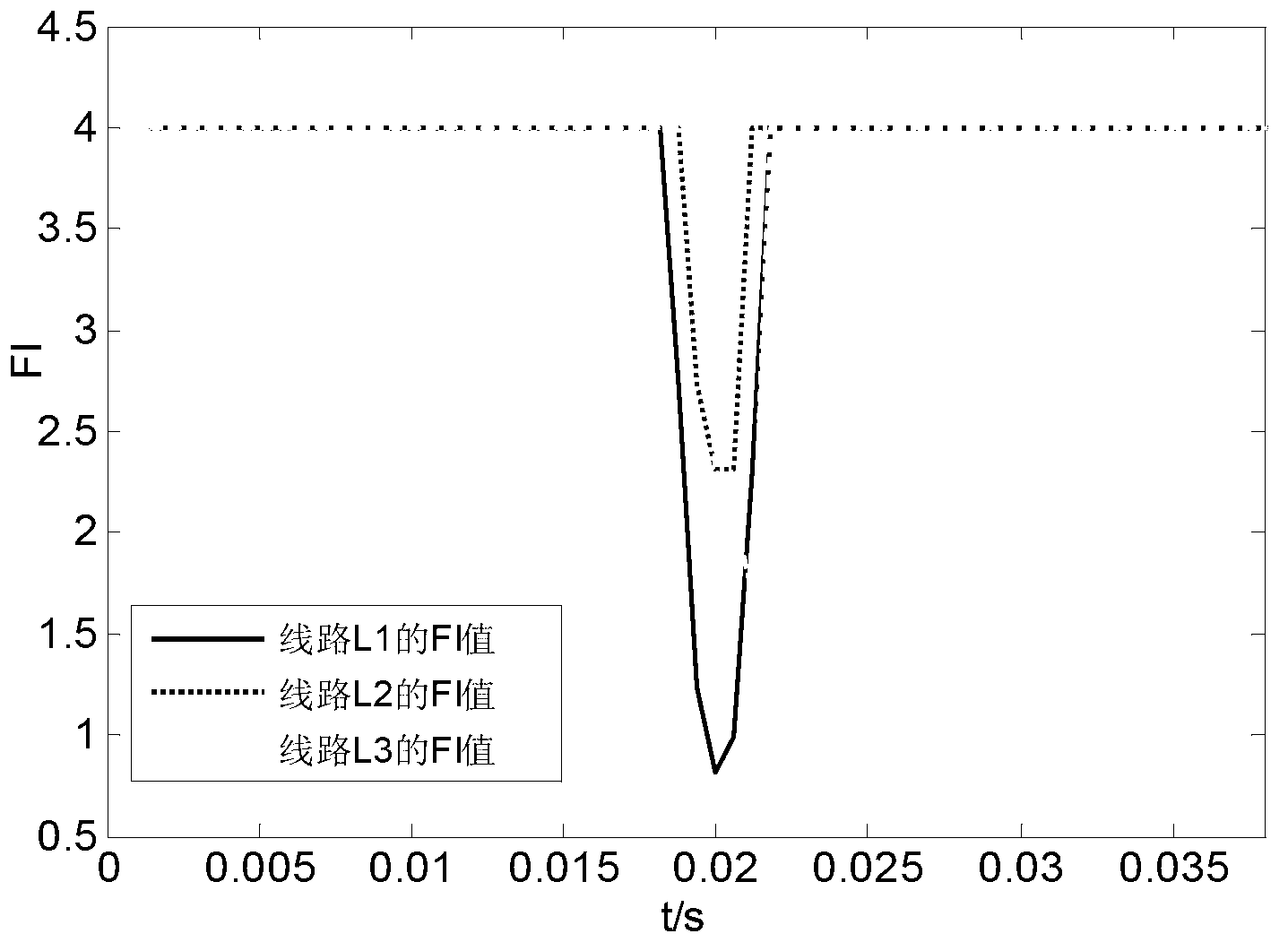
[0069] figure 2 It shows the zero-sequence current waveforms I01, I02, and I03 of each line when a single-phase ground fault occurs on line L1 at a distance of 10km from the busbar. image 3 Shown is the FI value (that is, the Fischer information value) calculated by the above method for the zero-sequence current signal of each line.
[0070] Figure 4 Shown is the zero-sequence current waveforms I01, I02, and I03 of the three lines when a single-phase ground fault occurs on line L1 at a distance of 20km from the busbar, the...
example 2
[0071] Example 2: An example of line selection for a single-phase ground fault in a neutral point grounded system through an arc suppression coil.
[0072] Table 1 lists the line selection results of the neutral point through the arc suppression coil grounding system under different fault conditions. When the arc suppression coil is grounded, the overcompensation method is adopted, and the compensation degree is 8%. Other parameters are the same as above.
[0073] Table 1: Line selection results of the neutral point through the arc suppression coil grounding system
[0074]
[0075] It can be seen from the above embodiments that the present invention uses a dimensionless non-negative positive number as a single criterion to realize the problem of line selection for single-phase grounding faults in small current grounding systems. Compared with the prior art, it has the following advantages:
[0076] Under different grounding methods, it can effectively distinguish the faul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com