A method for measuring the magnetic field intensity of martensitic transformation induced in steel at constant temperature
A technology of martensitic phase transformation and magnetic field strength, applied in the direction of the size/direction of the magnetic field, magnetic performance measurement, etc., can solve the problem that the constant temperature is difficult to control accurately
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0028] (1) Pretreatment of steel
[0029] 15.5Cr-4.8Mo-8.2Co-3.1Ni low carbon steel was selected, and after vacuum melting treatment in the early stage, it was cast into a 100 kg material ingot, and high temperature forged into a bar with a diameter of about 22 mm. Cut the bar stock into cylindrical samples with a diameter of 20mm and a length of 15mm. The quenching temperature of the cylindrical sample was 1 080 ℃, and the holding time was 40 min. The quenched low-carbon steel cylinder sample was cut into block samples with a diameter of 3 mm and a length of 3 mm by electric discharge method.
[0030] (2) Magnetic test
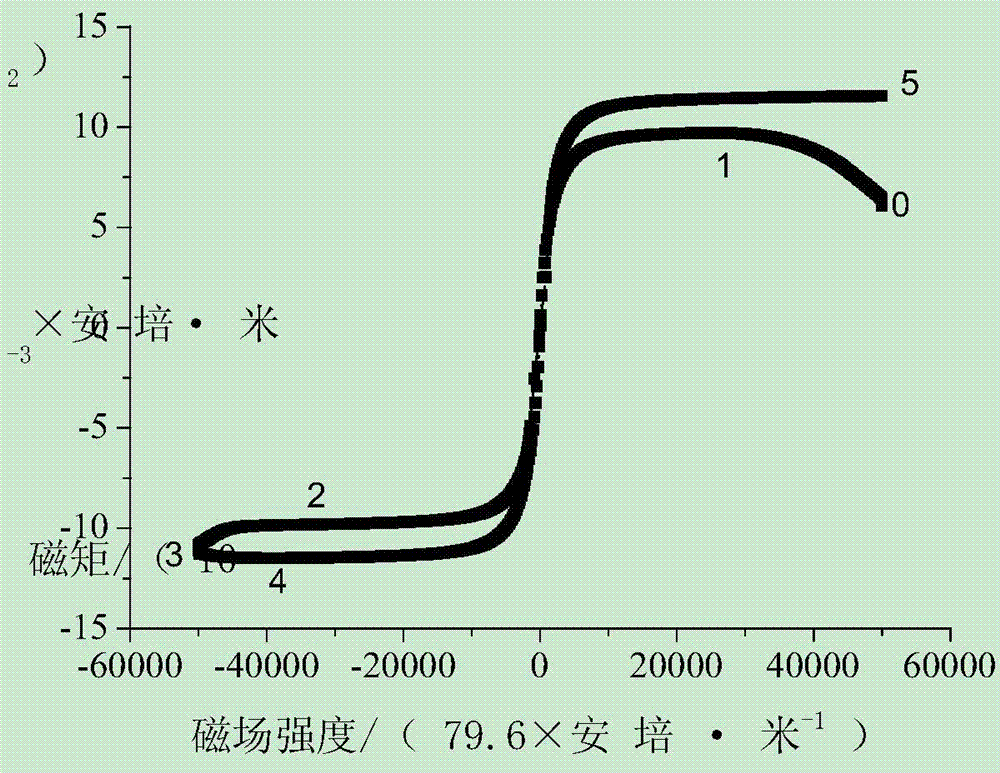
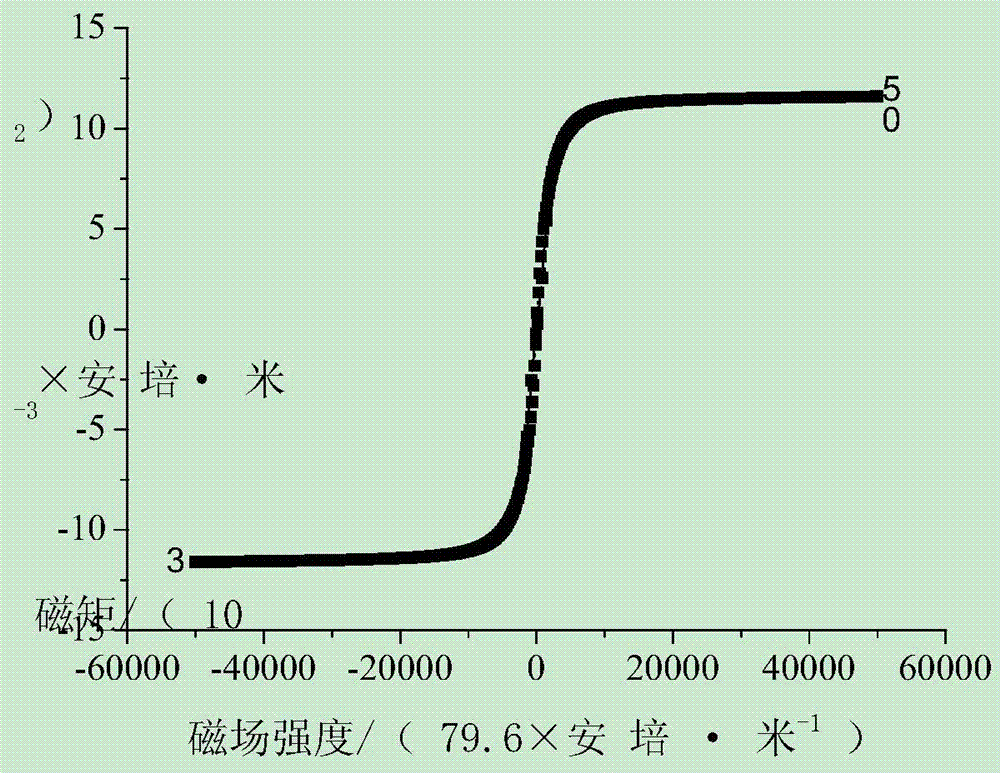
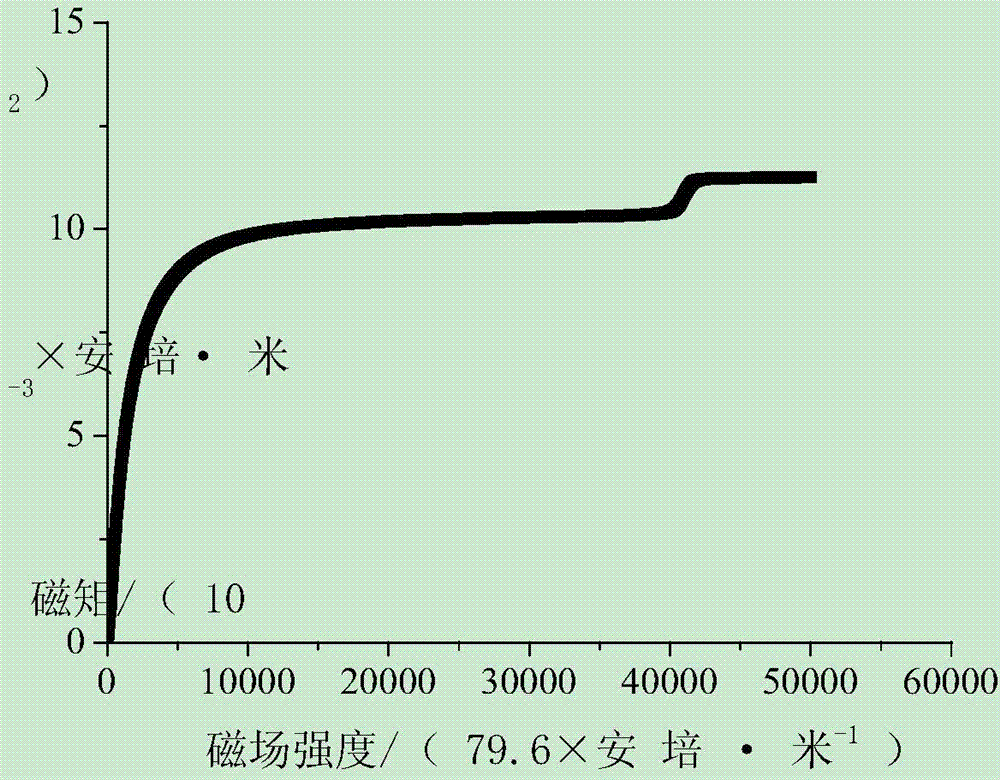
[0031] Install the vibrating sample magnetometer on the comprehensive physical property measurement system, and conduct a magnetic test on the above-mentioned samples. The form of the magnetic test is constant temperature M-H curve (hysteresis loop).
[0032] Test conditions: constant temperature (30...
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Pretreatment of steel
[0041] Select 15.5Cr-4.8Mo-8.2Co-3.1Ni low carbon steel, after the vacuum melting treatment in the early stage, cast it into 100 kg material ingot, and forge it into a bar with a diameter of about 22 mm at high temperature. Cut the bar into a cylindrical sample with a diameter of 20mm and a length of about 15mm. The quenching temperature of the cylindrical sample was 1060 °C, and the holding time was 40 min. The quenched low-carbon steel cylinder sample was cut into block samples with a diameter of 3 mm and a length of 3 mm by electric discharge method.
[0042] (2) Magnetic test
[0043] Install the vibrating sample magnetometer on the comprehensive physical property measurement system, and conduct a magnetic test on the sample. The form of the magnetic test is constant temperature M-H curve (magnetization curve).
[0044] Test conditions: constant temperature (300K); maximum external magnetic field strength: 50 000 Oe; changing field ra...
Embodiment 3
[0049] (1) Pretreatment of steel
[0050] 15.5Cr-4.8Mo-8.2Co-3.1Ni low carbon steel was selected, and after vacuum melting treatment in the early stage, it was cast into a 100 kg material ingot, and high temperature forged into a bar with a diameter of about 22 mm. Cut the bar into a cylindrical sample with a diameter of 20mm and a length of about 15mm. The quenching temperature of the cylindrical sample was 1040 °C, and the holding time was 40 min. The quenched low-carbon steel cylinder sample was cut into block samples with a diameter of 3 mm and a length of 3 mm by electric discharge method.
[0051] (2) Magnetic test
[0052] Install the vibrating sample magnetometer on the comprehensive physical property measurement system, and conduct a magnetic test on the sample. The form of the magnetic test is constant temperature M-H curve (magnetization curve).
[0053] Test conditions: constant temperature (300K); maximum external magnetic field strength: 50 000 Oe; changing f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com