Photoinduced bending flexible electro-conductive baseplate and preparation method thereof
A photobending and flexible conductive technology, applied in the field of bionics, can solve the problems of no conductive substrate, failure of photobending actuators or robot integration and miniaturization, and achieve the effect of accelerating application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
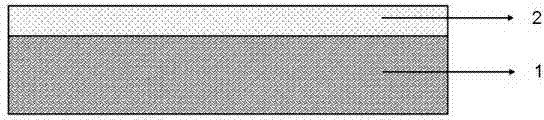
[0036] like figure 1 As shown, the photobending flexible substrate 1 of the substrate is a cross-linked liquid crystal polymer, the conductive layer 2 is carbon nanotubes, and the thickness of the conductive layer is 200 nm. The entire device structure is described as:
[0037] Cross-linked liquid crystal polymer / carbon nanotubes
[0038] The preparation method is as follows:
[0039] ① Use acetone, ethanol solution and deionized water to ultrasonically clean the surface of the glass substrate with a surface roughness less than 1 nm, and blow dry with dry nitrogen after cleaning.
[0040] ② The conductive layer of carbon nanotubes was prepared by spin-coating. The spin-coating speed was 1000 rpm, the duration was 30 s, and the film thickness was 200 nm. Then, the substrate was thermally annealed at 130 °C;
[0041] ③ Drop-coat the cross-linked liquid crystal polymer on the substrate, first heat the substrate to 100°C for 10 minutes. Then cool down to the clearing point of ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] like figure 1 As shown, the photobending flexible substrate 1 of the substrate is liquid crystal gel, the conductive layer is silver nanowires, and the thickness of the conductive layer is 180 nm. The entire device structure is described as:
[0047] Liquid crystal gel / silver nanowire
[0048] The preparation process is similar to Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0050] like figure 1 As shown, the photobending flexible substrate 1 of the substrate is a liquid crystal elastomer, the conductive layer 2 is silver nanowires, and the thickness of the conductive layer is 160 nm. The entire device structure is described as:
[0051] Liquid crystal elastomer / gold nanowire
[0052] The preparation process is similar to Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com