Method for manufacturing light emitting device
A light-emitting device and manufacturing method technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as reduced luminous efficiency, reduced surface cleanliness of lower electrodes, and changes in surface oxidation degree, so as to improve luminous efficiency , reduce the effect of display failure and reduce the degree of reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] Various exemplary embodiments, features, and aspects of the invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
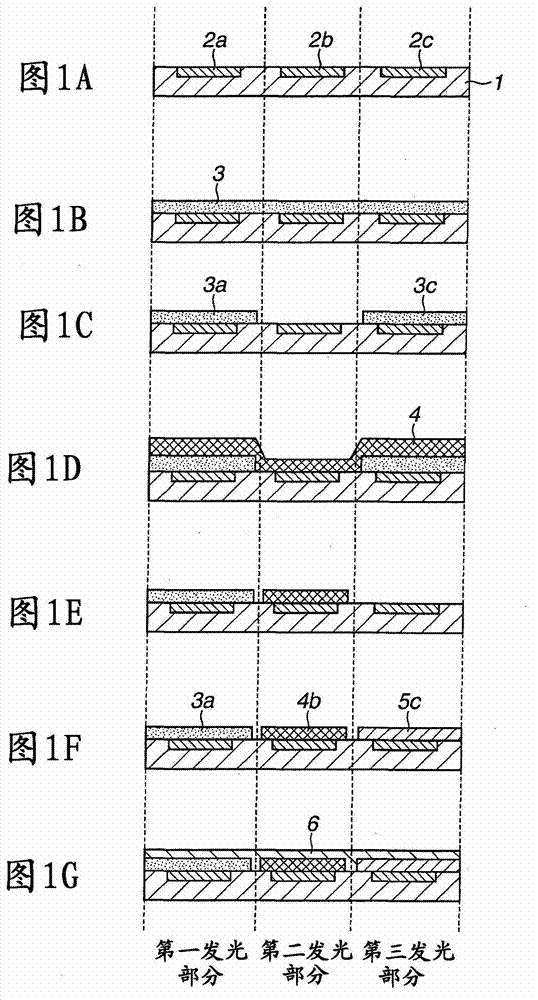
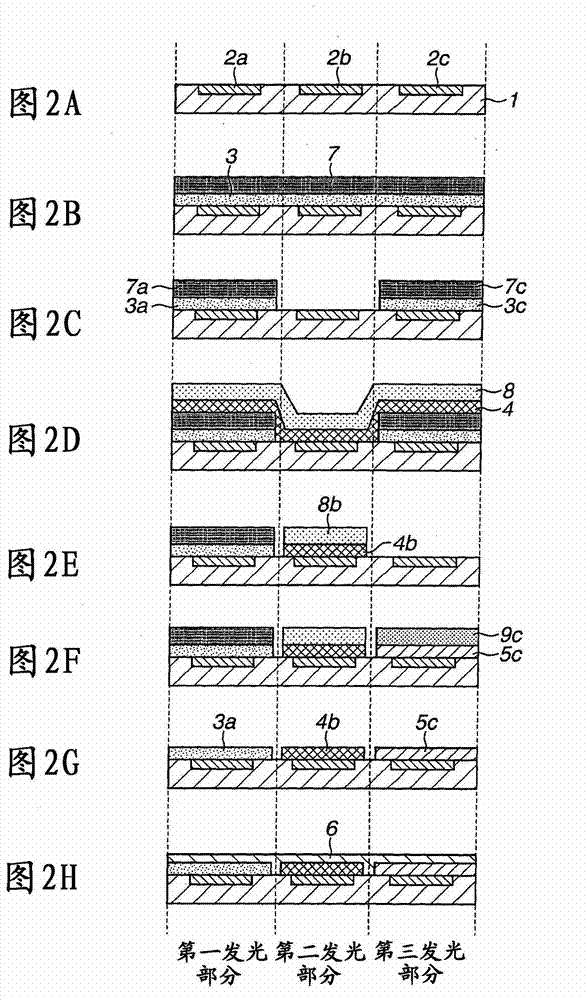
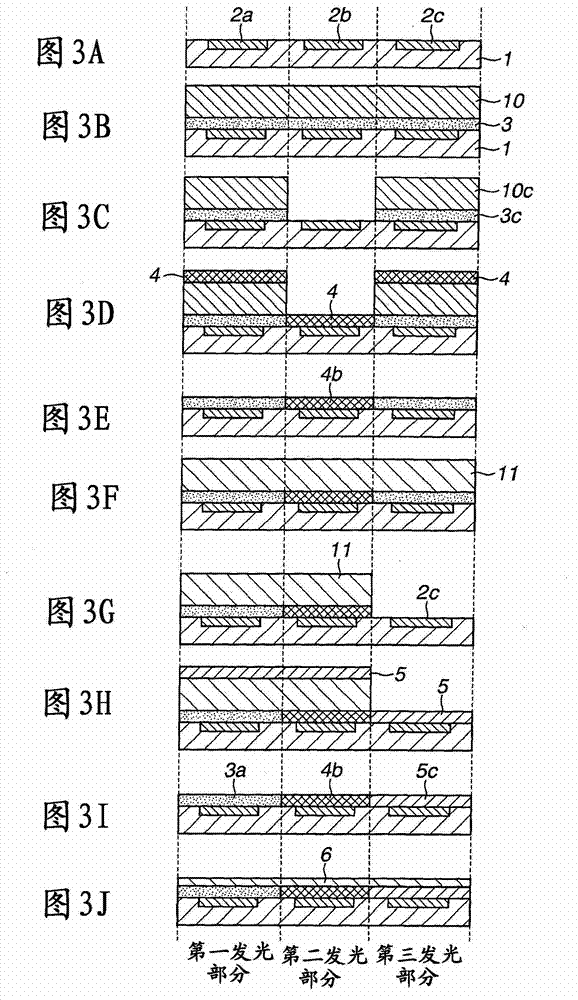
[0023] A light-emitting device manufactured by the method according to the present invention includes a light-emitting element typified by an organic electroluminescent element. The organic electroluminescent element includes a layer including an organic substance between a lower electrode and an upper electrode, and the organic substance includes an electroluminescent material of one of red, blue, or green. Three types of organic EL elements emitting light of these different colors are integrated as a group to constitute a pixel. In the case of an active matrix display device, a plurality of lower electrodes are individually formed on a substrate, and voltages are applied independently. The upper electrode is commonly used for all light emitting elements. In the case of a passive matrix, upper and lower electrodes are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com