Magnesium or magnesium alloy-porous hydroxyapatite composite and preparation method thereof
A technology of porous hydroxyapatite and hydroxyapatite, which is applied in heat exchange equipment, stators, transmissions, etc., can solve the problems of inability to guarantee the dual connectivity of hydroxyapatite, the existence of porous morphology, and limited osteoinductivity , to achieve the effect of increasing strength, avoiding fragmentation, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
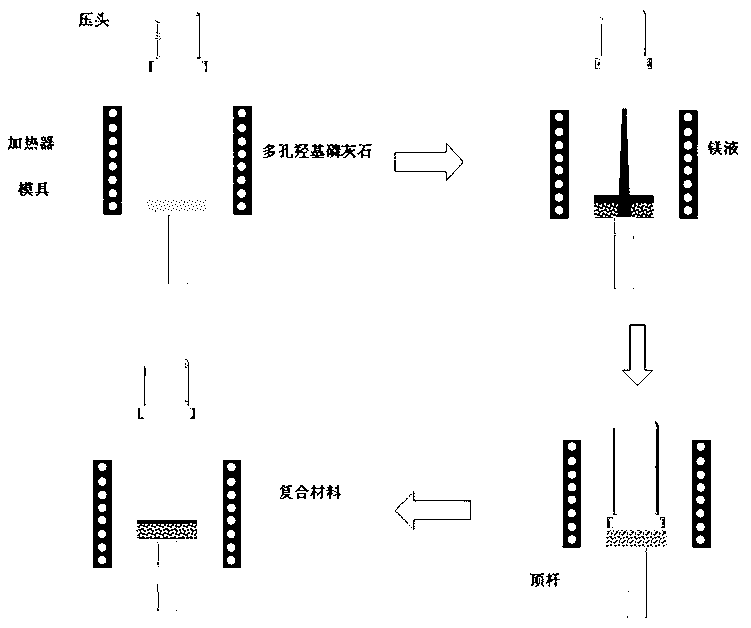
[0029] In this example, porous hydroxyapatite is prepared by the organic foam method, and its pore size is 300 microns; the magnesium alloy is AZ91, and the magnesium alloy-porous hydroxyapatite composite material is prepared by the following method:
[0030] (1) Preheating: Put the porous hydroxyapatite (HA) into the mold, and then preheat both the porous hydroxyapatite and the mold to 400°C;
[0031] (2) The magnesium alloy melt penetrates into the pores of porous hydroxyapatite: the magnesium alloy is melted, and the obtained magnesium alloy melt is added to the above-mentioned mold, and then extrusion casting is performed to infiltrate the magnesium alloy melt into the In the pores of the porous hydroxyapatite, the pressure head of the squeeze casting applies a first pressure during the process, and the first pressure does not exceed 10Mpa, so as to ensure that the porous hydroxyapatite is not broken; wherein, the melting of the magnesium alloy One step can be carried out ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] In this example, porous hydroxyapatite was prepared by the organic foam method, and its pore size was 100 microns; the magnesium alloy was Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy, and the magnesium alloy-porous hydroxyapatite composite material was prepared by the following method:
[0037] (1) Preheating: Put the porous hydroxyapatite into the mold, and then preheat both the porous hydroxyapatite and the mold to 500°C;
[0038] (2) The magnesium alloy melt penetrates into the pores of porous hydroxyapatite: the magnesium alloy is melted, and the obtained magnesium alloy melt is added to the above-mentioned mold, and then extrusion casting is performed to infiltrate the magnesium alloy melt into the In the pores of the porous hydroxyapatite, the pressure head of the extrusion casting applies a first pressure during the process, and the first pressure does not exceed 10Mpa, so as to ensure that the porous hydroxyapatite is not broken; wherein, the melting of the magnesium alloy One ...
Embodiment 3
[0042]In this example, porous hydroxyapatite was prepared by the organic foam method, and its pore size was 50 microns; the magnesium alloy was made of pure magnesium, and the magnesium alloy-porous hydroxyapatite composite material was prepared by the following method:
[0043] (1) Preheating: Put the porous hydroxyapatite into the mold, and then preheat both the porous hydroxyapatite and the mold to 450°C;
[0044] (2) Magnesium melt penetrates into the pores of porous hydroxyapatite: Magnesium is melted, and the obtained magnesium melt is added to the above mold, and then extrusion casting is performed to infiltrate the magnesium melt into the porous hydroxyapatite In the pores of the stone, in the process, the pressure head of the extrusion casting applies the first pressure, and the first pressure does not exceed 10Mpa, so as to ensure that the porous hydroxyapatite is not broken; wherein, the melting step of magnesium can be related to the first ( 1) Steps are carried ou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com