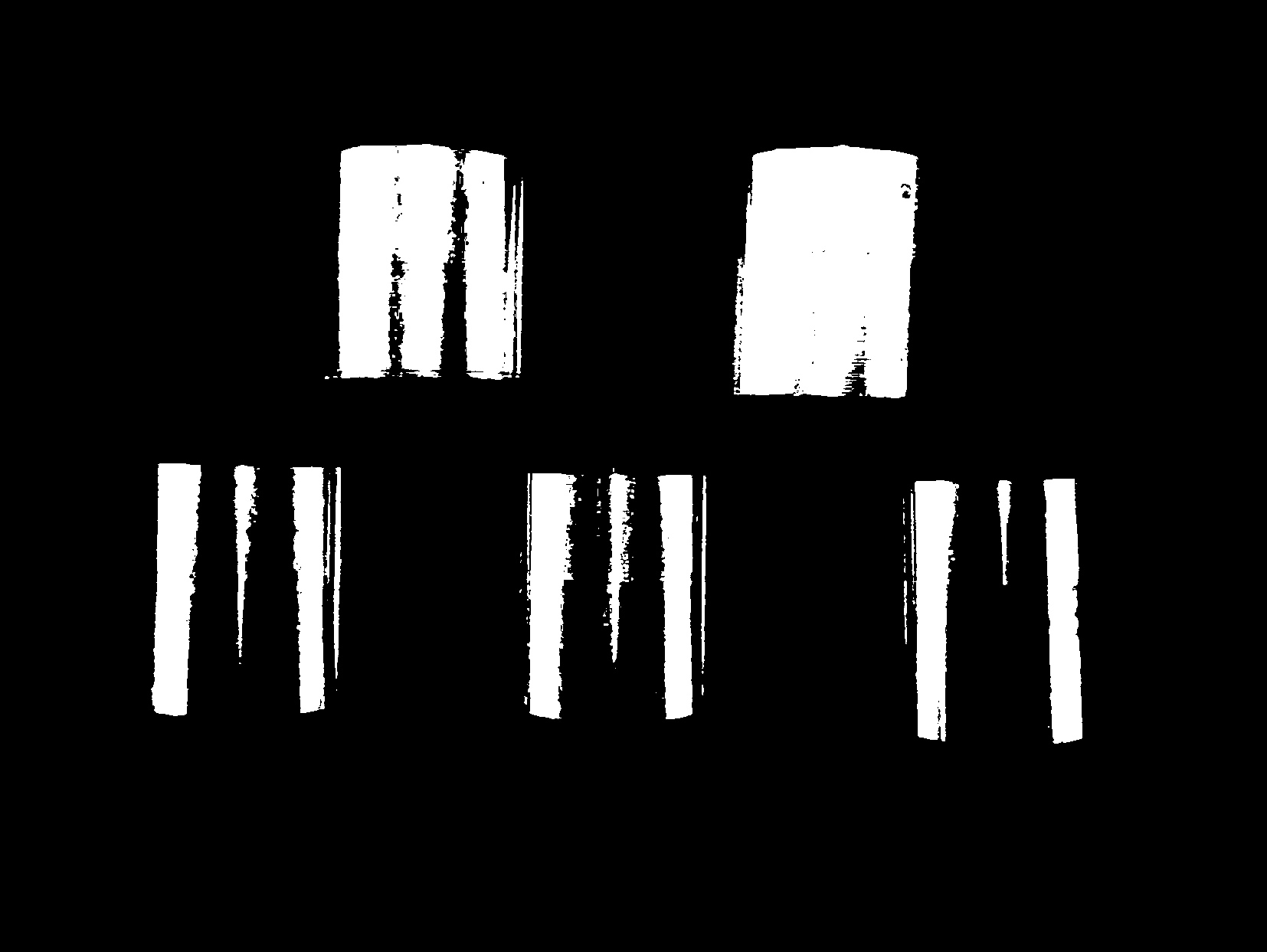Low-nickel leadless free-cutting cupronickel and preparation method thereof
A technology of easy-cutting and white copper, which is applied in the preparation of the alloy, in the field of low-nickel lead-free white copper alloy, can solve the problems that the research of low-nickel lead-free free-cutting white copper alloy material has not yet been seen, and achieve good cutting performance and low production cost. Low, the effect of avoiding pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] In the preparation method of low-nickel lead-free free-cutting cupronickel of the present invention, the batching calculation needs to select alloy elements and their dosages according to the performance requirements and alloy properties of the cupronickel alloy, carry out alloy composition design and batching calculation, and prepare alloy charge.
[0035] The low-nickel lead-free free-cutting cupronickel of the present invention is smelted and cooled to 1100-1200 DEG C for casting. The alloy ingot is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it has a silvery white luster.
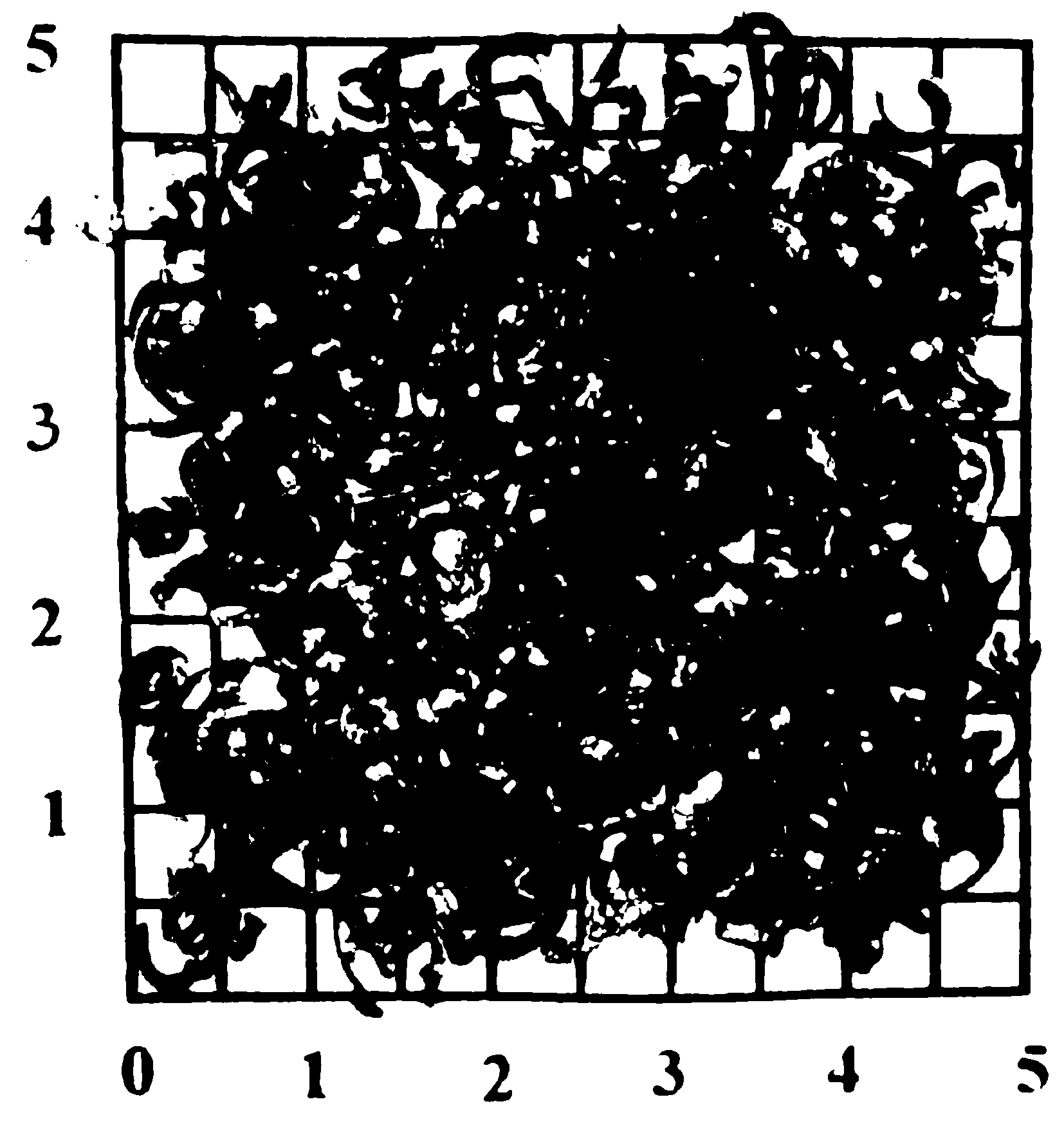
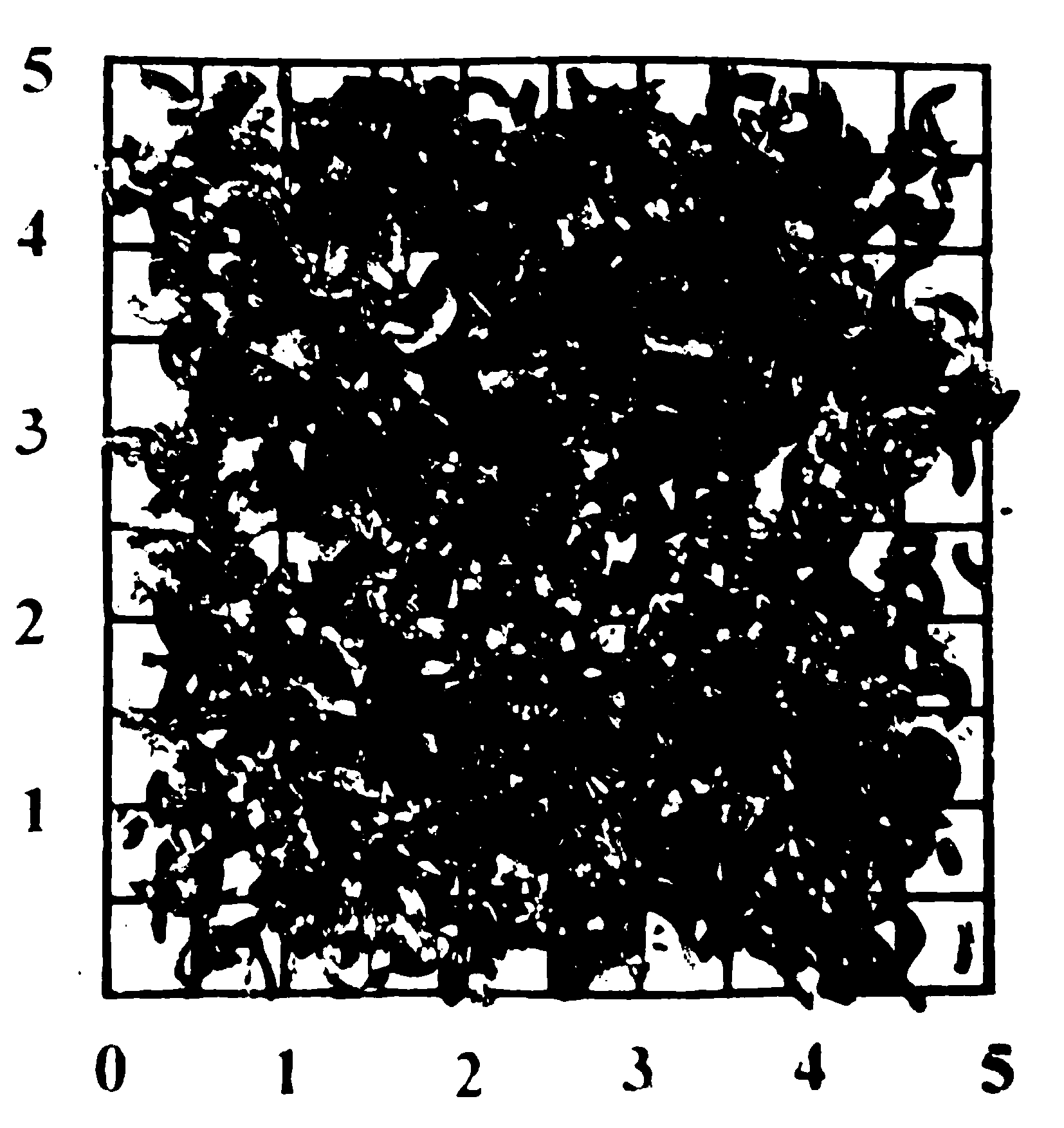
[0036] Test and analyze the cutting performance of alloy ingots, and analyze alloy samples such as Figure 2-Figure 6 As shown, the results show that the alloy prepared by the method of the present invention has good machinability.
Embodiment 1
[0038] According to the test plan described in Table 1, 77.35% of electrolytic copper, 12% of Mn, and 1% of Ni were added to the crucible and placed in the melting furnace; after adding borax as a covering agent, the temperature was raised to 1250-1350 °C; electrolytic copper , after the manganese and nickel are completely melted, add 0.65% "Mg+30%Ca" master alloy, and smelt for 15 to 20 minutes; cool down to 1200℃, add 1% pure aluminum and 8% pure zinc after stirring, and smelt 5 ~10 minutes, heat preservation for 5 ~ 10 minutes; cooling to 1100 ~ 1200 ℃ for casting and ingot casting.
[0039] Table 1 Example of the test scheme of the present invention (alloying elements and content %)
[0040] alloy element
Embodiment 2
[0042] According to the test plan described in Table 2, 76% of electrolytic copper, 12% of Mn and 2% of Ni were added to the crucible and placed in the melting furnace; after adding borax as a covering agent, the temperature was raised to 1250-1350 °C; After the manganese and nickel are completely melted, add 1.0% "Mg+30%Ca" master alloy and smelt for 15-20 minutes; cool down to 1200℃, add 1% pure aluminum and 8% pure zinc after stirring, and smelt 5 ~10 minutes, heat preservation for 5 ~ 10 minutes; cooling to 1100 ~ 1200 ℃ for casting and ingot casting.
[0043] Table 2 Example of the test scheme of the present invention (alloying elements and content %)
[0044] alloy element
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com