Optical fiber sensing device based on composite material
An optical fiber sensing and composite material technology, which is applied in the use of optical devices, measuring devices, and the measurement of force by measuring the change of optical properties of materials when they are stressed, can solve the problem of restricting the popularization and use of optical fiber sensors and affecting the use of sensing devices. and accuracy, fracture sensor and other issues, to achieve the effect of excellent environmental adaptability, flexible use and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
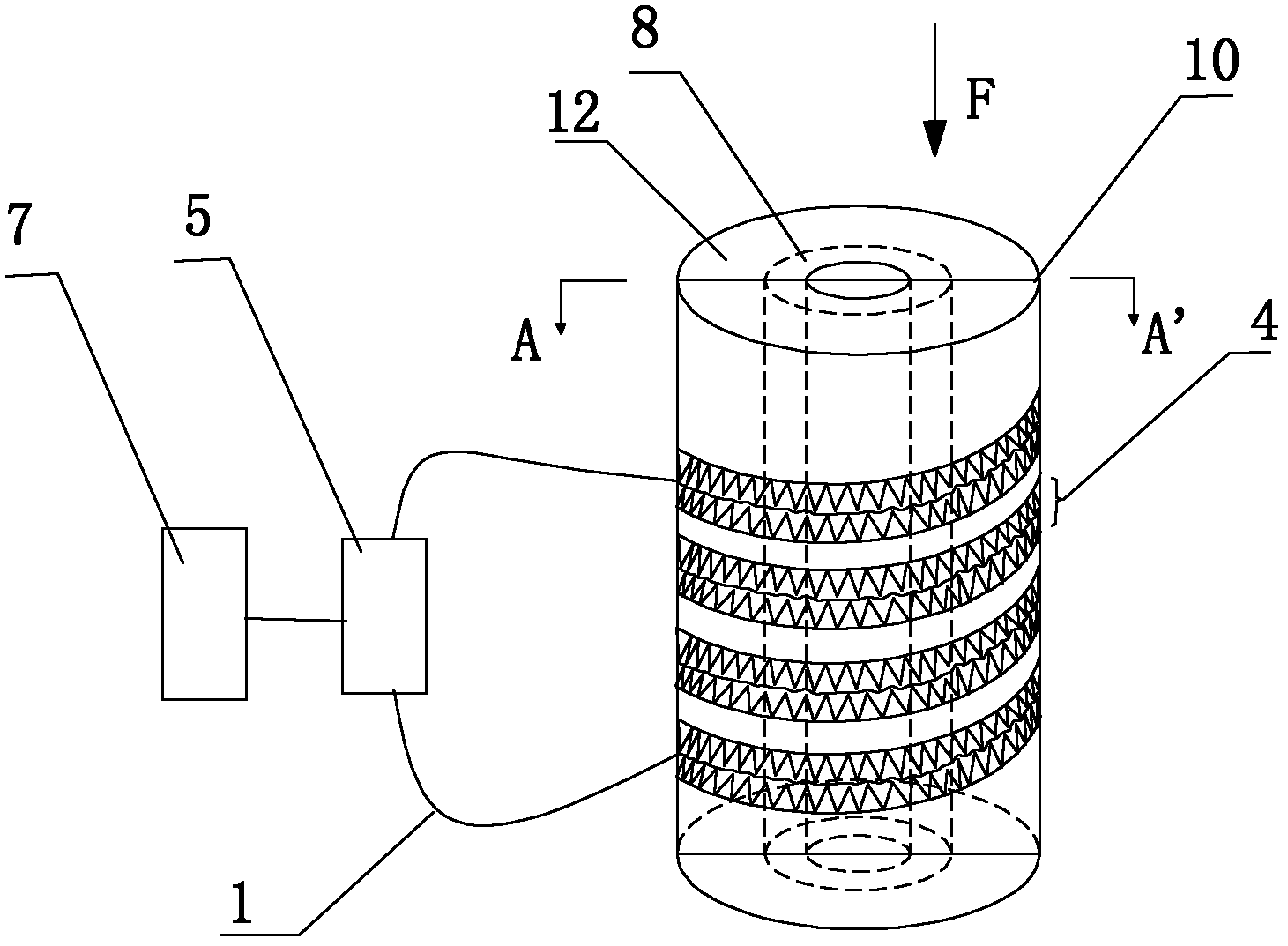
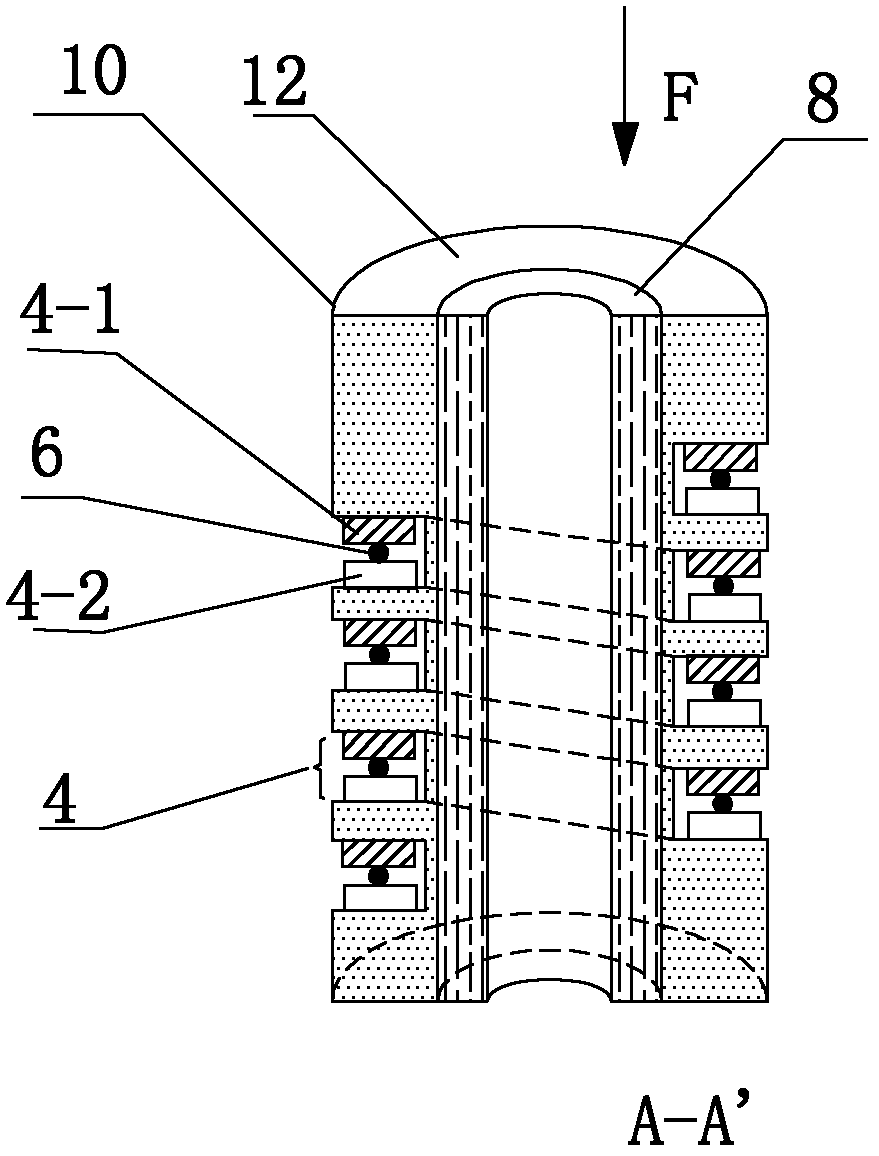
[0032] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the present invention includes grooves 4 distributed on the cylinder 10, the opposite sides of the grooves 4 respectively have A-side deformation teeth 4-1 and B-side deformation teeth 4-2 corresponding to each other, and in the grooves There is a signal optical fiber 6 sandwiched between the deformed teeth on opposite sides of 4, the signal optical fiber 6 is connected to the test unit 5 through the extension optical fiber 1, and the processing unit 7 is connected behind the test unit 5, especially the cylinder 10 is composed of different materials , that is, it is composed of the reinforcement layer 8 and the outermost layer 12 .
[0033] Preferably, the reinforcing layer 8 is made of polymer material and reinforced fiber composite material, so that the column 10 not only has a certain rigidity, but also has a large deformation capacity; when the column 10 is deformed under stress, the groove The width of 4 changes, so that the...
Embodiment 2
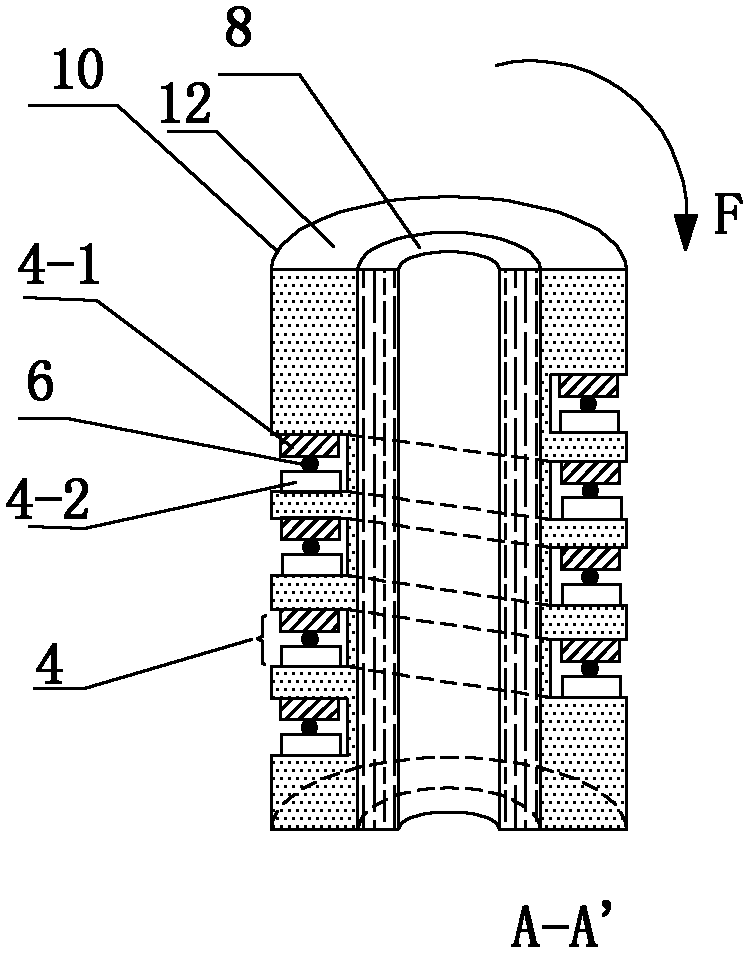
[0039] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the applied stress F acts on the upper end or the lower end of the cylinder 10, so that the cylinder 10 presents an overall bending. In this embodiment, the structures, connections and working principles of other parts are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the cylinder 10 is composed of three layers of materials.
[0042] Preferably, the base material of the reinforcing layer 8 is hot-melt adhesive, and its reinforcing fibers are steel wires, so as to ensure the rigidity and deformability of the column 10, the cost can be reduced, and it is easy to popularize and implement.
[0043] Preferably, the outermost layer of the cylinder 10 is made of rigid polyvinyl chloride, and the grooves are also distributed on this layer of material.
[0044] Preferably, the material of the innermost layer of the cylinder 10 is polyethylene.
[0045] In this embodiment, the structures, connections and working principles of other parts are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com