High-simulation three-dimensional wood-grain artificial board and production method thereof
A wood-based panel and wood-grain technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, layered products, building structures, etc., can solve the problems of poor wood-grain simulation and achieve a highly unified effect of texture and three-dimensional effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
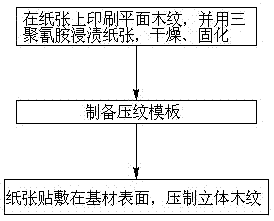
[0038] Take particle board and melamine impregnated paper as an example, such as figure 1 shown.
[0039] Step 1, print the plane wood grain on the paper. The printing process can adopt the printing process commonly used in the printing field, such as direct printing such as inkjet printing, or indirect printing processes such as transfer printing; use melamine to print the paper with plane wood grain. Dipping, curing and drying. The impregnation process can be implemented using any technique and method known to those skilled in the art.
[0040] Step 2, preparing a hot-pressed steel plate template (one of the embossed templates described in the present invention), the hot-pressed steel plate template is a convex-concave template, and the convex-concave structure is the three-dimensional structure of the printed wood grain in step 1, and the texture is consistent with the printed wood grain;
[0041] Step 2: Hot-press the melamine-impregnated paper printed with planar wood g...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Taking medium-density fiberboard and melamine-impregnated paper as examples, refer to the method described in Example 1.
[0045]Step 1, print the plane wood grain on the paper. The printing process can adopt the printing process commonly used in the printing field, such as direct printing such as inkjet printing, or indirect printing processes such as transfer printing; use melamine to print the paper with plane wood grain. Dipping, curing and drying. The impregnation process can be implemented using any technique and method known to those skilled in the art.
[0046] Step 2, preparing a cold-pressed steel plate template (one of the embossed templates described in the present invention), the cold-pressed steel plate template is a convex-concave template, and the convex-concave structure is the three-dimensional structure of the printed wood grain in step 1, and the texture is consistent with the printed wood grain;
[0047] Step 2: Hot press the melamine-impregnated p...
Embodiment 3
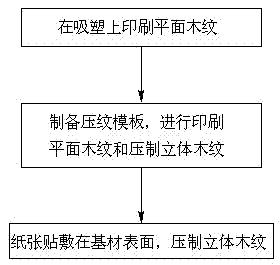
[0049] Take hard fiberboard and PVC blister film as an example, refer to figure 2 .
[0050] Step 1, preparing a planar wood grain printing template, and an embossing template with a concave-convex structure whose texture is consistent with the planar wood grain printing template, and the concave-convex structure of the embossing template is a three-dimensional structure of planar wood grain.
[0051] Step 2, first print the planar wood grain structure on the PVC film by the printing machine, and then print the three-dimensional wood grain of the convex-concave structure in the wood-based panel surface decoration material through the embossing template and the rolling machine, so that the three-dimensional wood grain texture is consistent with the plane wood grain. corresponding to the grain texture.
[0052] In step 3, the PVC blister film is adsorbed on the surface of the substrate by negative pressure.
[0053] In this embodiment, the three-dimensional structure is forme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com