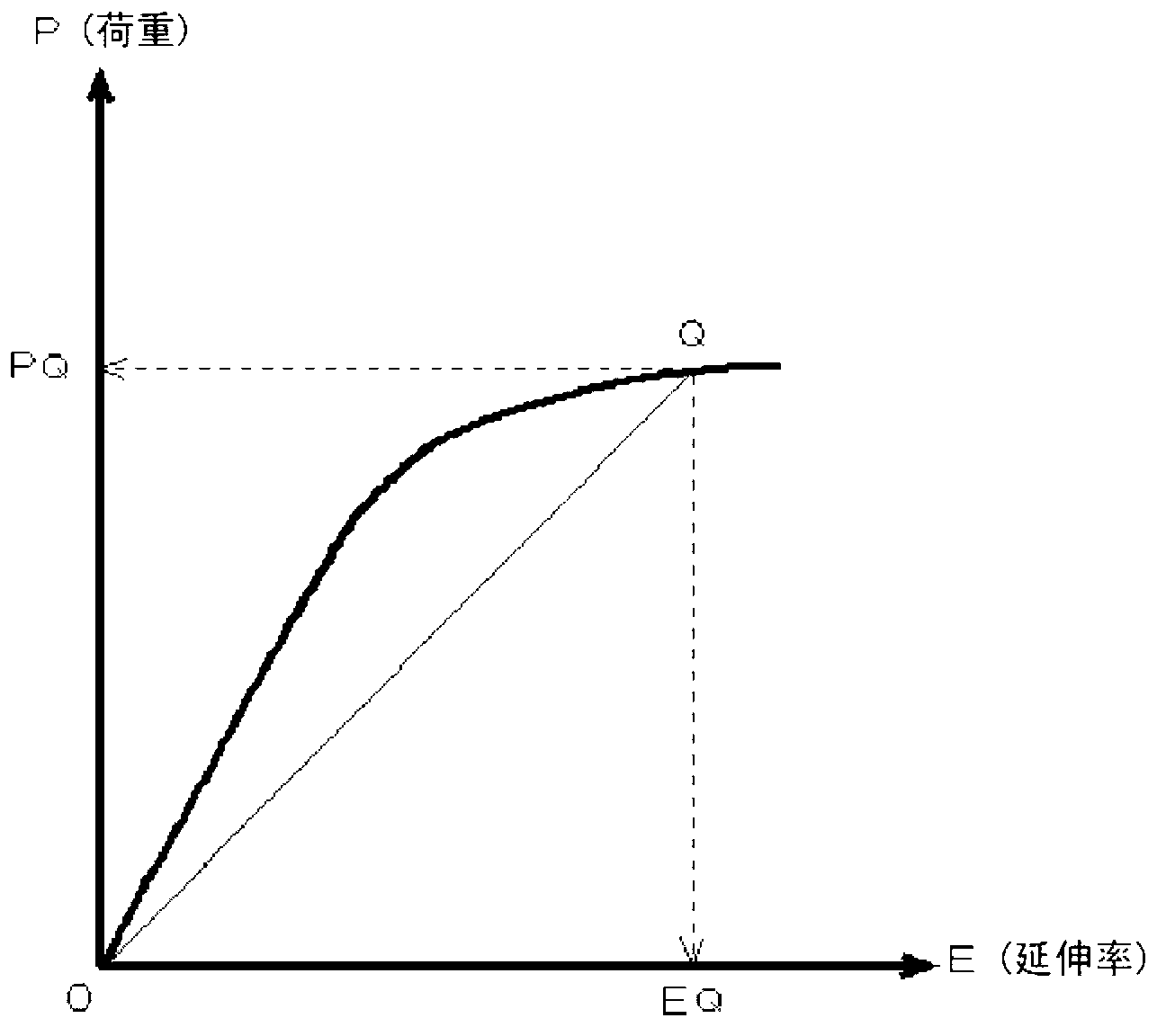
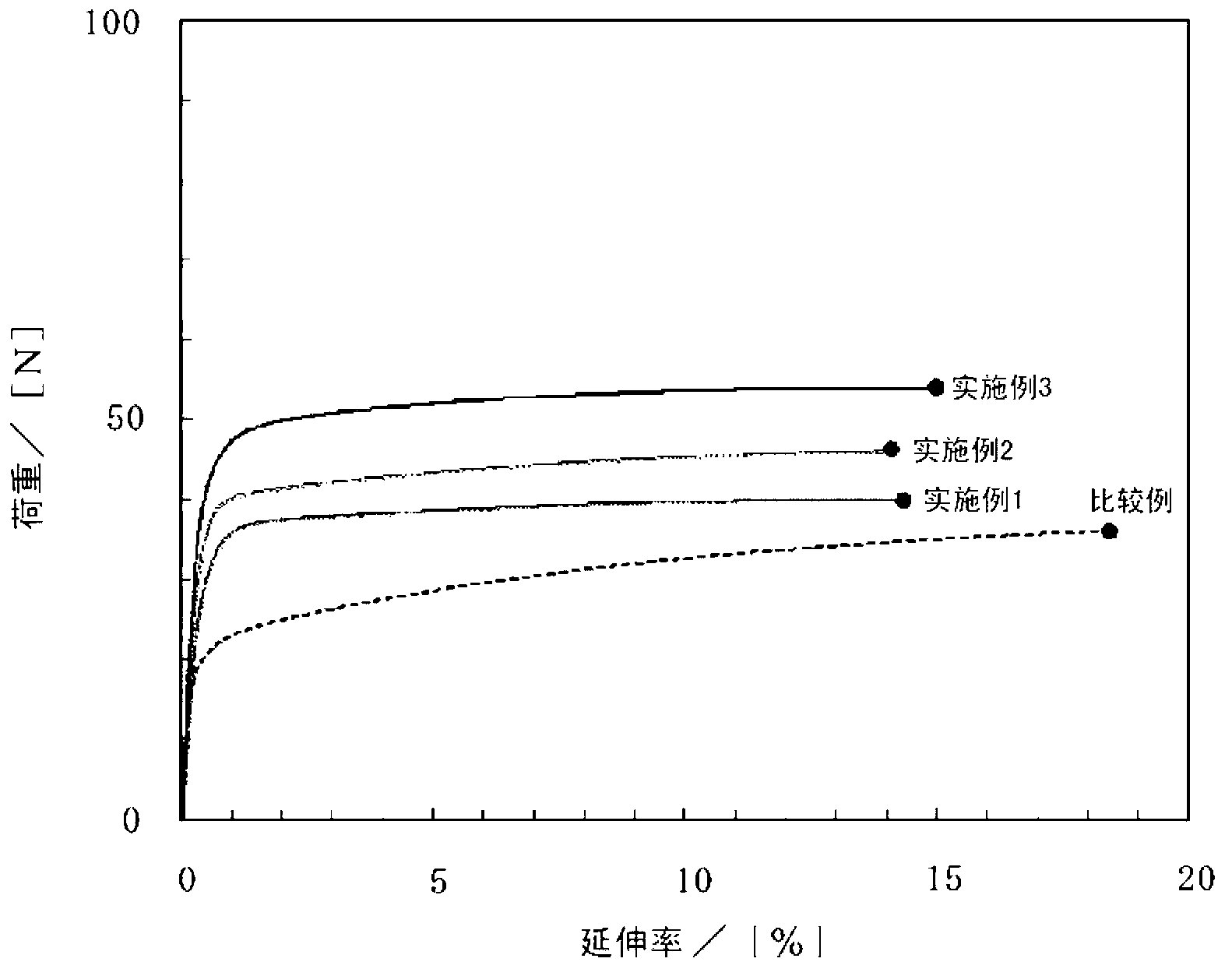
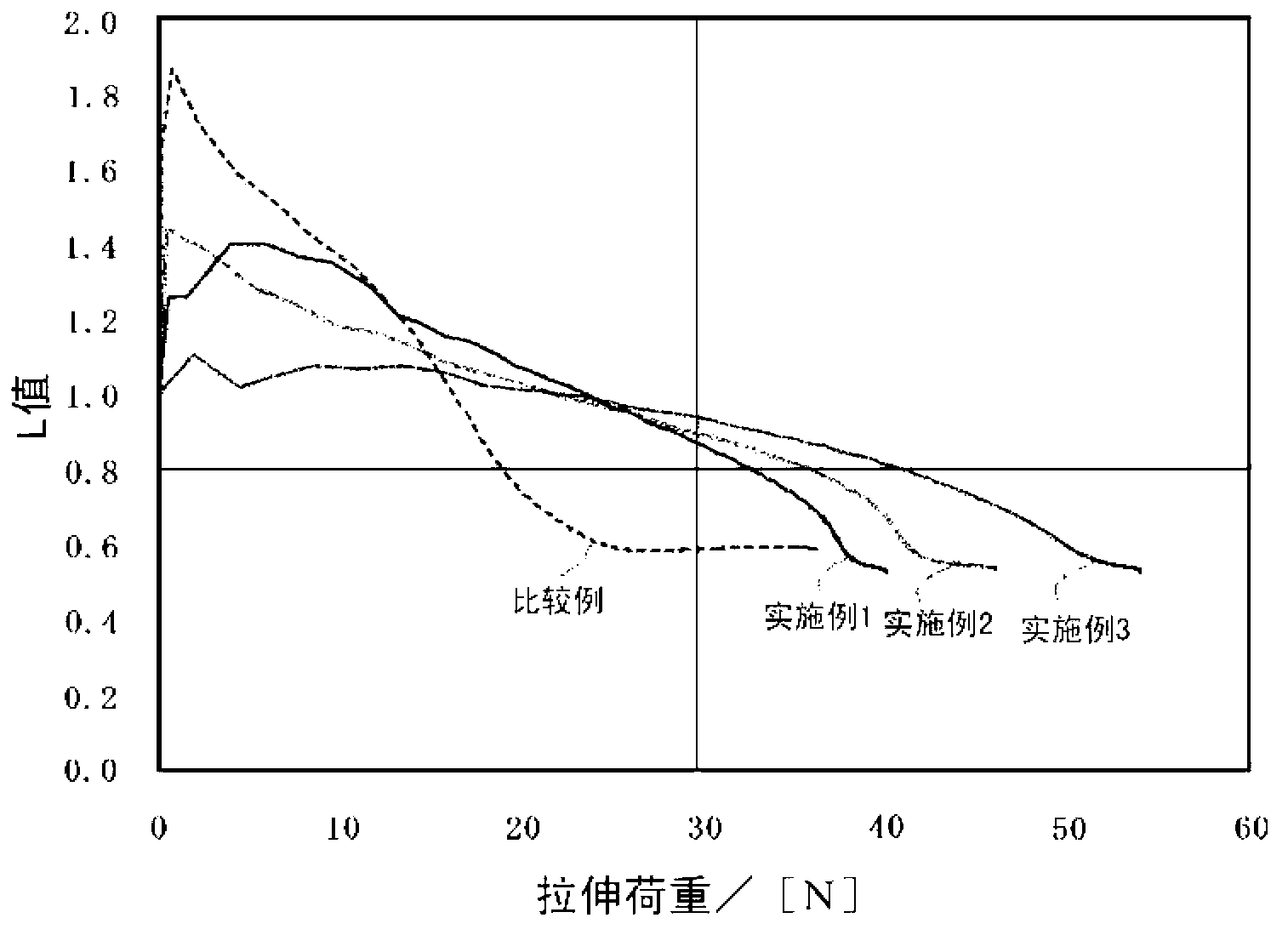
Copper foil for lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode collector, lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode material, and method for selecting lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode collector
A negative electrode current collector and secondary battery technology, which is applied in the direction of secondary batteries, electrode carriers/current collectors, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of reduced capacity, reduced durability of charge and discharge cycles, and hindrance to electrode reactions, etc., to achieve high Effects of increased energy density and higher capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064]
[0065] Electrodeposited copper foil production process: In Example 1, the electrolytic copper foil 1 was produced by the following process as the copper foil for lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode current collectors. When manufacturing this electrolytic copper foil 1, the known electrolytic copper foil manufacturing apparatus which has a rotating cathode is used. Continuously supply the electrolyte solution with copper ion content of 80g / L, sulfuric acid content of 250g / L, chloride ion content of 2.7ppm, and gelatin content of 2ppm, at a liquid temperature of 50°C and a current density of 60A / dm 2 Electrolysis is carried out under certain conditions, so that copper is deposited on the surface of the rotating cathode. The copper foil plated on the surface of the rotating cathode was peeled off to produce an electrolytic copper foil 1 having a converted thickness of 12 μm (measured thickness: 12 μm). Here, the converted thickness refers to the thickness...
Embodiment 2
[0073] In Example 2, except that an electrolytic copper foil 2 with a converted thickness of 15 μm (measured thickness is 15 μm) was produced in the electrolytic copper foil manufacturing process, the electrolytic copper foil 2 only was produced by the same process as in Example 1. Negative electrode material 2 - 1 provided with a negative electrode mixture layer on one surface, and negative electrode material 2 - 2 provided with negative electrode mixture layers on both surfaces of electrode copper foil 2 . Among them, for the electrolytic copper foil 2 produced in Example 2, the surface roughness (Ra) of the rougher surface was 0.36 μm, and the surface roughness (Ra) of the other surface was 0.32 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0075]In Example 3, except that the electrolytic copper foil 3 with a converted thickness of 17 μm (measured thickness is 18 μm) was produced in the electrolytic copper foil production process, the same process as in Example 1 was used to produce electrolytic copper foil 3 only. Negative electrode material 3 - 1 provided with a negative electrode mixture layer on one surface, and negative electrode material 3 - 2 provided with negative electrode mixture layers on both surfaces of electrode copper foil 3 . Among them, for the electrolytic copper foil 3 produced in Example 3, the surface roughness (Ra) of the one surface with the larger roughness was 0.37 μm, and the surface roughness (Ra) of the other surface was 0.31 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com