Ultra-thin electromagnetic wave converging and diverging lens design method based on phase discontinuous surface
A technology of divergent lens and design method, which is applied in the field of electromagnetics, can solve the problem of lens thickness limit, etc., and achieve the effect of small structure size, high transmittance, and thin thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
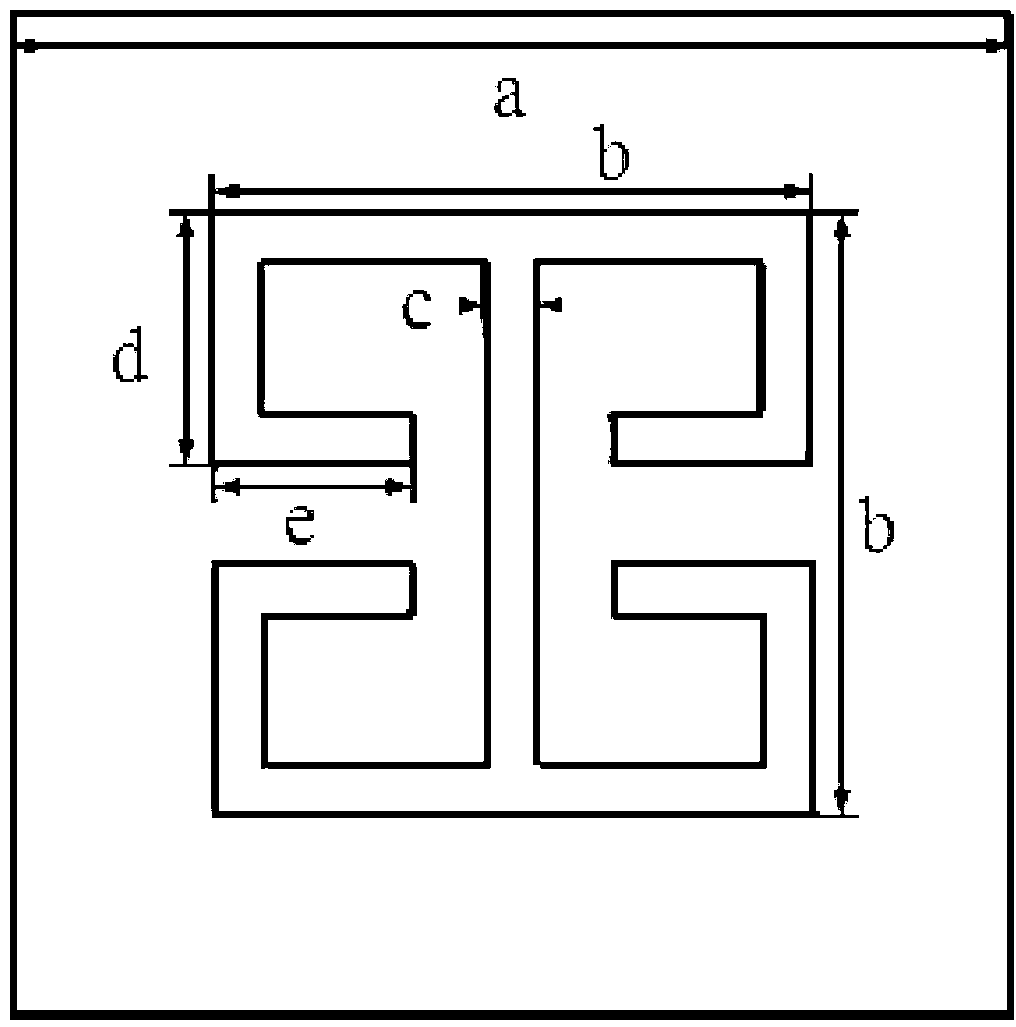
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the design method of the ultra-thin electromagnetic wave converging and diverging lens based on the phase discontinuous surface described in this embodiment, the design method is:
[0022] Step 1. First, set the f of the lens to be made, where f is the focal length of the focus point;
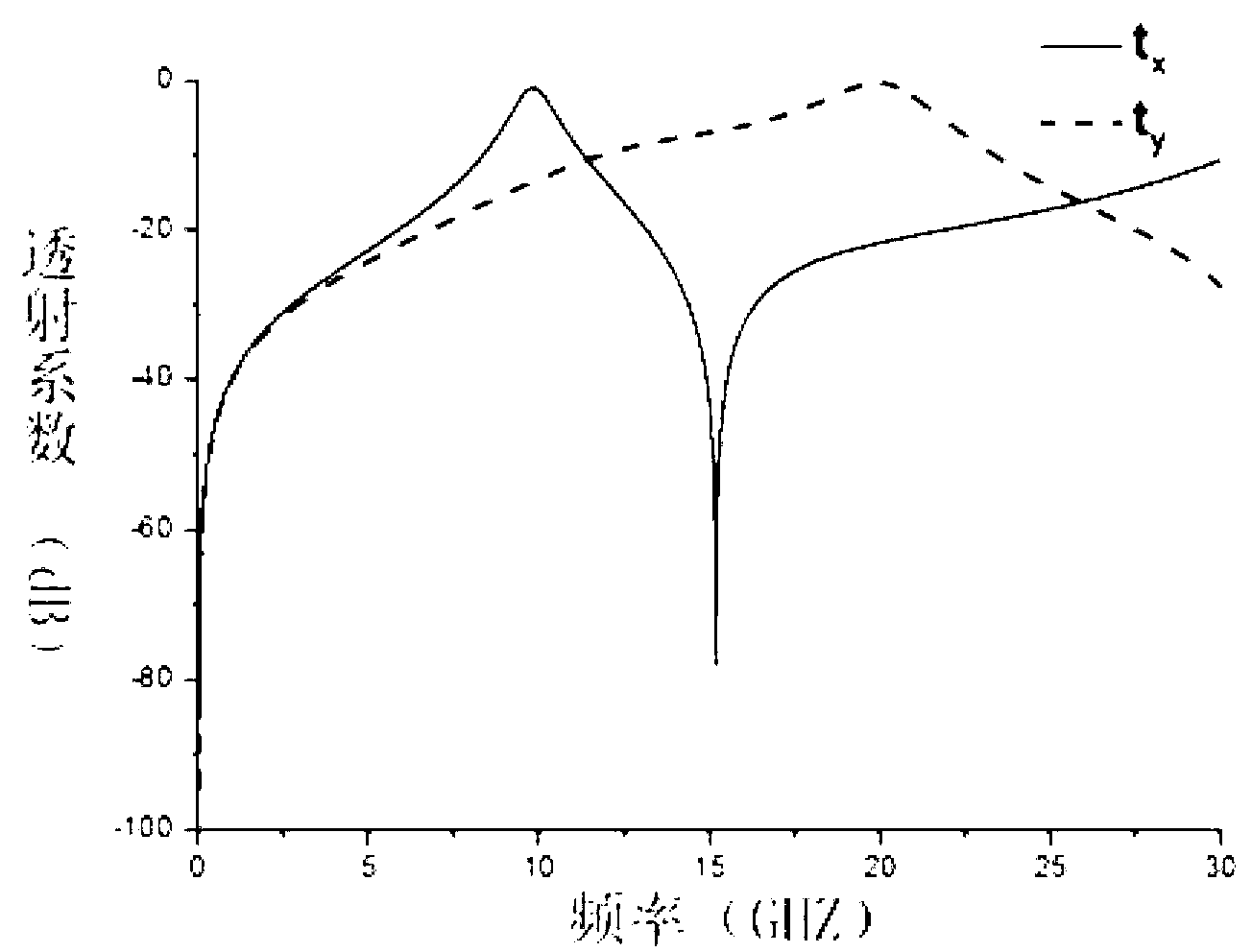
[0023] Step 2. According to the principle of the Pancharatnam–Berry phase device, for a unit structure with a side length a=5mm, the electric field is polarized along the X-axis and Y-axis of the unit structure for vertically incident electromagnetic waves, then the transmission coefficient of the unit structure is t x and t y , the first-order resonance frequency point is 9.81GHz, at the first-order resonance frequency point, the transmission coefficient t x =1,t y =0, for the transmitted component with the opposite hand direction to the incident circularly polarized wave, a phase shift rel...
specific Embodiment approach 2
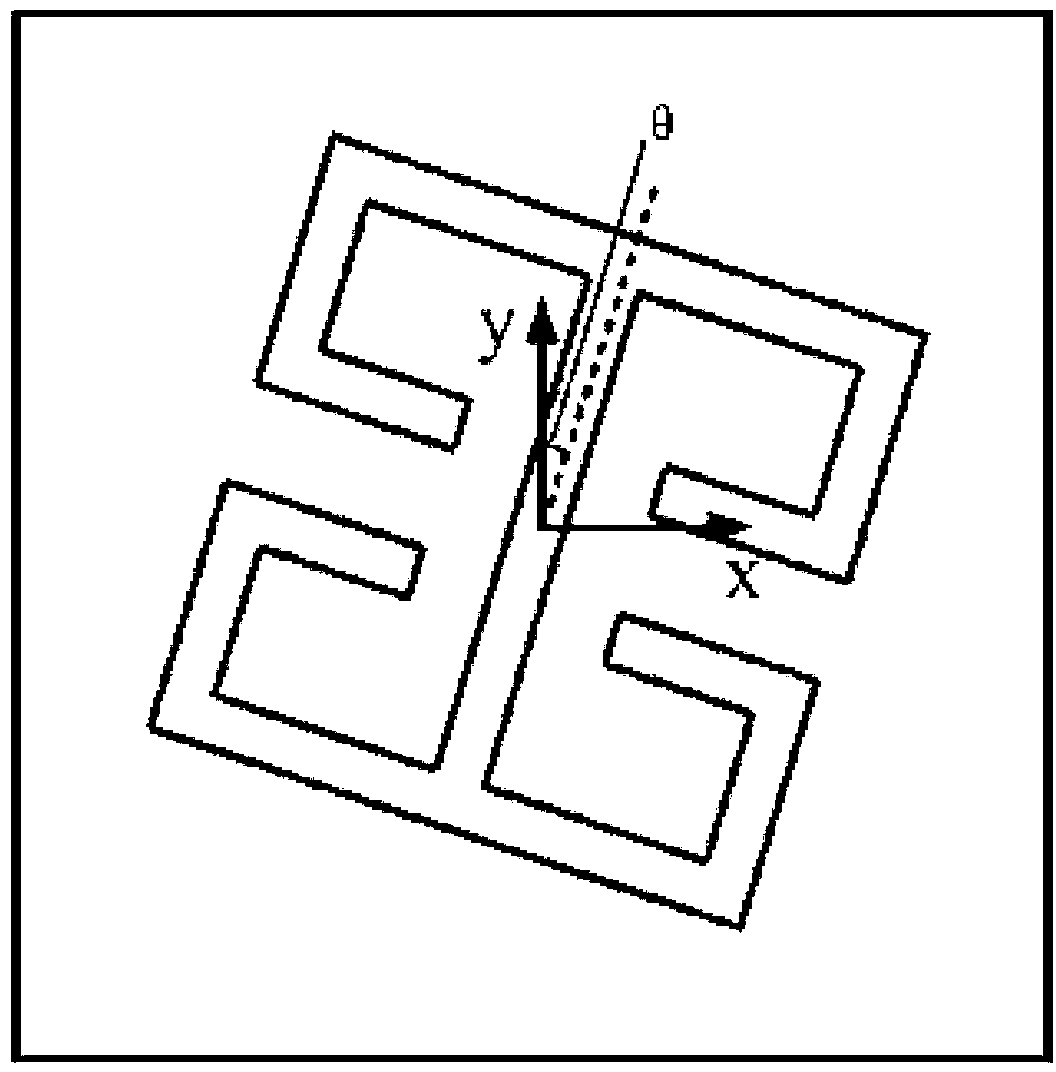
[0029] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1, the principle of the Pancharatnam-Berry phase device described in step 2 of this embodiment refers to: introducing an arbitrary phase to the opposite handedness transmission component of the incident circularly polarized wave For a left-handed or right-handed circularly polarized vertically incident wave, after each unit structure rotates θ around its axis, its transmission field is expressed as:
[0030]
[0031] in η E = | 1 2 ( t x + t y e iφ ) | ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com