Motor control device
A motor control and motor technology, applied in the direction of program control, damping device, control system, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient vibration suppression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
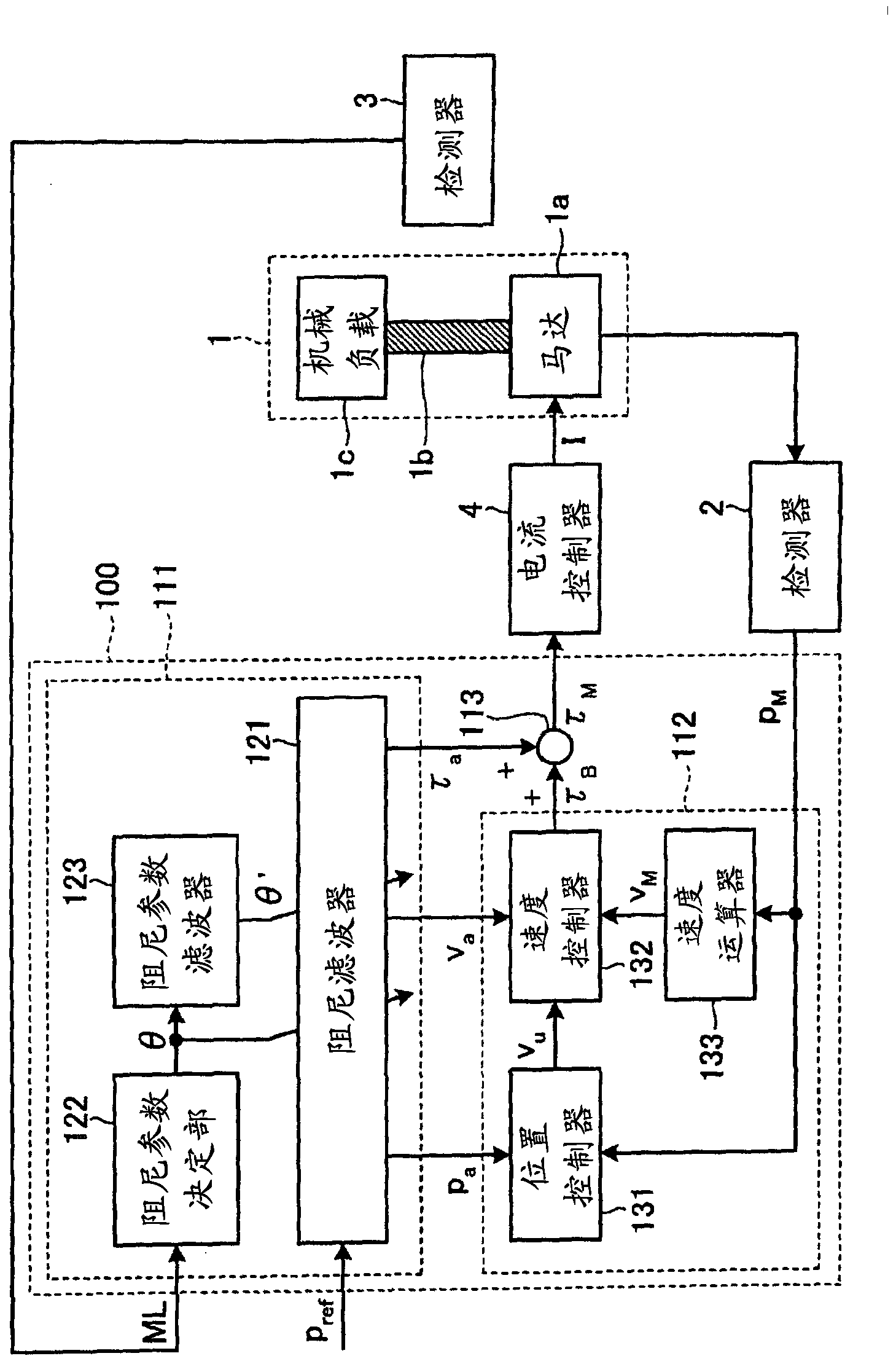
[0028] use figure 1 The configuration of the motor control device 100 according to Embodiment 1 will be described. figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the motor control device 100 according to the first embodiment.
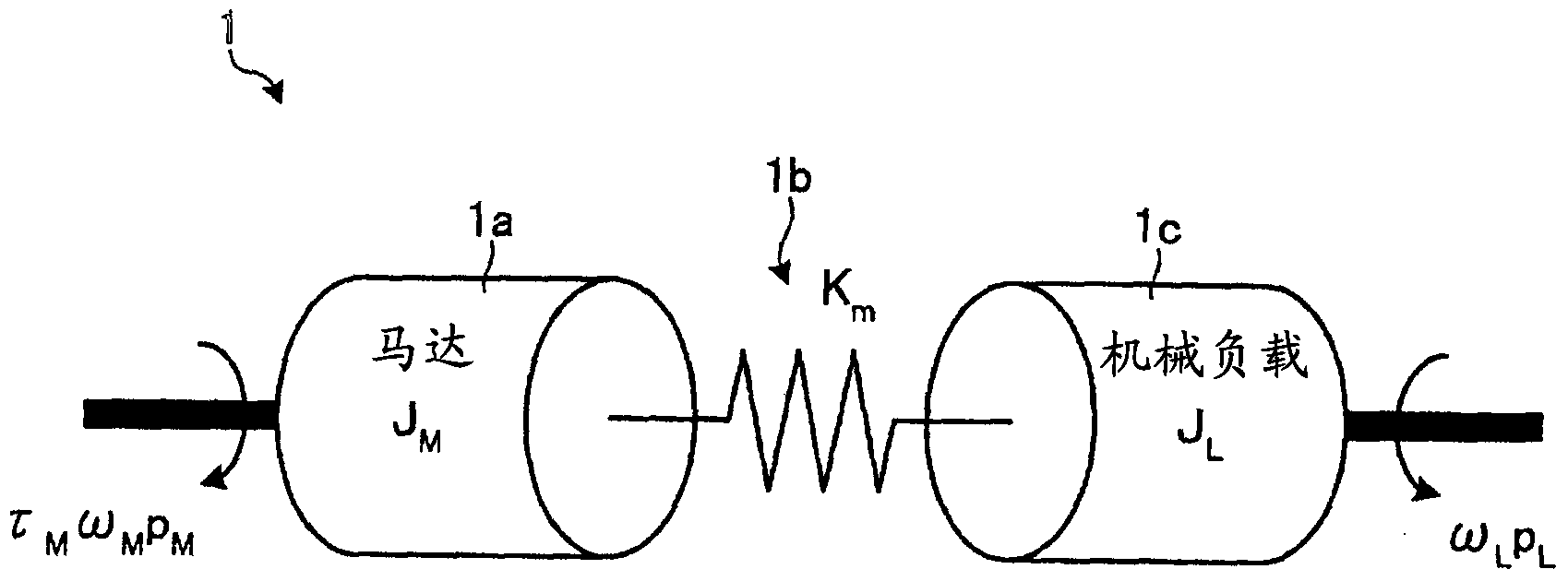
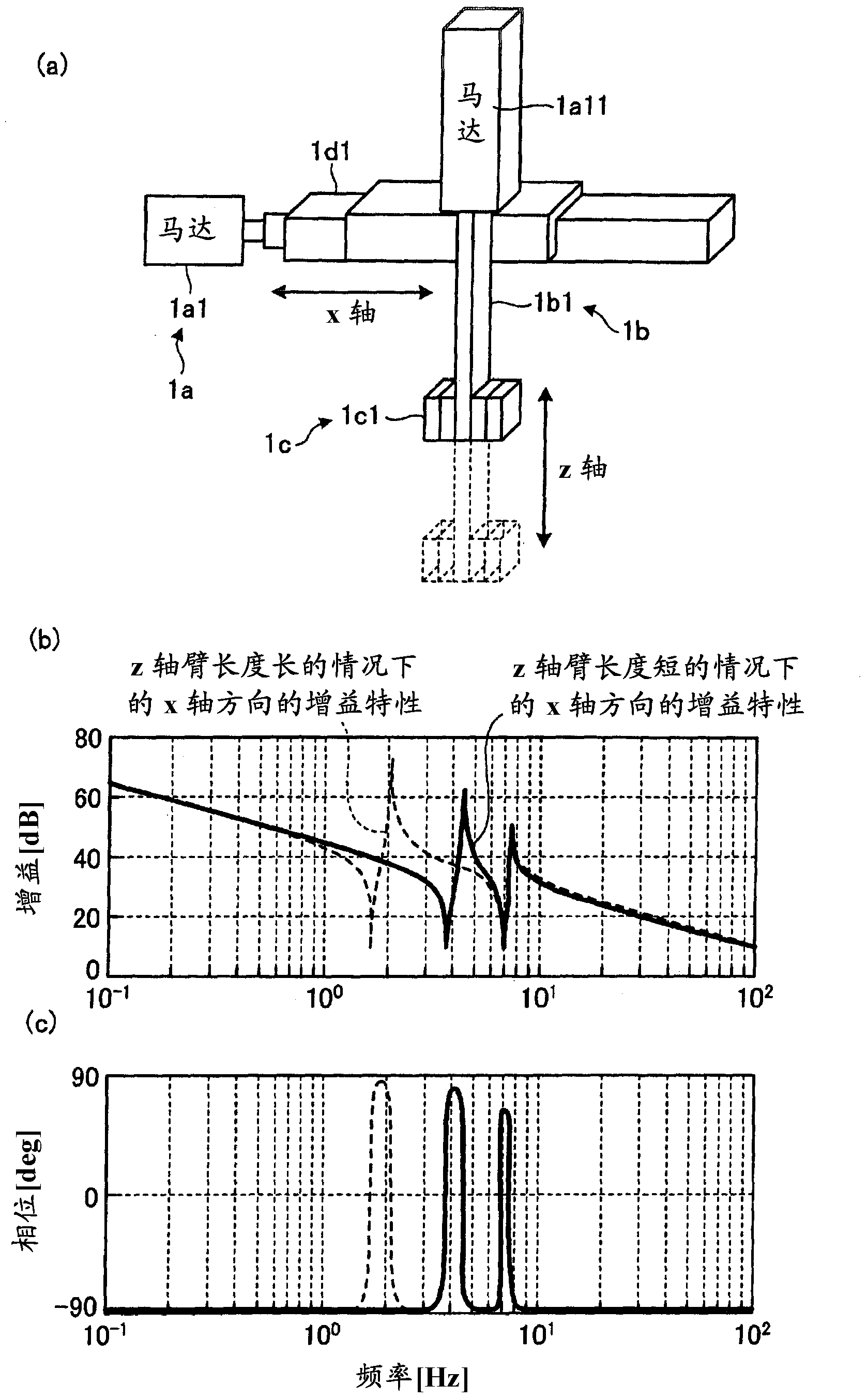
[0029] The motor control device 100 receives from the outside (for example, a host controller not shown) an operation target value (position command) pref indicating a position target value of the driven control object 1 , and receives from the detector 2 ( For example, the motor operation detection value p detected by an encoder) indicating the position of the motor 1a (for example, the rotational position of the rotor inside the motor 1a or the driving position of the movable element) M . In addition, the motor control device 100 receives a parameter change signal (state information) ML indicating the state of the controlled object 1 related to the vibration characteristics of the controlled object 1 from the detector 3 . The motor con...
Embodiment approach 2
[0119] Next, the motor control device 200 according to Embodiment 2 will be described. Hereinafter, description will focus on points different from Embodiment 1. FIG.
[0120] The difference between the motor control device 200 of the present embodiment and the motor control device 100 of the first embodiment lies in the content of processing in the damping filter (calculation method of model position, model velocity, and model torque). That is, at the resonant frequency ω p and anti-resonance frequency ω z Roughly equal (ω p ≈ω z ) case, generate the target value p from the action ref The motion compensation signal (model position p a ), perform the first-order differential and second-order differential of the generated motion compensation signal to calculate the model velocity v a , model torque τ a .
[0121] Specifically, the motor control device 200 has Figure 7 The feedforward control unit 211 as shown. Figure 7 It is a block diagram showing the internal conf...
Embodiment approach 3
[0144] Next, a motor control device 300 according to Embodiment 3 will be described. Hereinafter, description will focus on points different from Embodiment 1. FIG.
[0145] The difference between the motor control device 300 of the present embodiment and the motor control device 100 of the first embodiment lies in the content of processing in the damping filter (calculation method of model position, model velocity, and model torque). That is, even at the resonant frequency ω of the controlled object 1 p , anti-resonance frequency ω z In different cases, the target value p from the action is still generated ref The motion compensation signal (model position p a , Resonant frequency compensation signal p cp ), for the generated motion compensation signal (model position p a ) to calculate the model velocity v a , and the action compensation signal (resonant frequency compensation signal p cp ) to calculate the model torque τ a .
[0146] Specifically, the motor control...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com